Would you be okay to have these injected in you?
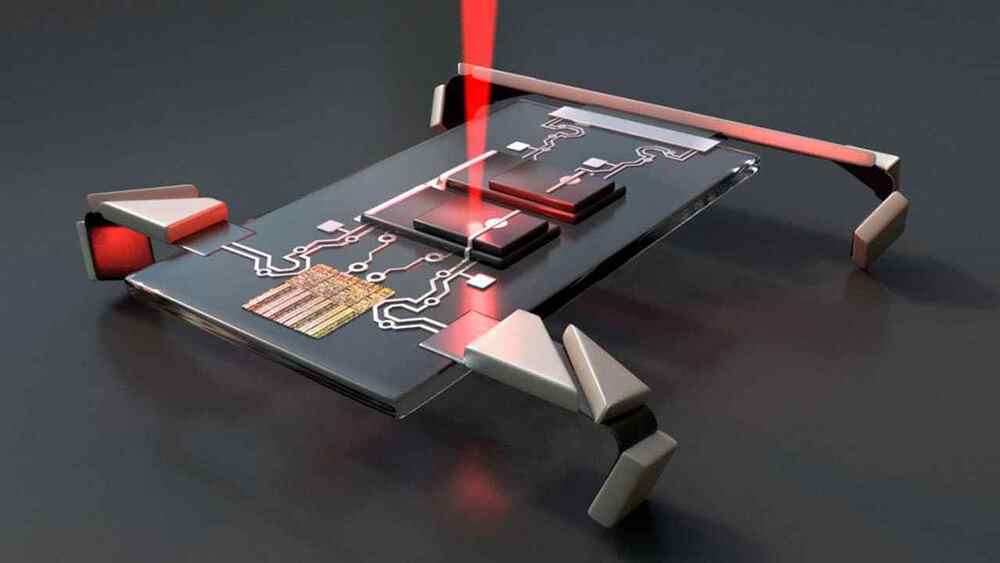
Engineers at Cornell University developed a microscopic robot – so small it’s invisible to the naked eye – that walks. It’s so tiny that ten could fit within a period. The team says they can manufacture one million of the robots per week.
The new robot is essentially a microchip on four origami-inspired legs that can be activated by lasers. It was designed to crawl inside the human body, find and eliminate diseases. It can be steered by beaming a laser at its feet, which causes their leg to bend.
Itai Cohen and Paul McEuen Labs, leaders of this invention, envisions them as a beneficial medical tool to do things like hunt down and destroy cancer cells. The micro-bots are so small they can be injected into the body.