The Pacific Ocean is becoming more acidic, and the cash-crabs that live in its coastal waters are some of its first inhabitants to feel its effects.
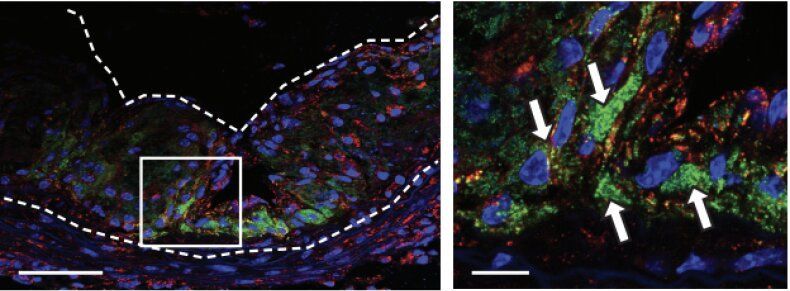
The Dungeness crab is vital to commercial fisheries in the Pacific Northwest, but lower pH levels in its habitat are dissolving parts of its shell and damaging its sensory organs, a new study found.
Their injuries could impact coastal economies and forebode the obstacles in a changing sea. And while the results aren’t unexpected, the study’s authors said the damage to the crabs is premature: The acidity wasn’t predicted to damage the crabs this quickly.






 We are delighted to announce that
We are delighted to announce that 