The applications are almost endless.
In “Hacking the Code of Life”, Nessa Carey explores advances that are giving us new powers to alter the genome.
The applications are almost endless.
In “Hacking the Code of Life”, Nessa Carey explores advances that are giving us new powers to alter the genome.

It becomes obvious, that there are clump risks in the current setup of the global drug production.
There may soon be a shortage of certain drugs, such as some antibiotics (•, as the only production facilities in China stopped producing them, due to the current Corona virus outbreak.
(• e.g. consider that 97% of the antibiotics used in America are made in China according to an article by ABC7 news.
The world’s pharmaceutical supply chain is in danger as the virus spreads across China and jeopardizes travel and trade.

Lifespan.io is hosting its third annual conference on aging and rejuvenation biotechnology.
The Life Extension Advocacy Foundation/Lifespan.io, a nonprofit company promoting aging research, is hosting its third annual Ending Age-Related Diseases: Investment Prospects and Advances in Research conference on August 20–21 at the Stern Auditorium of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (New York City, USA).
The goal of this conference is to promote scientific and public discussion in order to foster the development of interventions that target aging and are capable of relieving our aging society from the burden of age-related diseases. Key topics of the conference include biomarkers of aging, discoveries in fundamental research, the development of interventions targeting the root mechanisms of aging, investment strategies, and regulatory issues that are relevant to rejuvenation research.
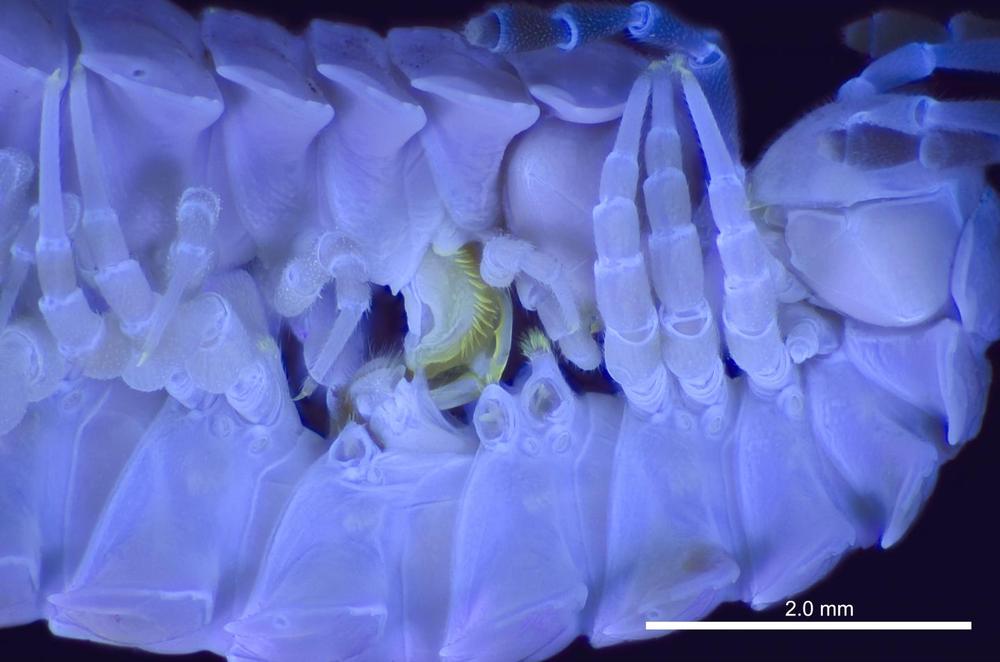
A team of US scientists has just solved a long-standing biological mystery – how exactly do millipedes mate? Using a variety of novel imaging methods, including microscopic ultraviolet photography and micro-CT scanning, the research finally figured out how these tiny creatures get it on.
“This is the first time we’ve been able to understand these millipedes’ mechanism of insertion, how the male and female organs interact with each other,” says Petra Sierwald, from Chicago’s Field Museum and one of the study’s authors. “Before this, we had no idea how he would actually get the sperm into her.”
Millipedes can generally be somewhat shy organisms, so getting them to mate in laboratory conditions hasn’t been easy. The new study focused on a type of small, brown North American millipede called Pseudopolydesmus, known for being more than willing to mate, even in the most exhibitionist situations.


As the novel coronavirus outbreak continues to batter China, the country’s central bank has implemented a new strategy to contain the virus — deep cleaning and destroying potentially infected cash.
The new measures, announced by the People’s Bank of China on Saturday, aim to contain the spread of the virus, officially known as Covid-19. There is still a lot unknown about the virus, which has infected more than 71,000 people globally and killed 1,775, the majority in China — but it appears to survive for at least several hours on surfaces, according to the World Health Organization.
This is why buildings in affected areas are regularly disinfecting elevator buttons, door handles, and other commonly-touched surfaces — and why people are worried about cash, which changes hands multiple times a day.
The Human Genome Project launched in 1990 with the goal to read genomes. Now scientists are working to write them.
Gene editing of human embryos — yes or not?
If there is a discernible duty here it is surely to create the best possible child. That is what it is to act for the best, all things considered. This we have moral reasons to do; but they are not necessarily overriding reasons.
Steven Hawking initially predicted that we might have about 7.6 billion years to go before the Earth gives up on us; he recently revised his position in relation to the Earth’s continuing habitability as opposed to its physical survival: “We must also continue to go into space for the future of humanity,” he said recently. “I don’t think we will survive another thousand years without escaping beyond our fragile planet.”
We will at some point have to escape both beyond our fragile planet and our fragile nature. One way to enhance our capacity to do both these things is by improving on human nature where we can do so in ways that are “safe enough”. What we all have an inescapable moral duty to do is to continue with scientific investigation of gene editing techniques to the point at which we can make a rational choice. We must not stop now.
In October 2019, Liu and his colleagues published a paper in Nature, describing an even newer technology, called prime editing. Prime editing can not only make all twelve of the possible base substitutions, it can also make multiple-base insertions or deletions, without requiring a double-strand break. It achieves this with a multi-step operation that first cuts one strand, then performs the appropriate substitution, insertion, or deletion, and then nicks the second strand to allow the bases on the second strand to be replaced by bases that complement the ones substituted, inserted into or deleted from the first strand. The result is a modified stretch of DNA that had never been completely separated. This has the effect of massively reducing the number of off-target modifications.
This new prime editing variant of CRISPR technology, can make the same corrections to the defects that cause sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia that standard CRISPR/Cas9 has now made in human subjects, but with less opportunity for unwanted off-target changes. Furthermore, its possible applicability is much wider. The ClinVar database lists over 75,000 pathogenic mutations in the human genome. Of these, over 89% are potentially correctable by prime editing.
From zinc fingers to TALE, to CRISPR/Cas9 to base editing and now to prime editing, progress in gene editing has been accelerating. The next advances are currently being aggressively pursued in laboratories all over the world. It will probably be several years before the therapies that are currently being researched are applied routinely in a clinical setting. However, for people who up until recently have had no hope for a cure to a disease suffered by their child, or even themselves, these are exciting times. The prospect of effective treatments, or even cures, is now a valid cause for hope.