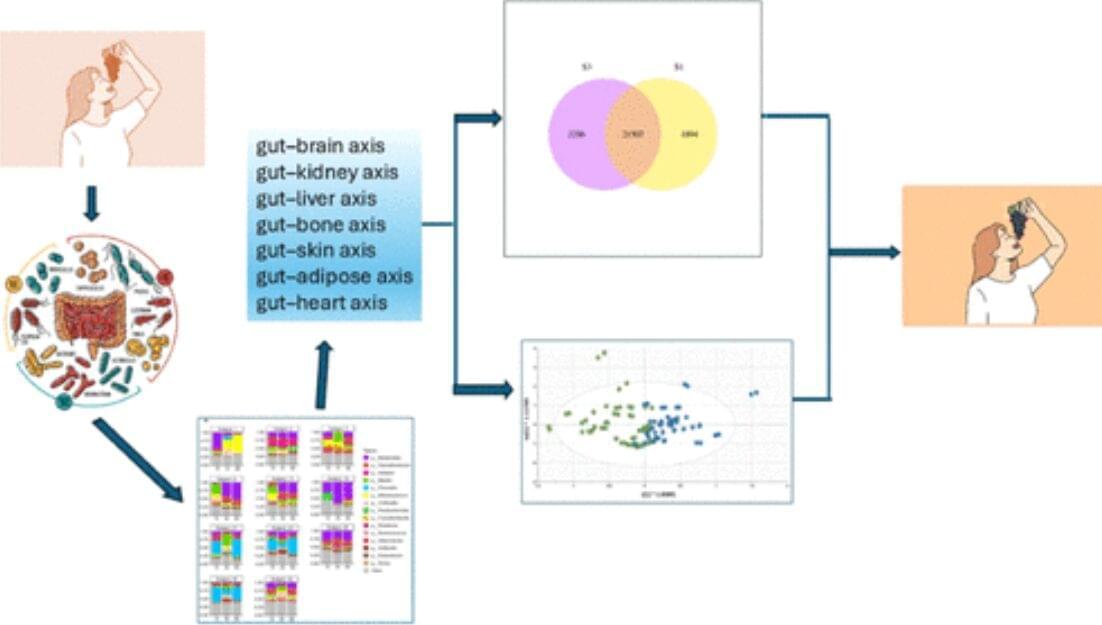
Fresh grapes contain a potent mix of over 1,600 compounds that benefit heart, brain, skin, and gut health. New evidence suggests they deserve official superfood recognition, with benefits even at the genetic level.
A new article appearing in the current issue of the peer-reviewed Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry explores the concept of “superfoods” and makes a case that fresh grapes have earned what should be a prominent position in the superfood family. The author, leading resveratrol and cancer researcher John M. Pezzuto, Ph.D., D.Sc., Dean of the College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences at Western New England University, brings forth an array of evidence to support his perspective on this issue.
As noted in the article, the term “superfood” is a common word without an official definition or established criteria. Mainstream superfoods are typically part of the Mediterranean Diet and generally rich in natural plant compounds that are beneficial to a person’s health. Pezzuto addresses the broader topic of superfoods in detail, then makes the scientific case for grapes, noting that fresh grapes are underplayed in this arena and often not included with mention of other similar foods, such as berries.