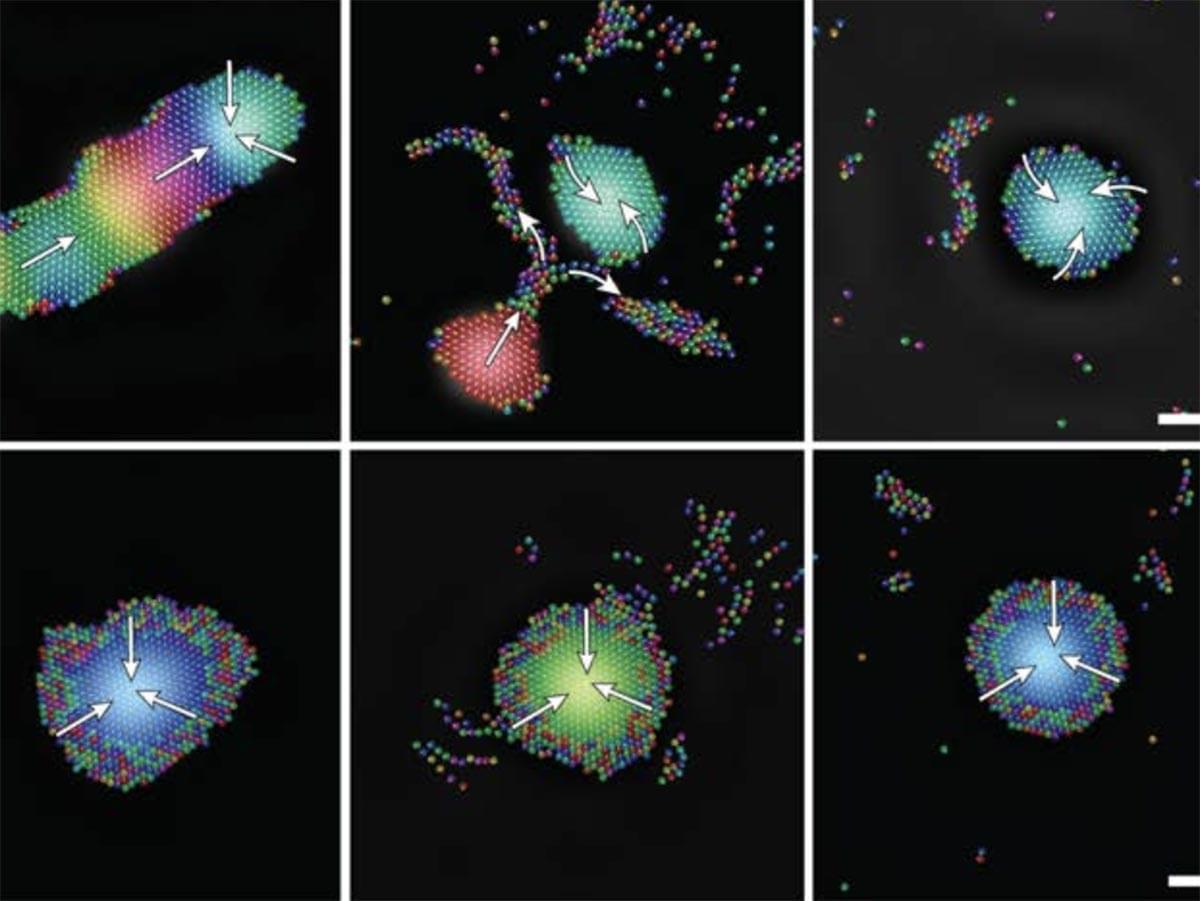
Could tiny magnetic objects, that rapidly clump together and instantly fall apart again, one day perform delicate procedures inside the human body? A new study from researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart and at ETH Zurich introduces a wireless method to stiffen and relax small structures using magnetic fields, without wires, pumps, or physical contact.
In music, “jamming” refers to the spontaneous gathering of musicians who often improvise without aiming for a predefined outcome. In physics, jamming describes the transition of a material from a fluid-like to a solid-like state—like a traffic jam, where the flow of cars suddenly stops. This transformation can also be triggered on demand, offering a powerful and versatile way to control stiffness for robotic systems.
In most robotic applications, jamming is achieved using vacuum systems that suck air out of flexible enclosures filled with materials such as particles, fibers, or grains. But these systems require pumps, valves, and tubing—making them difficult to miniaturize.