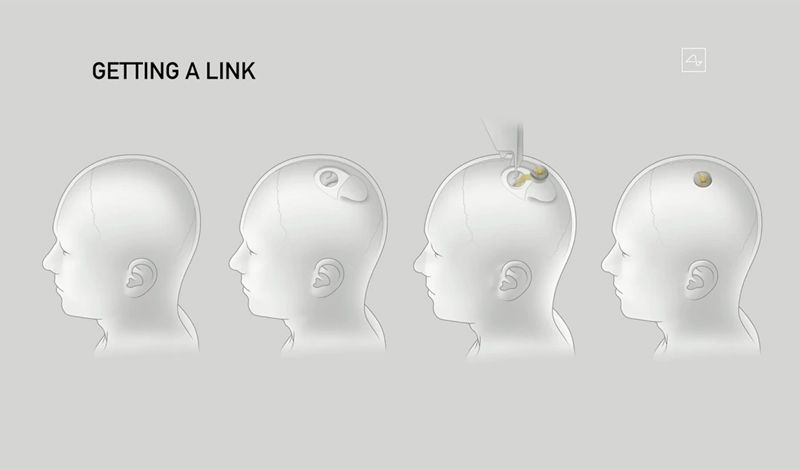
In this video, Elon Musk demonstrates a prototype brain–computer interface chip – implanted in a pig – that his company, Neuralink, has been working on. The device could one day be used by humans to augment their abilities.
Founded in 2016, the Neuralink Corporation remained highly secretive about its work until July 2019, when Musk presented his concept at the California Academy of Sciences. It emerged that he planned to create brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) not only for diseased or injured patients, but also healthy individuals who might wish to enhance themselves.
Yesterday, in a livestream event on YouTube, Musk unveiled a pig called Gertrude with a coin-sized chip in her brain. Simpler and smaller than the original revealed last year, the read/write link device can nevertheless pack 1,024 channels with megabit wireless data rate and all-day battery life. This latest prototype – version 0.9 – has now been approved as an FDA breakthrough device, allowing it to be used in limited human trials under the US federal guidelines for testing medical devices. The chip is removable, Musk explained, as he showed another pig called Dorothy, who no longer had the implant and was healthy, happy and indistinguishable from a normal pig.