Solar cells are vital for the green energy transition. They can be used not only on rooftops and solar farms but also for powering autonomous vehicles, such as planes and satellites. However, photovoltaic solar cells are currently heavy and bulky, making them difficult to transport to remote locations off-grid, where they are much needed.
In a collaboration led by Imperial College London, alongside researchers from Cambridge, UCL, Oxford, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin in Germany, and others, researchers have produced materials that can absorb comparable levels of sunlight as conventional silicon solar cells, but with 10,000 times lower thickness.
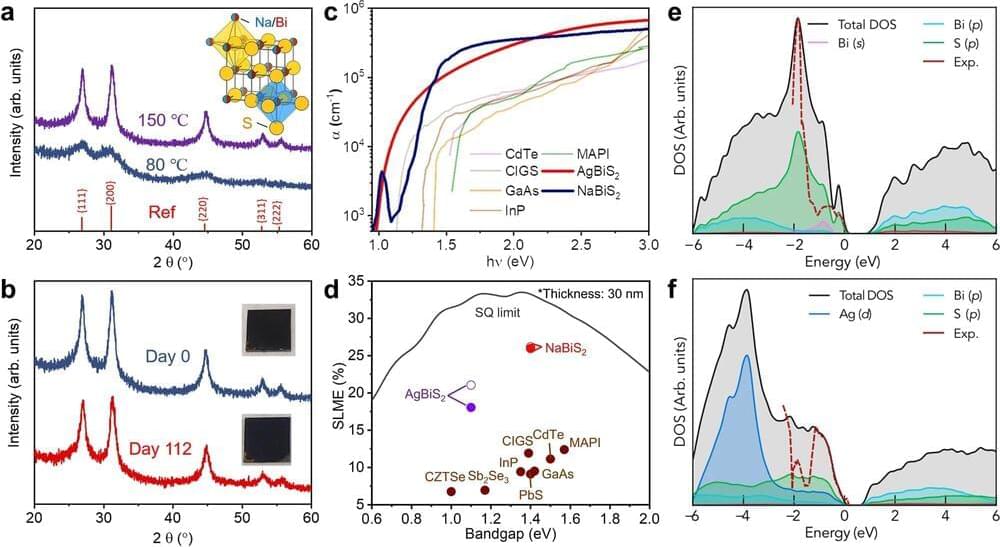
The material is sodium bismuth sulfide (NaBiS2), which is grown as nanocrystals and deposited from solution to make films 30 nanometers in thickness. NaBiS2 is comprised of nontoxic elements that are sufficiently abundant in the earth’s crust for use commercially. For example, bismuth-based compounds are used as a nontoxic lead replacement in solder, or in over-the-counter stomach medicine.