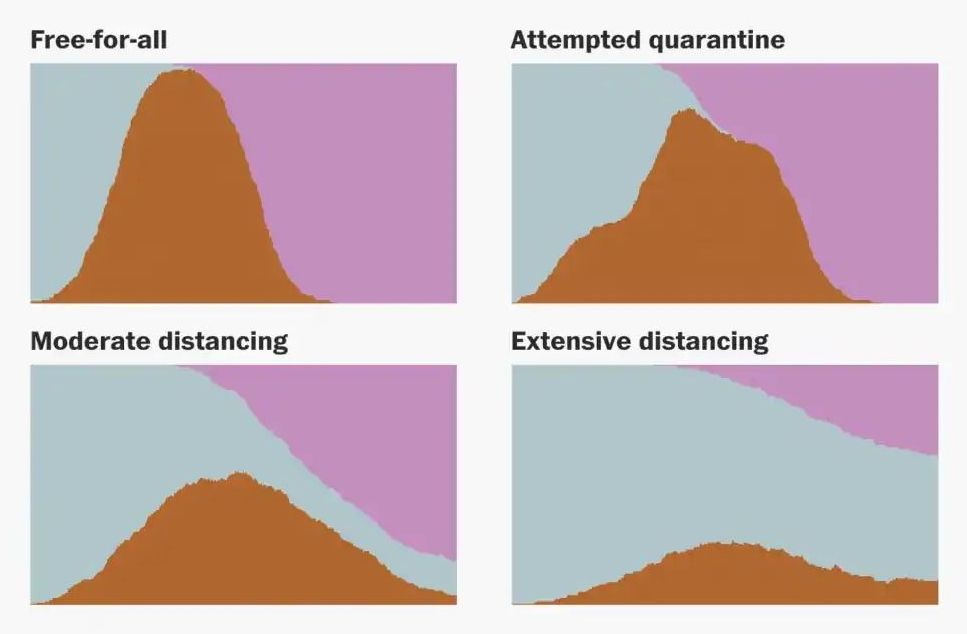
The early trickle of new coronavirus infections has turned into a steady current. By creating simple simulations, we can see how to slow it down.


Hong Kong’s government announced in late February that it would be giving every resident over the age of 18 a cash payout of 10,000 Hong Kong dollars, part of a package of measures aimed at reducing the financial blow to the territory from the COVID-19 outbreak and months of anti-government protests. At the time, the city’s Financial Secretary Paul Chan told CNBC the move could boost Hong Kong’s economy by around 1%.
The U.S. should follow Hong Kong’s lead and give a cash handout to its citizens amid the coronavirus pandemic, a strategist told CNBC Friday.
“This is not a financial crisis,” Andrew Freris, CEO of Ecognosis Advisory, told CNBC’s “Capital Connection.” “It is a crisis about the real economy.”
He noted that in 2008, central banks used stimulus to respond to the collapse of the U.S. mortgage market — but he said nothing of the kind was happening right now.

The Federal Reserve swept into action on Sunday in a new bid to save the U.S. economy from the fallout of the coronavirus, cutting its benchmark interest rate by a full percentage point to near zero and promising to boost its bond holdings by at least $700 billion.
The central bank also announced several other actions, including letting banks borrow from the discount window for as long as 90 days and reducing reserve requirement ratios to zero percent. In addition, the Fed united with five other central banks to ensure dollars are available around the world via swap lines.
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell will hold a press conference at 6:30 p.m. Washington time to discuss the actions.

Here’s an exciting concept that was actually first discussed in 1959 by Richard Feynman in an article entitled “There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom”.
I am most interested in this technology for mind uploading.
“Battelle’s N3 concept for a minimally invasive neural interface system, called BrainSTORMS (Brain System to Transmit Or Receive Magnetoelectric Signals), involves the development of a novel nanotransducer that could be temporarily introduced into the body via injection and then directed to a specific area of the brain to help complete a task through communication with a helmet-based transceiver.”
COLUMBUS, Ohio—(BUSINESS WIRE)—Battelle has for years successfully demonstrated brain-computer interface (BCI) projects—just look at NeuroLife®, which has enabled a quadriplegic man to move his hand again using his thoughts. Now, the government’s forward-thinking Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has awarded a contract to a Battelle-led team that pushes researchers into the realm of what was once considered science fiction.
“This is one of the most exciting and challenging projects I have worked on” Tweet this
Imagine this: A soldier puts on a helmet and uses his or her thoughts alone to control multiple unmanned vehicles or a bomb disposal robot. That’s the basis for this effort for DARPA’s Next-Generation Non-Surgical Neurotechnology (N3) program. The N3 program seeks development of high-performance, bi-directional brain-machine interfaces for able-bodied service members. Most of the current BCI research, including Battelle’s NeuroLife technology, focuses on helping people with disabilities who must undergo invasive implant procedures, including brain surgery, to enable a BCI that can restore lost function. For the next BCI leap, in which the technology can be used by healthy military service members, it’s imperative to find lower-risk and less-invasive options.


Disaster emergency is in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic and the effects it is having on the city.
The City of Boulder has declared a local disaster emergency in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic and the effects it is having on the city.
City Manager Jane Brautigam issued a disaster emergency declaration today effective at 6 p.m. This creates a state of emergency for Boulder. The declaration provides the city manager with tools necessary to protect the public health and safety. The City Manager has authority to issue a disaster emergency declaration for a period of up to 7 days. To be effective for more than 7 days, the declaration must be confirmed and extended by the city council. Staff will ask the city council to consider doing so at the March 17, 2020 council meeting. The disaster emergency declaration provides the city manager with the authority to, among other things, order a curfew, limit large gatherings, close streets and sidewalks and order businesses to close. Violation of any emergency order would be punishable by a fine of up to $1000 and up to 90 days in jail.

March 9 (UPI) — Scientists have developed a technique for repairing damaged DNA. The breakthrough, published this week in the journal Nature Communications, could pave the way for new therapies for cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
The accumulation of DNA damage is responsible for aging, cancer and neurological diseases like motor neuron disease, also known as ALS.
Until now, scientists have struggled to find ways to repair this kind of damage. However, researchers have discovered a new protein called TEX264 that can combine with other enzymes to find and destroy toxic proteins that bind to DNA and trigger damage.
WASHINGTON (Reuters) — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Friday approved Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc’s coronavirus test, which would allow the firm to increase capacity to 1.4 million tests a week, a Trump administration official said.
“This will dramatically increase our ability to test people for the virus,” the official said. It was not immediately clear if capacity referred to test kit production or processing of tests performed on individual patients.
The move comes as the Trump administration struggles to meet demand for testing. The FDA has already approved emergency authorization for a faster coronavirus test made by Swiss diagnostics maker Roche.

