Researchers foresee myriad benefits for humanity, but also acknowledge ethical issues.

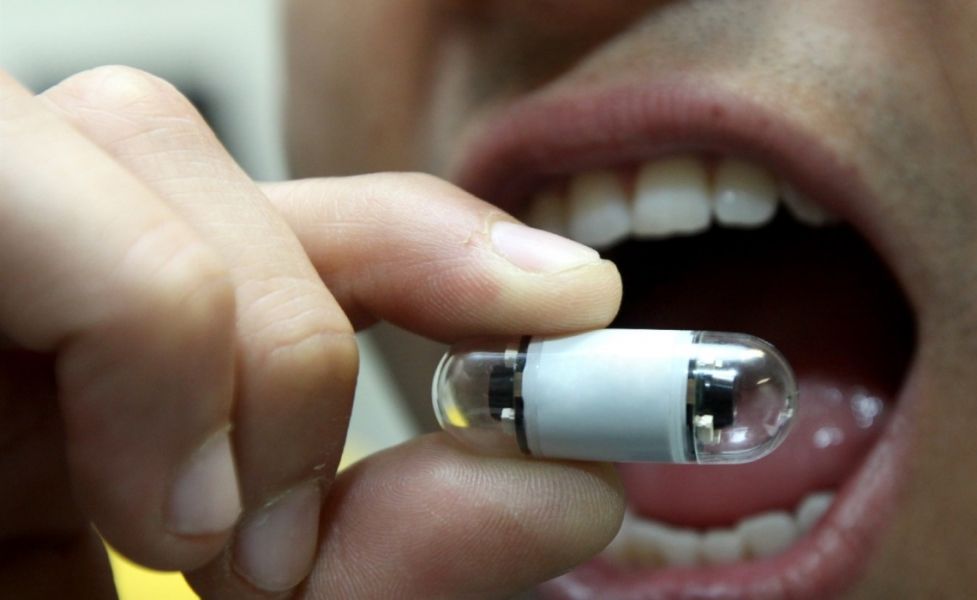
RIO DE JANEIRO, BRAZIL — Approved in Brazil almost four years ago, the colon capsule is finally starting to become popular and available in laboratories and diagnostic centers.
The capsule serves as an alternative to traditional colonoscopy, where a wired camera is introduced through the anus and guided throughout the large intestine.
“The new technology is less invasive and does not require sedation,” says Dr. Admar Borges, of the Brazilian Society of Digestive Endoscopy.
Researchers from the University Hospital and ETH Zurich have developed a machine that repairs injured human livers and keep them alive outside the body for one week. This breakthrough may increase the number of available organs for transplantation saving many lives of patients with severe liver diseases or cancer.

Circa 2018
Magnets may play a central role in the future of surgery. This summer, US surgeon Dr. Jeffrey Cadeddu performed the first of several magnet-assisted prostate cancer surgeries he has now done.
Circa 2013
The unique relationship between the coordinates in the bore of a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner and the magnetic field gradients used for MRI allows building a localization system based on the measurement of these gradients. We have previously presented a miniature 3D Hall probe integrated in a low cost, low voltage 0.35μm CMOS chip from which we were able to measure the magnetic gradient 3D maps of 1.5T and 3T MRI scanners. In this paper, this 3D Hall probe has been integrated in a magnetic tracking device prototype and an algorithm was built to determine the position of the probe. First experimental results show that the probe gives its position with accuracy close to a few millimeters, and that sub-millimeter localization in a one-shot-3ms-measurement should be readily possible. Such a prototype opens the way for the development of MRI compatible real time magnetic tracking systems which could be integrable in surgical tools for MR-guided minimally-invasive surgery.
Neuroregeneration entails not only neurogenesis, but also regrowth of lost connections and birth of non-neuronal cells. While adult neurogenesis in humans is only known to occur definitively in a few precisely circumscribed regions of the brain, work in other species suggests that science has only scratched the surface of the full regenerative potential of our own nervous systems.
The serotonergic system has widely been shown to control many aspects of neuroregeneration. In some regions, it facilitates neurogenesis, while in others, it seems to inhibit it. In the case of inhibition, a recent example has been published in PLOS Biology. The authors used a zebrafish model of Alzheimer’s disease to show that amyloid-induced interleukin-4 (IL4) promotes neurogenic stem cell proliferation by suppressing the production of serotonin. In these animals, there is a unique neuro-immune interaction through which IL4 secreted by dying neurons activates microglia. In turn, microglia reciprocate by revving up neural stem cell proliferation.
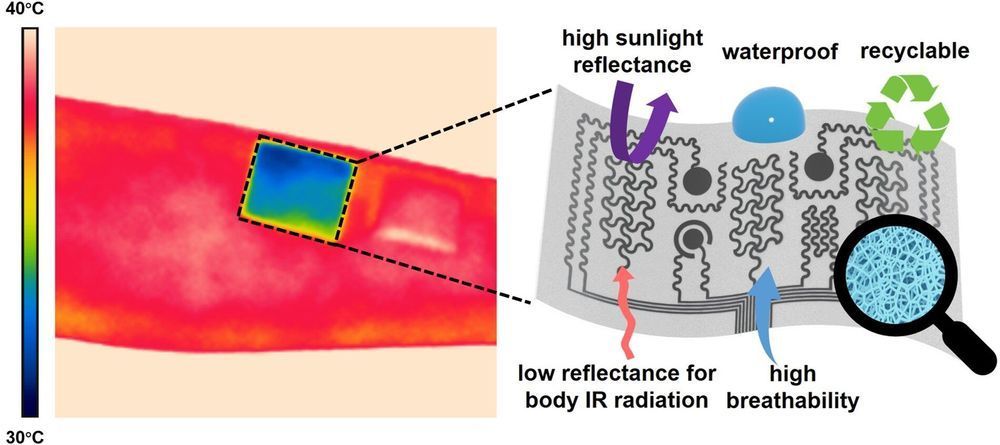
One day, soldiers could cool down on the military battlefield—preventing heat stroke or exhaustion—by using “wearable air conditioning,” an on-skin device designed by engineers at the University of Missouri. The device includes numerous human health care applications such as the ability to monitor blood pressure, electrical activity of the heart and the level of skin hydration.
The findings are detailed in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Unlike similar products in use today or other related concepts, this breathable and waterproof device can deliver personal air conditioning to a human body through a process called passive cooling. Passive cooling does not utilize electricity, such as a fan or pump, which researchers believe allows for minimal discomfort to the user.