Glucose is life’s main energy source. But a Stanford Medicine study reveals a surprising role as a master manipulator of tissue maturation, hinting at its importance in diabetes and cancer.
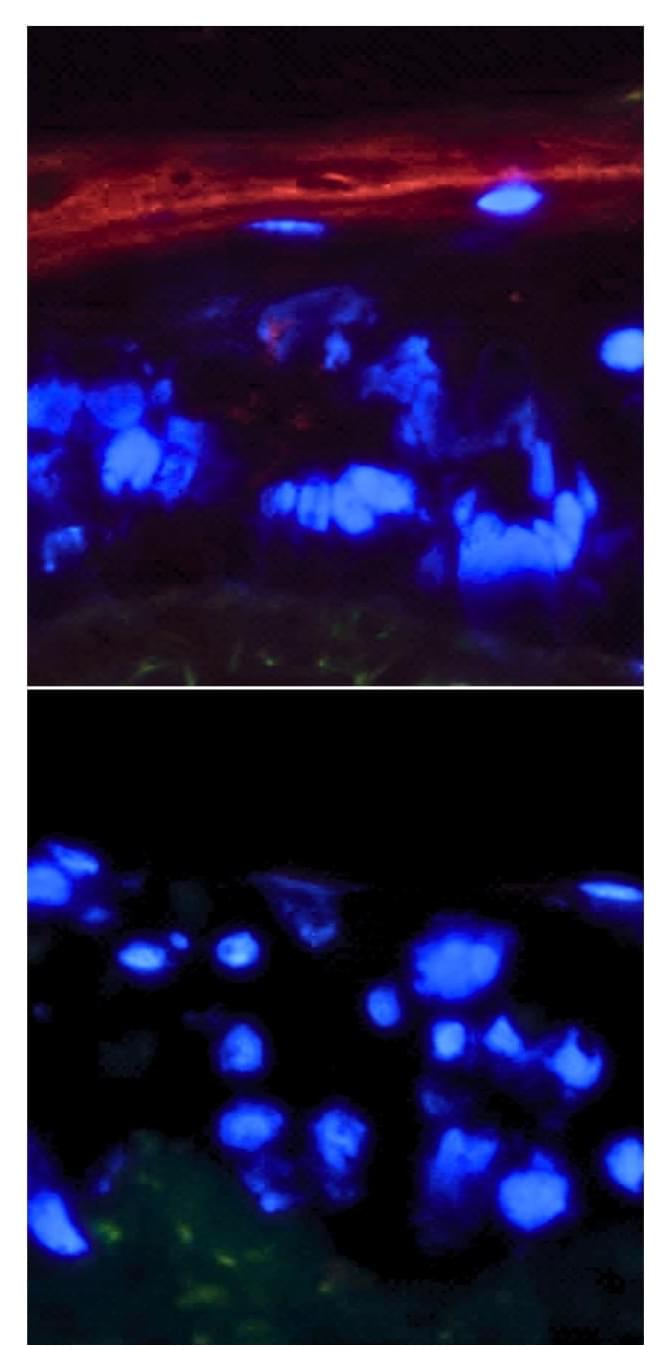

Glucose is life’s main energy source. But a Stanford Medicine study reveals a surprising role as a master manipulator of tissue maturation, hinting at its importance in diabetes and cancer.
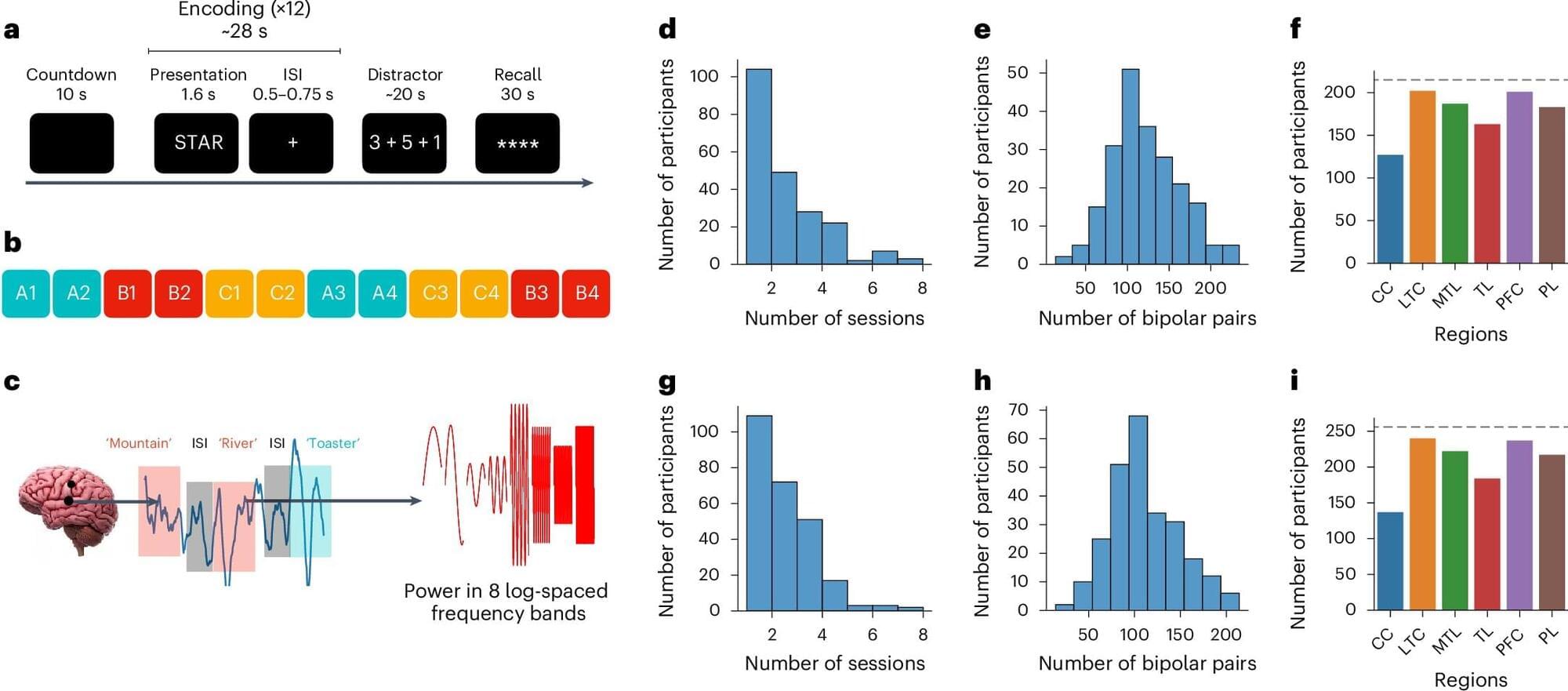
Past neuroscience and psychology studies have shown that after the human brain encodes specific events or information, it can periodically reactivate them to facilitate their retention, via a process known as memory consolidation. The reactivation of memories has been specifically studied in the context of sleep or rest, with findings suggesting that during periods of inactivity, the brain reactivates specific memories, allowing people to remember them in the long term.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and other institutions in the United States recently conducted a study exploring the possibility that the brain engages in a similar reactivation process during wakefulness to store important information for shorter periods of time. Their findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggest that the spontaneous reactivation of specific stimuli in the brain during the brief intervals between their encoding predicts the accuracy with which people remember them at the end of a memory task.
“Mike Kahana and I were both quite interested in the long history of thinking about rehearsal and its effects on the way in which people later recalled things,” Dr. David Halpern, the first author of the paper, told Medical Xpress. “Rehearsal is challenging to study since people often do it without any overt behavior (unless we ask them to rehearse out loud).”
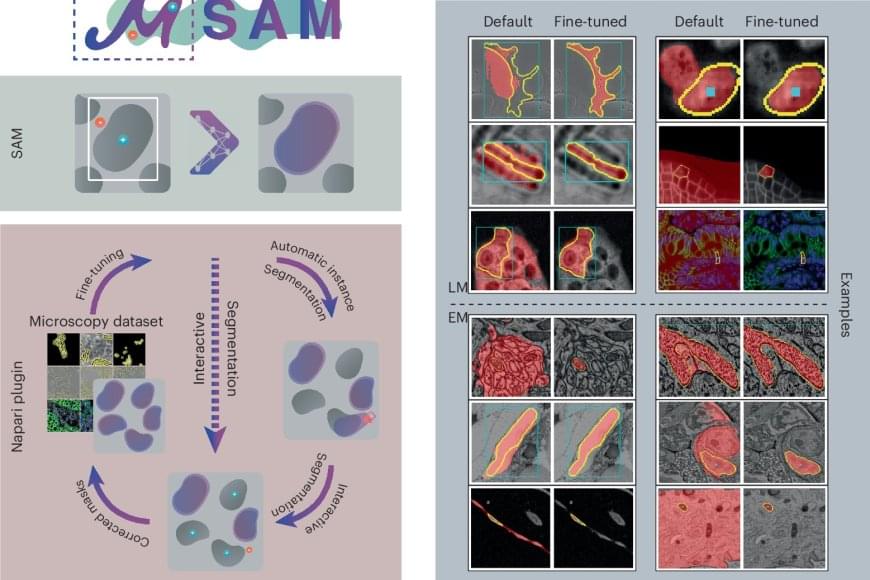
To adapt the existing software to microscopy, the research team first evaluated it on a large set of open-source data, which showed the model’s potential for microscopy segmentation. To improve quality, the team retrained it on a large microscopy dataset. This dramatically improved the model’s performance for the segmentation of cells, nuclei and tiny structures in cells known as organelles.
The team then created their software, μSAM, which enables researchers and medical doctors to analyze images without the need to first manually paint structures or train a specific AI model. The software is already in wide use internationally, for example to analyze nerve cells in the ear as part of a project on hearing restoration, to segment artificial tumor cells for cancer research, or to analyze electron microscopy images of volcanic rocks.
“Analyzing cells or other structures is one of the most challenging tasks for researchers working in microscopy and is an important task for both basic research in biology and medical diagnostics,” says the author.
Identifying and delineating cell structures in microscopy images is crucial for understanding the complex processes of life. This task is called “segmentation” and it enables a range of applications, such as analysing the reaction of cells to drug treatments, or comparing cell structures in different genotypes. It was already possible to carry out automatic segmentation of those biological structures but the dedicated methods only worked in specific conditions and adapting them to new conditions was costly.
An international research team has now developed a method by retraining the existing AI-based software Segment Anything on over 17,000 microscopy images with over 2 million structures annotated by hand.
Their new model is called Segment Anything for Microscopy and it can precisely segment images of tissues, cells and similar structures in a wide range of settings. To make it available to researchers and medical doctors, they have also created μSAM, a user-friendly software to “segment anything” in microscopy images. Their work was published in Nature Methods.

While researchers continue to work on a full cure for Alzheimer’s disease, they’re finding treatments that can help manage symptoms and delay their onset, including the recently approved next-gen therapies lecanemab and donanemab.
Both treatments have been approved by US regulators in the last couple of years, and they work by clearing out some of the amyloid protein plaques in the brain that are linked to Alzheimer’s. However, there’s some debate over how effective they are.
To quantify the effectiveness of lecanemab and donanemab in more meaningful terms, researchers from the Washington University School of Medicine (WashU Medicine) recruited 282 volunteers with Alzheimer’s, analyzing the impacts of taking these drugs over an average of nearly three years.

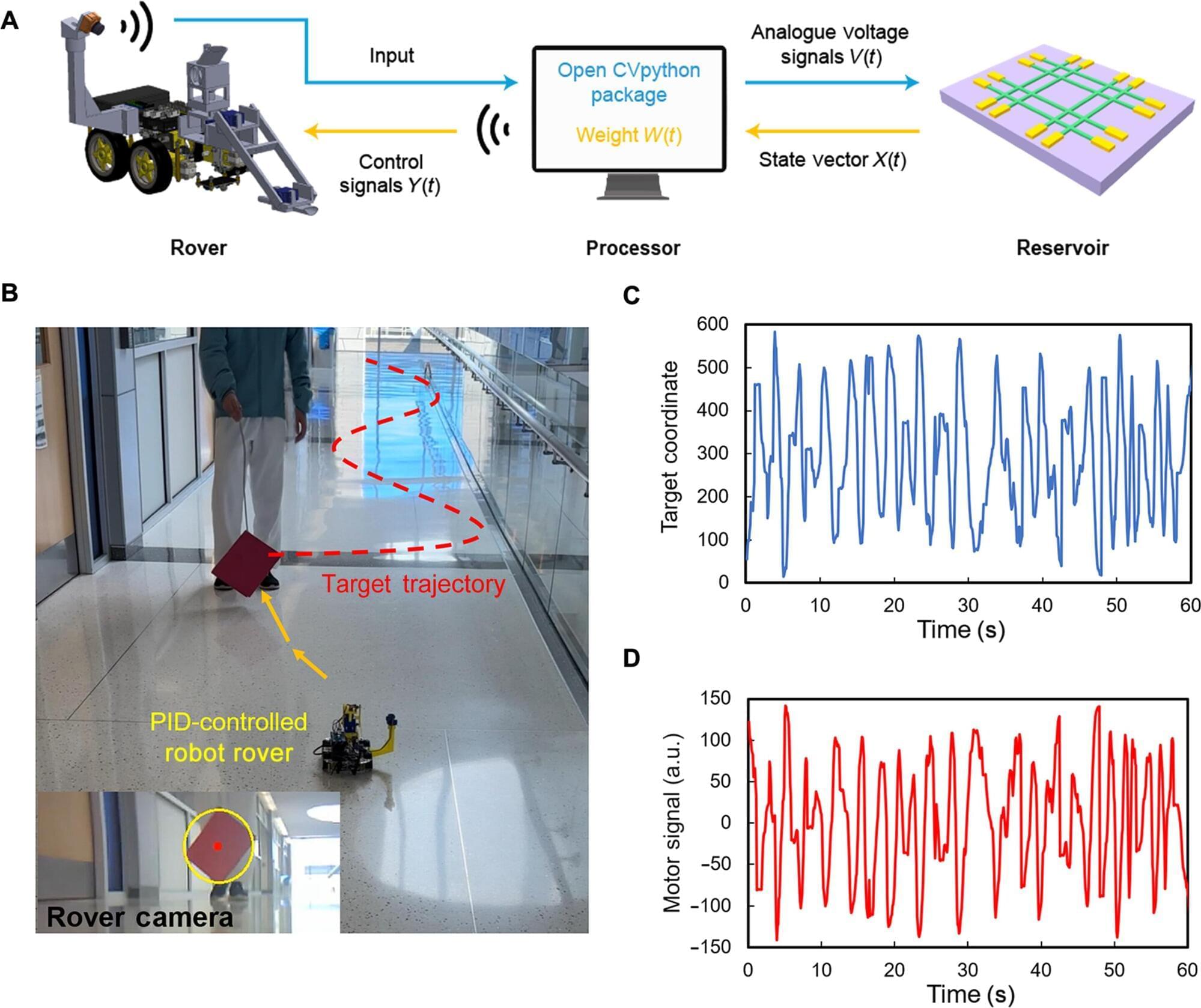
A smaller, lighter and more energy-efficient computer, demonstrated at the University of Michigan, could help save weight and power for autonomous drones and rovers, with implications for autonomous vehicles more broadly.
The autonomous controller has among the lowest power requirements reported, according to the study published in Science Advances. It operates at a mere 12.5 microwatts—in the ballpark of a pacemaker.
In testing, a rolling robot using the controller was able to pursue a target zig-zagging down a hallway with the same speed and accuracy as with a conventional digital controller. In a second trial, with a lever-arm that automatically repositioned itself, the new controller did just as well.
With rates of lung cancer climbing among non-smokers, new strategies are needed to detect lung cancer earlier. Drs. Sequist and Fintelmann at Mass General Brigham are discovering how AI can be used to address this growing concern.
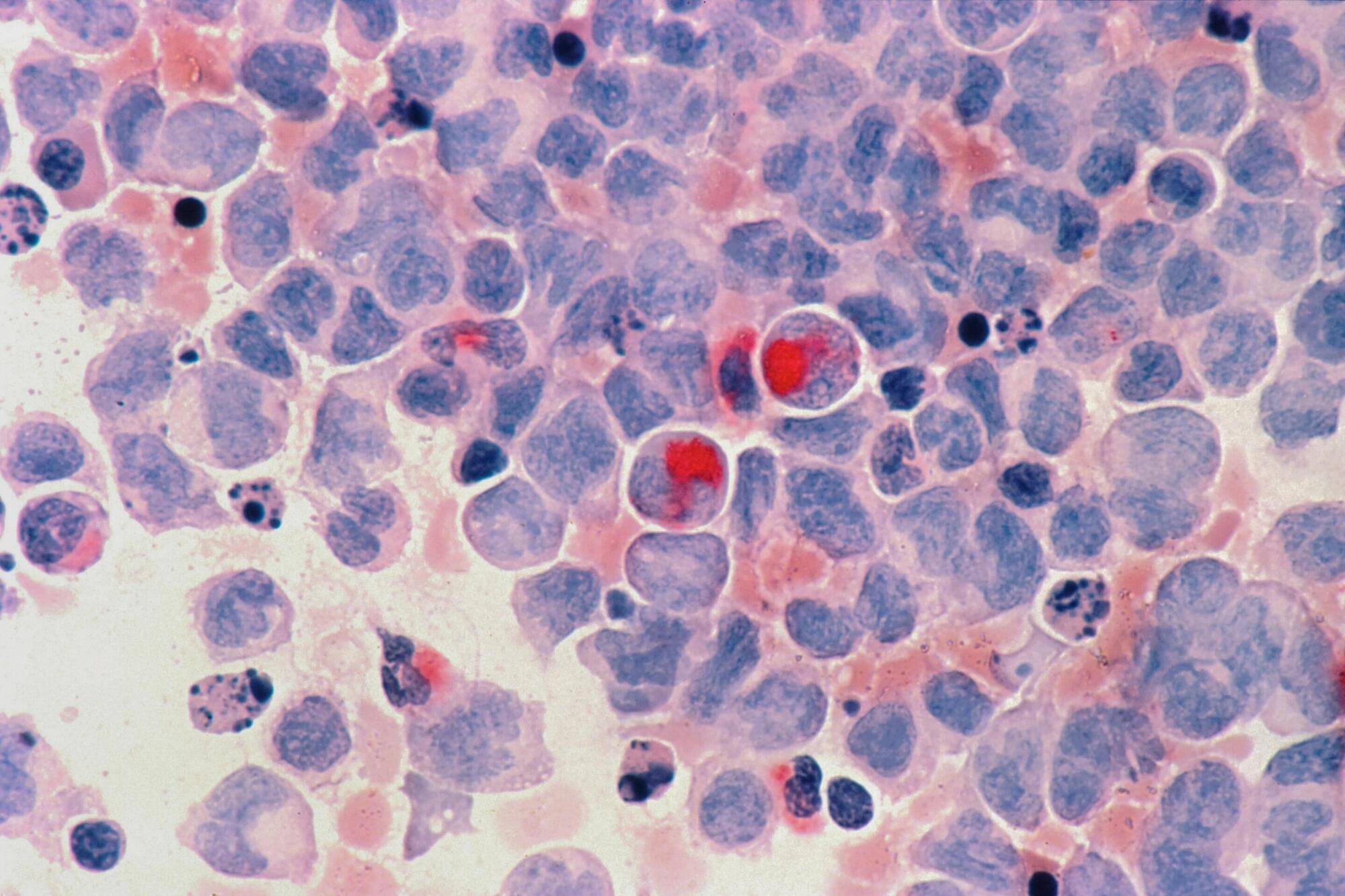
Investigators at Mass General Brigham have uncovered how resistance to chemotherapies may occur in some cancers. Researchers focused on a pathway that harnesses reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill cancer cells. The study found that mutations to VPS35, a key player in this pathway, can prevent chemotherapy-induced cell death. These results, published in Nature, could help pinpoint treatment-resistant tumors.
“ROS play an important role in healthy and diseased cells, but pathways that sense and control cellular ROS levels are not well understood,” said corresponding author Liron Bar-Peled, Ph.D., of the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at Mass General Cancer Center (MGCC), a member of the Mass General Brigham health care system. “A clearer understanding of ROS could help us understand why chemoresistance occurs in some cases.”
Low concentrations of ROS are required for normal cell signaling, but higher levels of ROS can damage cells and contribute to diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration. Researchers know that mitochondria play an important role in ROS production, but it has been unclear if ROS-sensing proteins influence the mitochondria. If they do, this could impact responses to some anti-cancer treatments.
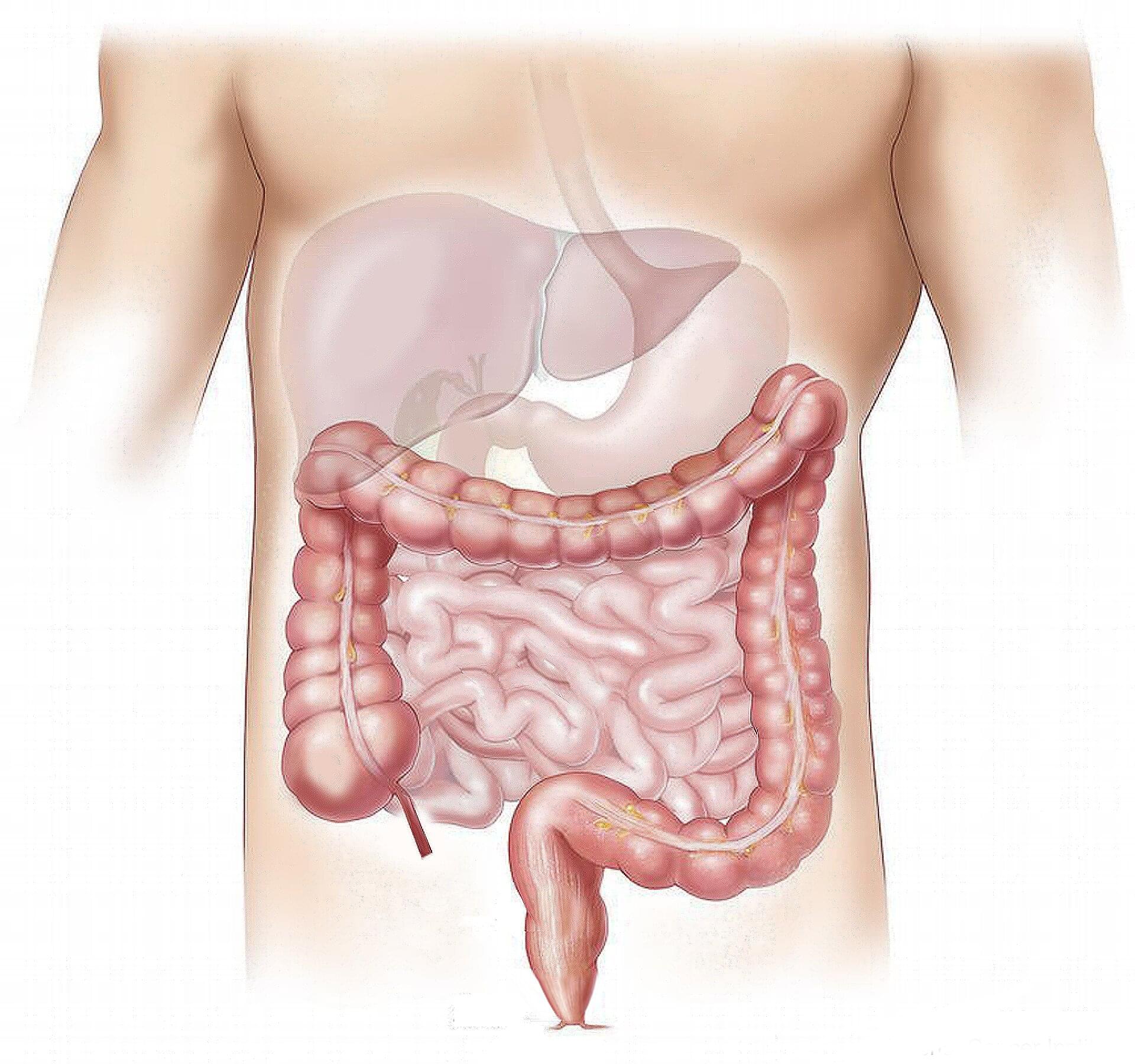
After every meal, the intestines perform an action called peristalsis—moving food through their hollow interiors with coordinated contractions and relaxations of the smooth muscle.
For more than a century, scientists have known that nerve cells in the gut propel the colon to move, allowing the organ to perform its life-sustaining function. But exactly how these intestinal nerve cells do their job has remained elusive.
Now a new study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified the mechanism behind this phenomenon, showing that the gut’s motility is altered by exercise, pressure, and inflammation.