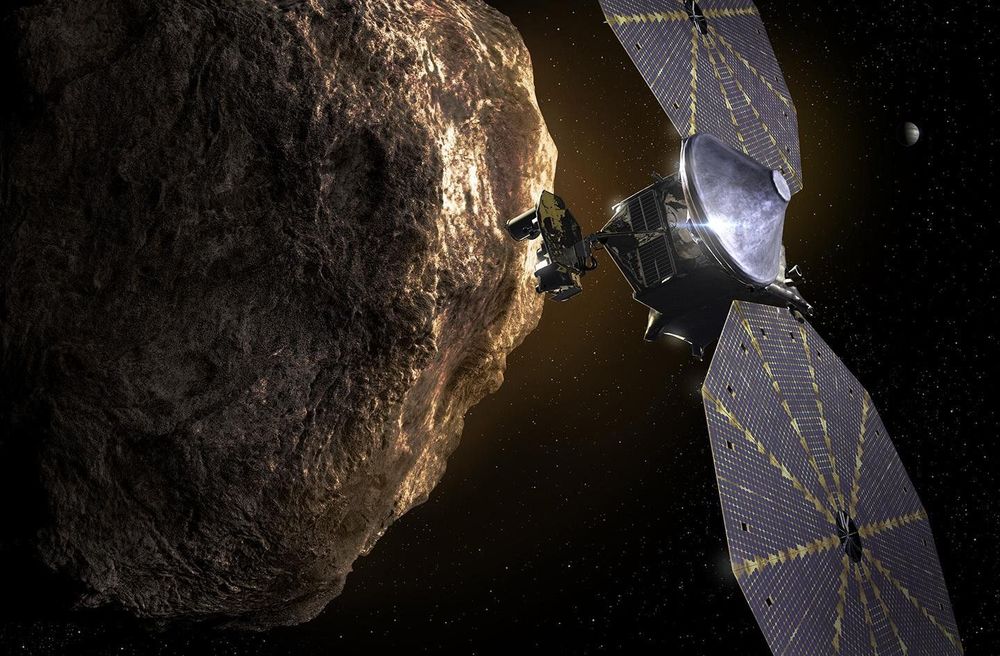
NASA’s Lucy mission, led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), has achieved an important milestone by passing its System Integration Review and clearing the way for spacecraft assembly. This NASA Discovery Program class mission will be the first to explore Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids, ancient small bodies that share an orbit with Jupiter and hold important insights to understanding the early solar system.
The Lucy spacecraft, during its nominal 12-year mission, will fly by and collect data from seven of these primitive worlds, plus a main belt asteroid. Because the Trojan asteroids are remnants of the primordial material that formed the outer planets, they hold vital clues to deciphering the history of the solar system. Lucy, like the human fossil for which it is named, will revolutionize the understanding of our origins.
Over the last few months, the Lucy team has focused on building and testing all the components of the spacecraft, including the scientific instruments, electronics, communications and navigation systems while observing all appropriate pandemic protocols. At this review, the Lucy team demonstrated to an independent senior review board, including NASA and external experts, that the systems and subsystems are on schedule to proceed to assembly, testing and integration.