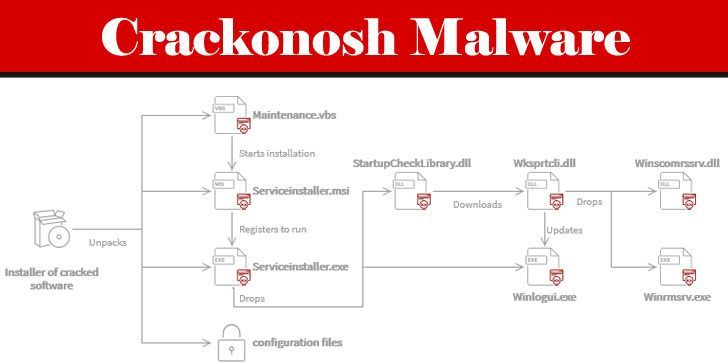
A malware called Crackonosh infected 222000 PCs in order to mine $2 million worth of Monero cryptocurrency.


Quick, accurate and easy-to-use, CRISPR-Cas9 has made genomic editing more efficient—but at the same time has made human germline editing much more feasible, erasing many of the ethical barriers erected to prevent scientists from editing the genes of heredity.
“The ethical debate about what is now called human gene editing has gone on for more than 50 years,” writes Dr. John H. Evans, co-director of the Institute for Practical Ethics at the University of California, San Diego. “For nearly that entire time, there has been consensus that a moral divide exists between somatic and human germline editing.”
In an essay published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Evans contends that many of the potent bioethical arguments that once made germline editing a verboten concept, have begun to dissolve in the era of CRISPR.

To understand how the clones can create millions of copies of themselves and yet remain functional, Oldroyd and his team compared the genomes of Cape honeybee workers with those of their queen and her offspring.
After forcing the Cape queen to reproduce asexually by fitting her with surgical tape that prevented her from mating, the team examined certain DNA sequences of both the Cape queen and the 25 larvae she produced. Then, they did the same for four Cape honeybee workers and their 63 larvae.
The team discovered that the asexually reproduced offspring of the queen had levels of recombination (DNA mixing) 100 times greater than the genetically identical cloned offspring of the workers — a finding that suggests the Cape worker bees have evolved a mutation that prevents recombination. Without the risk of a one-third loss of genetic material caused by the asexual reshuffling process, the workers are free to continually create perfect copies of themselves.
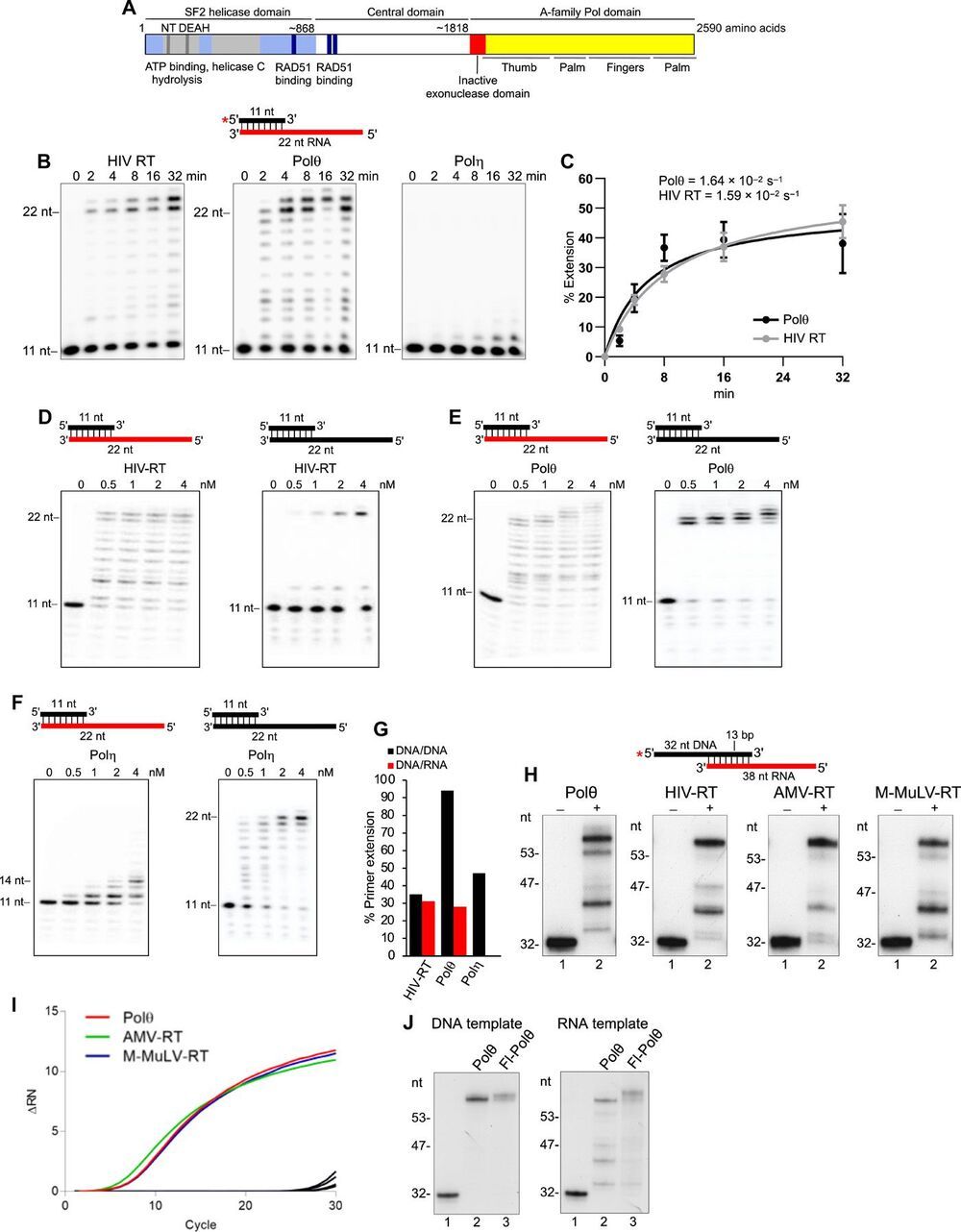
Genome-embedded ribonucleotides arrest replicative DNA polymerases (Pols) and cause DNA breaks. Whether mammalian DNA repair Pols efficiently use template ribonucleotides and promote RNA-templated DNA repair synthesis remains unknown. We find that human Polθ reverse transcribes RNA, similar to retroviral reverse transcriptases (RTs). Polθ exhibits a significantly higher velocity and fidelity of deoxyribonucleotide incorporation on RNA versus DNA. The 3.2-Å crystal structure of Polθ on a DNA/RNA primer-template with bound deoxyribonucleotide reveals that the enzyme undergoes a major structural transformation within the thumb subdomain to accommodate A-form DNA/RNA and forms multiple hydrogen bonds with template ribose 2′-hydroxyl groups like retroviral RTs. Last, we find that Polθ promotes RNA-templated DNA repair in mammalian cells. These findings suggest that Polθ was selected to accommodate template ribonucleotides during DNA repair.
Polymerase θ (Polθ) is a unique DNA polymerase-helicase fusion protein in higher eukaryotes whose A-family polymerase domain evolved from Pol I enzymes (Fig. 1A) (1, 2). However, contrary to most Pol I enzymes, Polθ is highly error-prone and promiscuous (3–6), performs translesion synthesis (TLS) opposite DNA lesions (3, 7, 8), and facilitates microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) of double-strand breaks (DSBs) by extending partially base-paired 3′ single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) overhangs at DSB repair junctions (5, 9–12). Polθ is not expressed in most tissues but is highly expressed in many cancer cells, which corresponds to a poor clinical outcome (13, 14). Furthermore, Polθ confers resistance to genotoxic cancer therapies and promotes the survival of cells deficient in DNA damage response pathways (11, 13–16). Thus, Polθ represents a promising cancer drug target.
Intriguingly, Polθ has an inactive proofreading domain due to acquired mutations (Fig. 1A) (2). Inactivating the 3′-5′ proofreading function of closely related A-family bacterial Pol I Klenow fragment (KF) enables this polymerase to reverse transcribe RNA like retroviral reverse transcriptases (RTs), which lack proofreading activity (fig. S1A) (17, 18). Because Polθ is highly error-prone and promiscuous and contains an inactive proofreading domain, we hypothesized that it has RNA-dependent DNA synthesis activity. Given that ribonucleotides are the most frequently occurring nucleotide lesion in genomic DNA that arrest replicative Pols and cause DNA breaks (19, 20), we also envisaged that Polθ would tolerate template ribonucleotides during its DNA repair activities and thus promote RNA-templated DNA repair synthesis (RNA-DNA repair). Although RNA-DNA repair mechanisms have been demonstrated in genetically engineered yeast cells (21, 22), they remain obscure in mammalian cells.
Saccharine, aspartame, sucralose.
New research has discovered that common artificial sweeteners can cause previously healthy gut bacteria to become diseased and invade the gut wall, potentially leading to serious health issues.
The study, published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, is the first to show the pathogenic effects of some of the most widely used artificial sweeteners—saccharin, sucralose, and aspartame—on two types of gut bacteria, E. coli (Escherichia coli) and E. faecalis (Enterococcus faecalis).
Previous studies have shown that artificial sweeteners can change the number and type of bacteria in the gut, but this new molecular research, led by academics from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), has demonstrated that sweeteners can also make the bacteria pathogenic. It found that these pathogenic bacteria can attach themselves to, invade, and kill Caco-2 cells, which are epithelial cells that line the wall of the intestine.

“We’re excited to share that AWS has acquired Wickr, an innovative company that has developed the industry’s most secure, end-to-end encrypted, communication technology,” Stephen Schmidt, Amazon Web Services’ vice president, wrote. With a nod to the company’s ever-deepening relationships with the military, and Washington in general, Schmidt added that Wickr’s features give “security conscious enterprises and government agencies the ability to implement important governance and security controls to help them meet their compliance requirements.” Schmidt himself has a background in this space: his LinkedIn profile notes he spent a decade at the FBI.
Wickr’s app — like secure messaging competitor Signal — has been popular with journalists and whistleblowers; it’s also been a go-to for criminals, Motherboard notes. It’s unclear if the proximity to the tech monolith will impact the app’s popularity for free users.
In Amazon’s case, Schmidt indicates the acquisition was at least partially influenced by the need to preserve information security while working remotely. “With the move to hybrid work environments, due in part to the COVID-19 pandemic, enterprises and government agencies have a growing desire to protect their communications,” he wrote.

STANFORD, Calif. — A groundbreaking “superhero” vaccine inspired by the DNA code of Olympic athletes could help transform society over the next decade, a top genetic scientist claims.
The vaccine would provide lifelong protection against three of the top ten leading causes of death, according to Euan Ashley, professor of medicine and genetics at Stanford University. The so-called “superhero” jab could offer simultaneous, long-term protection against heart disease, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and liver disease, thanks to advances in genetic engineering.
This breakthrough treatment would deliver the blueprint of “ideal” cells from men and women whose genes are more disease-resistant than those of the average person, together with an “instruction manual” to help the body “repair, tweak and improve” its own versions. A single dose could lead to a “body-wide genetic upgrade” that would cut the risk of premature death in some adults by as much as 50 percent.
“At first, we had a hard time believing the results. Many of these genes are classical hallmarks of aging and yet our results suggested that their activity is more a function of the presence of bacteria rather than the aging process,” said Dr. Shukla.
Notably, this included genes that control stress and immunity. The researchers tested the impact that the antibiotics had on these genes by starving some flies or infecting others with harmful bacteria and found no clear trend. At some ages, the antibiotics helped flies survive starvation or infection longer than normal whereas at other ages the drugs either had no effect or reduced the chances of survival.
NIH scientists discover that bacteria may drive activity of many hallmark aging genes in flies.
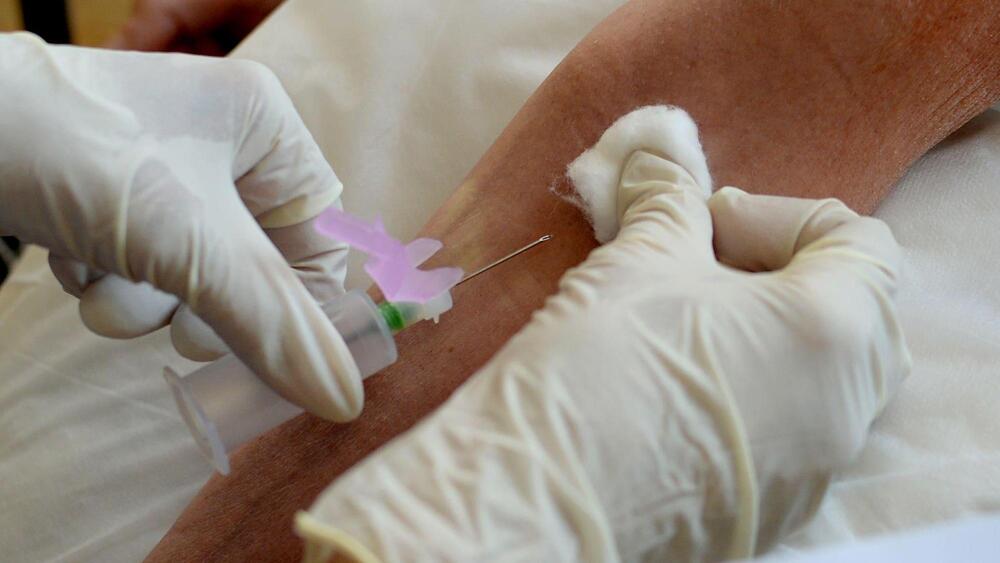
A simple blood test that can detect more than 50 types of cancer before any clinical signs or symptoms of the disease is accurate enough to be rolled out as a multi-cancer screening test, according to scientists.… See More.
The test is based on a type of DNA that is shed by tumours into the bloodstream.

I am waiting for tricorders.
The idea of visiting the doctor’s office with symptoms of an illness and leaving with a scientifically confirmed diagnosis is much closer to reality because of new technology developed by researchers at McMaster University.
Engineering, biochemistry and medical researchers from across campus have combined their skills to create a hand-held rapid test for bacterial infections that can produce accurate, reliable results in less than an hour, eliminating the need to send samples to a lab.
Their proof-of-concept research, published today in the journal Nature Chemistry, specifically describes the test’s effectiveness in diagnosing urinary tract infections from real clinical samples. The researchers are adapting the test to detect other forms of bacteria and for the rapid diagnosis of viruses, including COVID-19. They also plan to test its viability for detecting markers of cancer.