Scientists can now edit multiple sites in the genome at the same time to learn how different DNA stretches co-operate in health and disease.
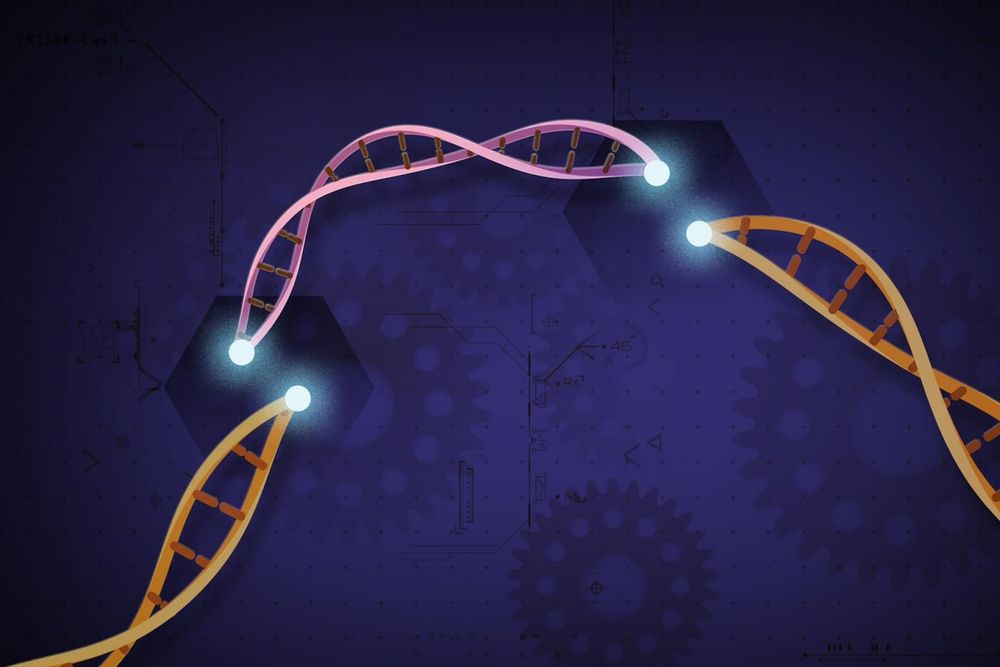
CRISPR-based DNA editing has revolutionized the study of the human genome by allowing precise deletion of any human gene to glean insights into its function. But one feature remained challenging—the ability to simultaneously remove multiple genes or gene fragments in the same cell. Yet this type of genome surgery is key for scientists to understand how different parts of the genome work together in the contexts of both normal physiology and disease.
Now such a tool exists thanks to the teams of Benjamin Blencowe and Jason Moffat, both professors of molecular genetics at the Donnelly Centre for Cellular and Biomolecular Research. Dubbed ‘CHyMErA’, for Cas Hybrid for Multiplexed Editing and Screening Applications, the method can be applied to any type of mammalian cell to systematically target the DNA at multiple positions at the same time, as described in a study published in the journal Nature Biotechnology.