Medcalf: Because you’re moving away from the economics of scale to closer to the clinic, the batches are smaller and some of the traditional paradigms for quality assurance, such as proof of sterility, are harder to arrange. Thus, you need to have a manufacturing system that includes quality assurance within the system itself.
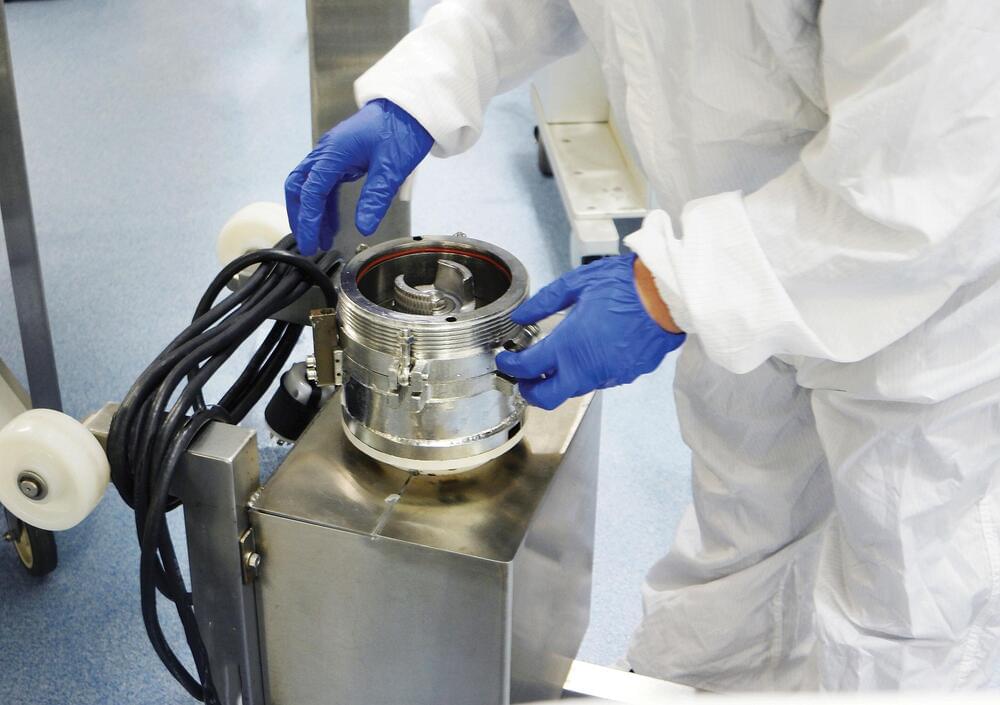
Automation is often presented as a way to remove the single largest source of infective risk, i.e. the human operator. For example, the self-sterilizing reusable units being developed at the University of Osaka under Professor Masahiro Kino-oka allow small-scale production with a high degree of confidence in the aseptic management of the environment.
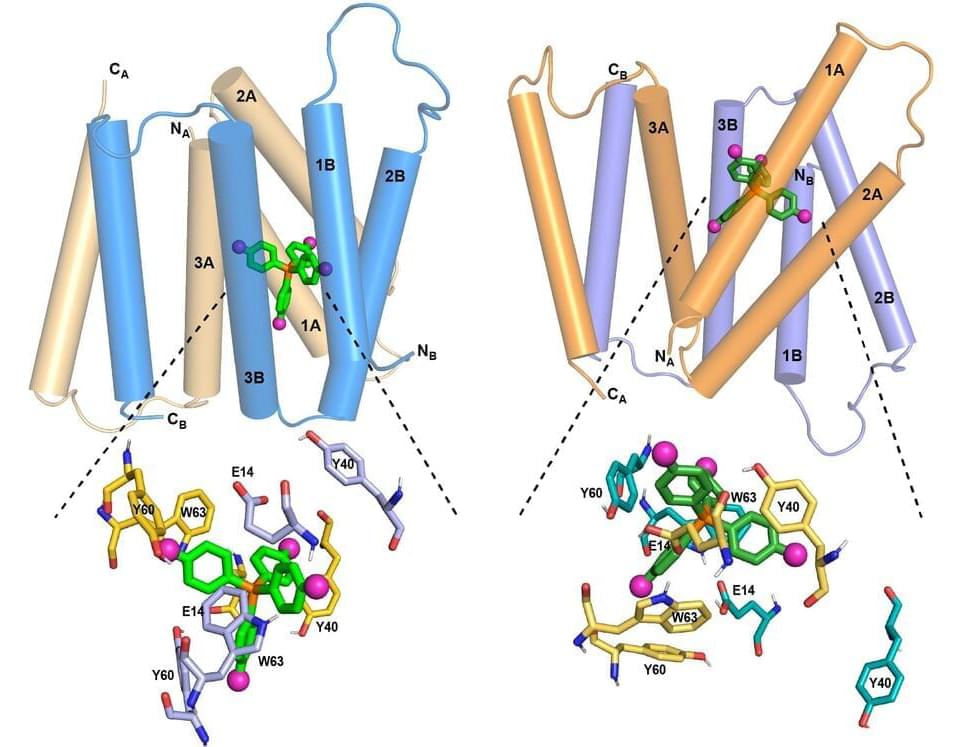
Another challenge is defining a product that has variable characteristics. The main reason for decentralizing is to allow customization to a patient, which means you need to have a hierarchy of levels of specification. For example, with bioprinting, which also produces a customized product, you need to define bulk properties, but you also need to set constraints around how it’s anchored or implanted into the patient.