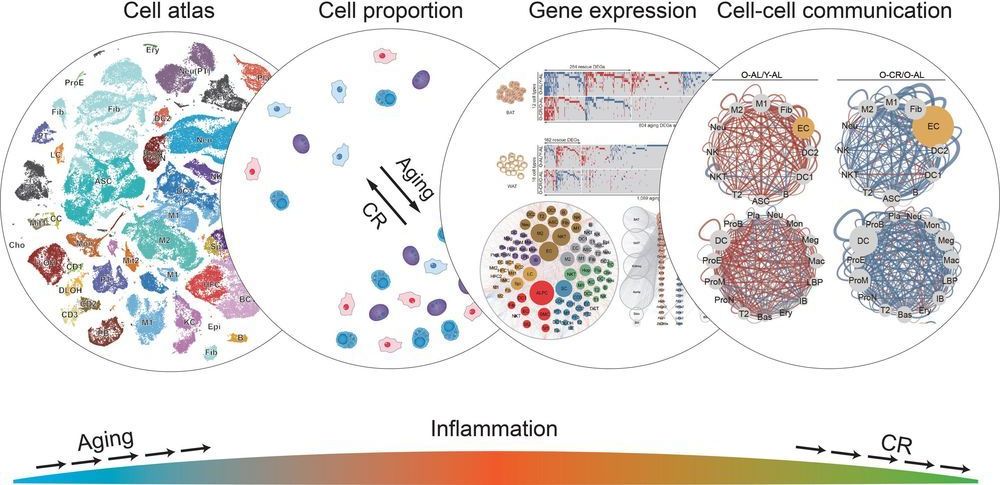
If you want to reduce levels of inflammation throughout your body, delay the onset of age-related diseases, and live longer—eat less food. That’s the conclusion of a new study by scientists from the US and China that provides the most detailed report to date of the cellular effects of a calorie-restricted diet in rats. While the benefits of caloric restriction have long been known, the new results show how this restriction can protect against aging in cellular pathways, as detailed in Cell on February 27, 2020.
“We already knew that calorie restriction increases life span, but now we’ve shown all the changes that occur at a single-cell level to cause that,” says Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, a senior author of the new paper, professor in Salk’s Gene Expression Laboratory and holder of the Roger Guillemin Chair. “This gives us targets that we may eventually be able to act on with drugs to treat aging in humans.”
Aging is the highest risk factor for many human diseases, including cancer, dementia, diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Caloric restriction has been shown in animal models to be one of the most effective interventions against these age-related diseases. And although researchers know that individual cells undergo many changes as an organism ages, they have not known how caloric restriction might influence these changes.