CORONAVIRUS cases in Germany have almost trebled in the past 24 hours sparking fears of a second wave of COVID-19 infections.


If you are interested in age reversal, and you haven’t read Dr David Sinclair (Harvard Medical School) yet, then I’d recommend this research paper.
“Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.”
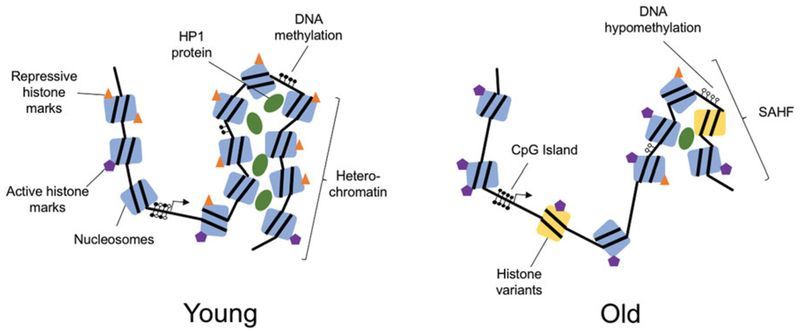
The aging process results in significant epigenetic changes at all levels of chromatin and DNA organization. These include reduced global heterochromatin, nucleosome remodeling and loss, changes in histone marks, global DNA hypomethylation with CpG island hypermethylation, and the relocalization of chromatin modifying factors. Exactly how and why these changes occur is not fully understood, but evidence that these epigenetic changes affect longevity and may cause aging, is growing. Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.
The term “epigenetics” is thrown around a lot. Originally, it was coined to describe heritable changes that were non-mendelian, but use of the term has evolved. These days, “epigenetics” more generally refers to all non-genomic information storage in cells including gene networks, chromatin structure and post-translational modifications to histones. With aging, there are distinct changes across the epigenome from DNA modifications to alterations in global chromatin organization. But key questions remain unanswered: How and why do these changes occur? Do these changes drive disease and aging? Are they reversible?
Genomic organization is determined by the complex structure of chromatin ( Figure 1 ). The basic unit of chromatin is the nucleosome, which is made up of 147 DNA base pairs wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins. This octamer usually comprises two copies each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 (Luger et al. 1997; Hansen 2002). Within nucleosomes, both histones and the DNA itself are subject to a range of chemical modifications that affect the chromatin structure and ultimately the expression of genes. Chromatin falls into one of two major subtypes: euchromatin, in which the chromatin is open and transcriptionally active and heterochromatin, in which the chromatin is tightly closed and transcriptionally silent (Wallrath 1998; Grewal and Moazed 2003). Regulating the epigenetic network are factors that modify chromatin including DNA- and histone-modifying enzymes, transcription factors, and the more recently identified noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs).
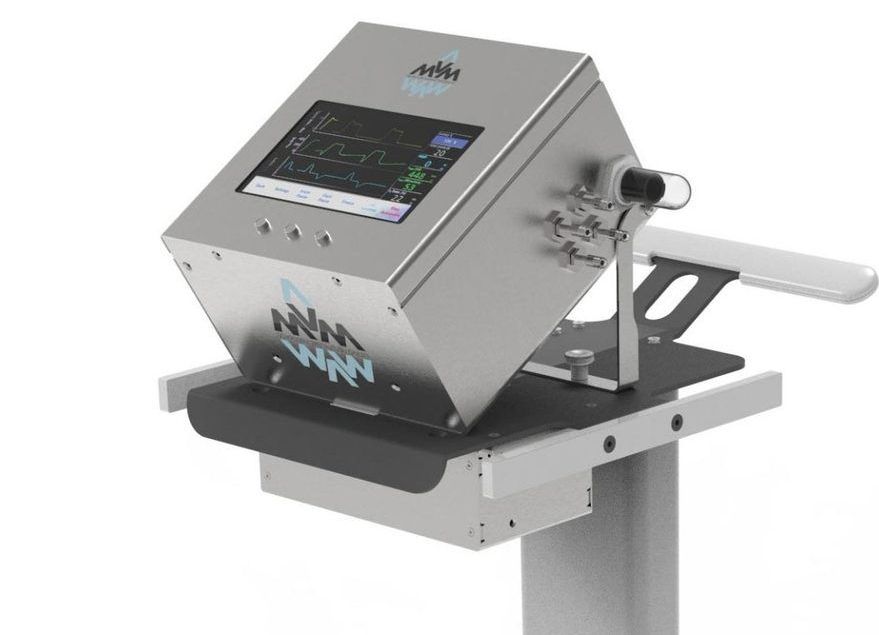

In a little over a month, a team of physicists and engineers from around the world took a simplified ventilator design from concept all the way through approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. This major milestone marks the ventilator as safe for use in the United States under the FDA’s Emergency Use Authorization, which helps support public health during a crisis.
The Mechanical Ventilator Milano, or MVM, is the brainchild of physicist Cristiano Galbiati. The Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University professor, who normally leads a dark matter experiment in Italy called DarkSide-20k, found himself in lockdown in Milan, a city hit hard by COVID-19. Hearing reports of ventilator shortages and wanting to help, Galbiati reached out to fellow researchers to develop a ventilator with minimal components that could be quickly produced using commonly available parts.
“The sense of crisis was palpable, and I knew the availability of ventilators was critical,” said Galbiati, who obtained his Ph.D from the University of Milan. “We had been doing some complicated projects in physics that required working with gases, and I thought it our duty to find a way to push oxygen into the lungs of patients.”
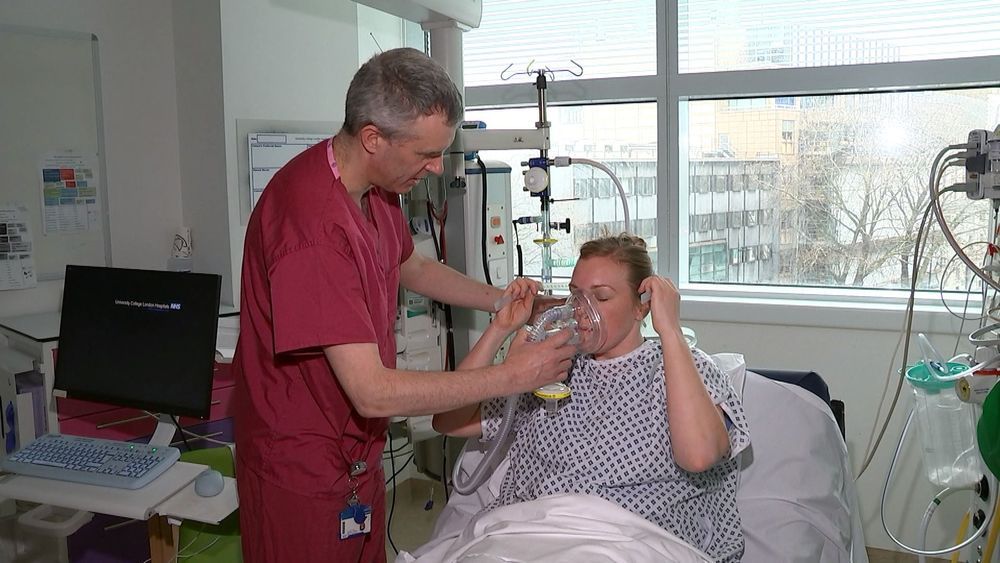
Brackley-based Mercedes has put aside traditional rivalries and joined forces with other F1 teams like Milton Keynes’ Red Bull and manufacturers — to produce a breathing aid called a CPAP that can help keep infected patients out of intensive care.
The device gets oxygen to the lungs without needing invasive treatment.
Watch Rebecca Haworth’s report.
A “cutting edge” alternative ventilator for coronavirus patients has been developed by a taskforce. The ‘exovent’ is a reinvention of the traditional iron lung, which saved the lives of countless polio victims during the 20th century.
Unlike the usual ventilators, which are positive pressure ventilators (PPV), the exovent is a non-invasive negative pressure ventilation (NPV) device, which could be used both in intensive care or on an ordinary hospital ward.
www.cambridge-news.co.uk/…/cambridge-coronavirus-ventillato…
Developed by a task force including Cambridge-based Marshall Aerospace and Defence Group, it can be manufactured in parallel with other ventilator designs.

A new study from researchers at North Carolina State University suggests that a material consisting of a polymer compound embedded with bismuth trioxide particles holds tremendous potential for replacing conventional radiation shielding materials, such as lead.
The bismuth trioxide compound is lightweight, effective at shielding against ionizing radiation such as gamma rays, and can be manufactured quickly—making it a promising material for use in applications such as space exploration, medical imaging and radiation therapy.
“Traditional radiation shielding materials, like lead, are often expensive, heavy and toxic to human health and the environment,” says Ge Yang, an assistant professor of nuclear engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper on the work. “This proof-of-concept study shows that a bismuth trioxide compound could serve as effective radiation shielding, while mitigating the drawbacks associated with traditional shielding materials.”
Intersting to look at.
‘A major challenge to defeating viruses is that a vaccine or drug might no longer be effective if the virus has mutated’

Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to change under the influence of experience and activities. Several aspects of neuroplasticity are noteworthy: neurogenesis (development of new nerve cells) and synaptogenesis (development of new contacts between nerve cells) among them. Neuroplasticity used to be thought of as a limited phenomenon, mostly restricted to the early years of life. More recently it has been demonstrated that neuroplasticity continues throughout life, even in advanced age. This provides the conceptual basis for a wide range of therapeutic efforts aiming to slow the detrimental effects of aging on the brain and to treat various brain disorders.
What are the factors influencing neuroplasticity? The question is compelling both as a scientific challenge and because of the therapeutic promise of neuroplasticity once we know how to control and harness it. Among such factors, the environmental factors influencing neuroplasticity are particularly intriguing. It turns out that a strong relationship exists between what people do with their brains and how their brains age.
Both anecdotal observations and formal research suggest that education confers a protective effect against dementia. Highly educated people are less likely to succumb to its effects. Robert Katzman was the first to note that the prevalence of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, is lower in people with advanced education. The MacArthur Foundation Research Network on Successful Aging sponsored a study of the predictors of cognitive change in older persons. Education emerged as by far the most powerful predictor of cognitive vigor in old age.

‘s COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Pulitzer Center.
A group of prominent academic scientists that has been advising the U.S. government on security matters since the Cold War is conducting a quick-turnaround, pro bono study of a new threat to national security—the impact of COVID-19 on academic research. And this time it’s personal.
Last month, some 30 members of Jason began to tackle the thorny question of how to reopen university laboratories safely in the midst of the coronavirus pandemic. Nobody is paying for the study, a rare departure for the group, whose work is usually financed by government agencies and often involves classified information. But the study’s leader, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) physicist Peter Fisher, says several federal agencies have expressed interest in the group’s analysis of the technical challenges facing every university that wants to resume research operations without jeopardizing the health of the faculty, students, and staff who work in those labs.