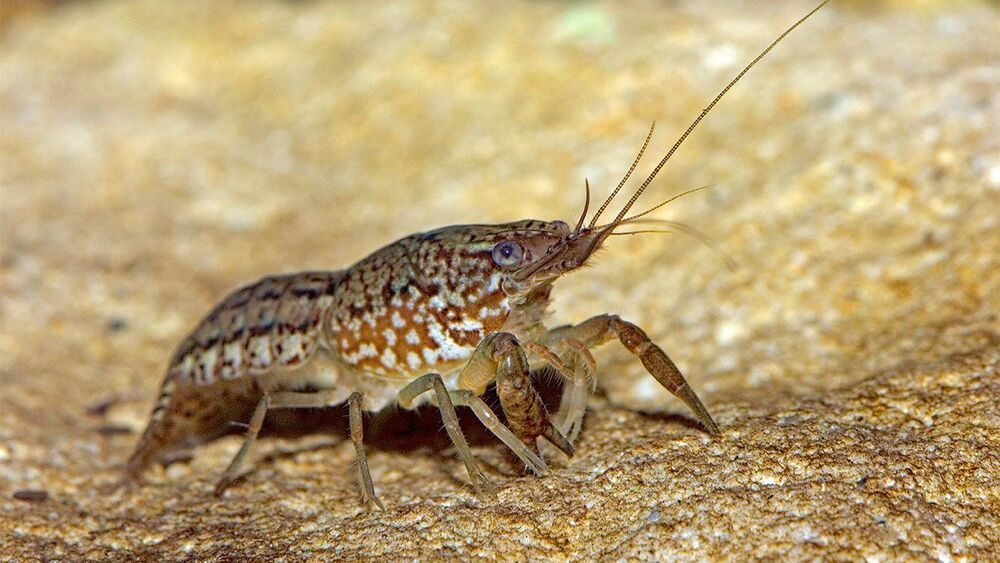
Crayfish DNA can help us conquer cancer finally.
Finding may also provide clues to how cancer spreads.

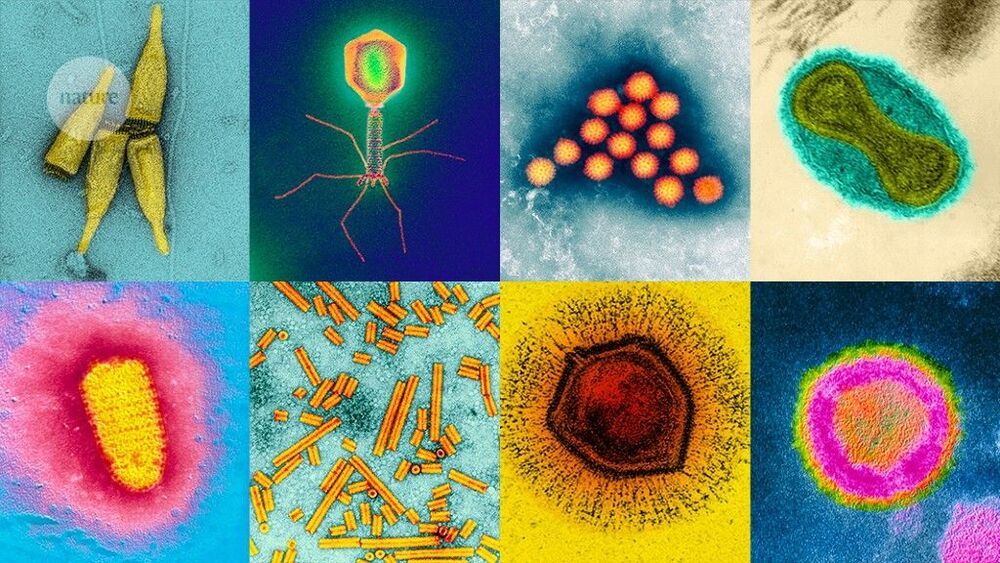
Over the past ten years, the number of known and named viruses has exploded, owing to advances in the technology for finding them, plus a recent change to the rules for identifying new species, to allow naming without having to culture virus and host. One of the most influential techniques is metagenomics, which allows researchers to sample the genomes in an environment without having to culture individual viruses. Newer technologies, such as single-virus sequencing, are adding even more viruses to the list, including some that are surprisingly common yet remained hidden until now. It’s an exciting time to be doing this kind of research, says Breitbart. “I think, in many ways, now is the time of the virome.”
SARS-CoV-2 is just one of nonillions of viruses on our planet, and scientists are rapidly identifying legions of new species.
Fortunately, automakers, suppliers and government leaders are examining things like electric vehicles and where batteries and other parts come from as they push for North American production. The Department of Energy has released a National Blueprint for Lithium Batteries, and a plan to support the domestic battery production to meet growing needs as people go back to work and school in the fall.
It is tempting to see the chip storage problem as just a technology story. But it also has real-world implications for our national security as so much of defense relies on computers and communications in the era of modern warfare.
As Americans celebrate our independence, we have to re-commit to being independent when it comes to reliance on others for goods and services that fuel our lives. We can’t make everything at home, but we can make more and ensure that disruptions abroad don’t reverberate, negatively, at home. As Congress continues to debate infrastructure and other major legislation, and the COVID-19 pandemic retreats, we will need to work together to ensure that we are prepared for whatever 2022 might bring.
#mendelslawofindependentassortment #Genetics #genes #molecularbiology #biology #biotech #recombinants #Genetic
This video explains the mendel’s law of independent assortment.
Thank You For Watching.
Please Like And Subscribe to Our Channel: https://www.youtube.com/EasyPeasyLearning.
Like Our Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/learningeasypeasy/
Join Our Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/460057834950033
Support Our Channel: https://www.patreon.com/supereasypeasy
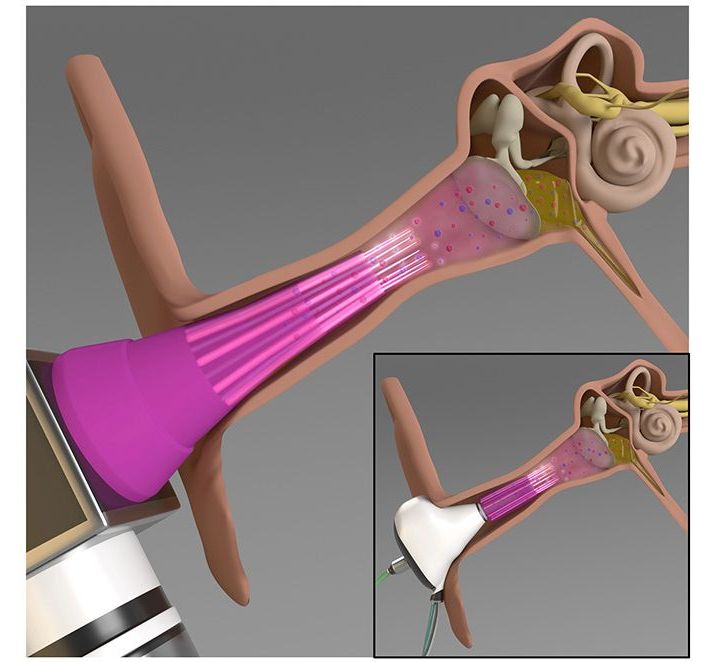
Bacterial infections of the middle ear are quite common, particularly in children, yet they can be difficult to treat. An experimental new device has been designed to help, by zapping the bacteria with plasma.
Usually, such infections are treated with topically applied antibiotics. According to the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, however, such an approach is ineffective in over 30 percent of acute infections. This is because the antibiotics have trouble penetrating the bacterial biofilm that has formed on the surface of the inner ear tissue.
Additionally, the greater the amount of antibiotics that are used, the greater the chances that the bacteria will develop a tolerance to them over time. With these limitations in mind, U Illinois scientists set out to develop an alternative treatment, or at least one that would allow smaller amounts of antibiotics to be more effective.
Not sure how interesting this will be to people who know a lot on aging/longevity research.
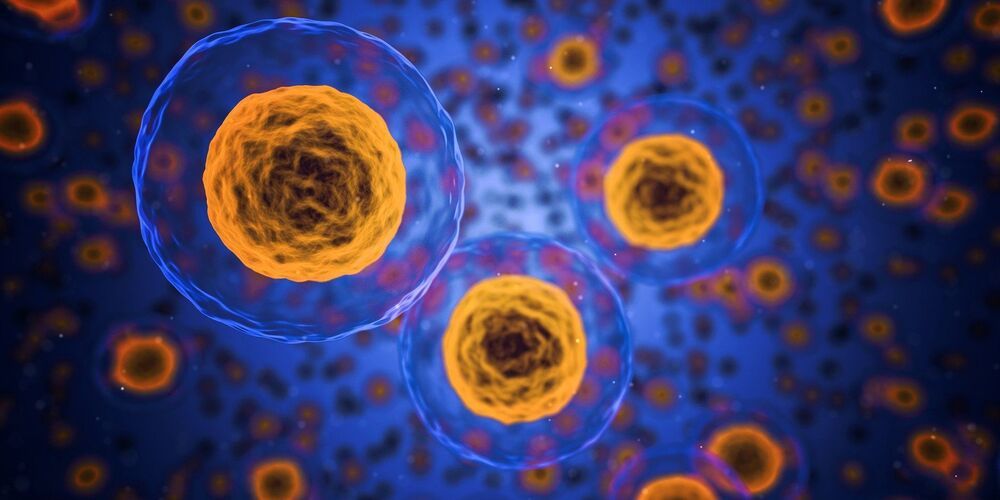
A team of researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School have found evidence of mouse and human germline cells resetting their biological age. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes their study of the aging process in germline cells and what they found by doing so.
As animals grow older, all of the cells in their body replicate themselves repeatedly. As the process continues, errors in replicating and other external factors (such as exposure to pollutants) lead to gradual decay in cell quality, which is all part of the natural aging process. In this new effort, the researchers have found evidence showing that germline cells have a mechanism for resetting this process, allowing offspring to reset their aging clocks.
Germline cells pass on genetic material from parent to offspring during the reproductive process. For many years, scientists have wondered why these cells do not inherit the age of their parents. And for many years, they assumed that the cells were ageless, but recent work has shown that they do, in fact, age. So that raised the question of how offspring are able to begin their lives with fresh cells.
A team of biohackers is on a David-versus-Goliath mission to make insulin affordable to an increasing number of diabetics.
The human body contains hundreds of different types of cells, with stem cells working like blank canvases that can be adapted and reproduced to help our tissues grow and repair themselves. However, once hijacked, the same kind of cell proliferation can be damaging, as happens in cancer tumors.
Scientists have now discovered a new resting phase for neuroepithelial cells — the stem cells of the central nervous system — which appears to put them in a kind of dormancy. If we can work out how to apply this to cancer cells too, we could get to the stage of being able to put brain tumors to ‘sleep’.
“The primary feature of any cancer is that the cells are proliferating,” says biomedical engineer Christopher Plaisier, from Arizona State University. “If we could get in there and figure out what the mechanisms are, that might be a place to slow them down.”


Walmart will offer a less expensive private label version of analog insulin for diabetes patients who struggle to afford their medication, the retail and pharmacy giant said June 29.
Novo Nordisk will manufacture the insulin, called ReliOn NovoLog. Walmart said it will become available at Walmart pharmacies the week of June 27 and at Sam’s Club pharmacies in mid-July.
A vial of ReliOn NovoLog will cost $72.88, and a package of prefilled pens will cost $85.88. Walmart said these products will save patients between 58 and 75 percent of the price of other insulin products on the market.