A relationship is a physiologic process, as real and as potent as any pill or surgical procedure.


00:00 Intro.
02:44 Kernel Flow brain interface.
08:03 Seeing my brain activity.
12:42 Reversing aging-Project Blueprint.
18:18 Overcoming depression.
26:42 Starting Kernel.
34:40 Why non-invasive?
36:43 Comparison to Tesla/ Neuralink.
43:52 Elon considered joining Kernel?
44:52 Kernel hiring.
46:17 Participate in the studies.
Participate & experience Kernel Flow: https://www.kernel.com/participate.
Information: Kernel Flow: https://www.kernel.com/flow.
Kernel Careers: https://jobs.lever.co/kernel-2
Neura Pod Episode about Kernel & Bryan Johnson: https://youtu.be/c0VFiEhDg6I
Bryan Johnson LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/bryanrjohnson/
Bryan Johnson Personal Page: https://www.bryanjohnson.co/
Blueprint Website: https://blueprint.bryanjohnson.co/
After selling his company, Braintree/Venmo, for $800 million and battling chronic depression for 10 years, Bryan Johnson is now on a mission to help us measure and gather more data about the organ that makes us oh-so human: our brain.
In this episode, Ryan Tanaka and Omar Olivares share an exclusive, behind the scenes look of Kernel’s headquarters near Los Angeles, California. Ryan interviews Bryan Johnson, tries on Kernel’s wearable brain-interface, ‘Flow,’ and learns about the engineering and technology developments needed to make it all happen. CTO, Ryan Field and Director of Applied Neuroscience, Katherine Perdue also share insights about Kernel’s wearable Flow headset.
Disclaimer: Thanks to Kernel for opening their office for us to film in and for supporting our travel and accommodation.
Neura Pod is a series covering topics related to Neuralink, Inc. Topics such as brain-machine interfaces, brain injuries, and artificial intelligence will be explored. Host Ryan Tanaka synthesizes informationopinions, and conducts interviews to easily learn about Neuralink and its future.


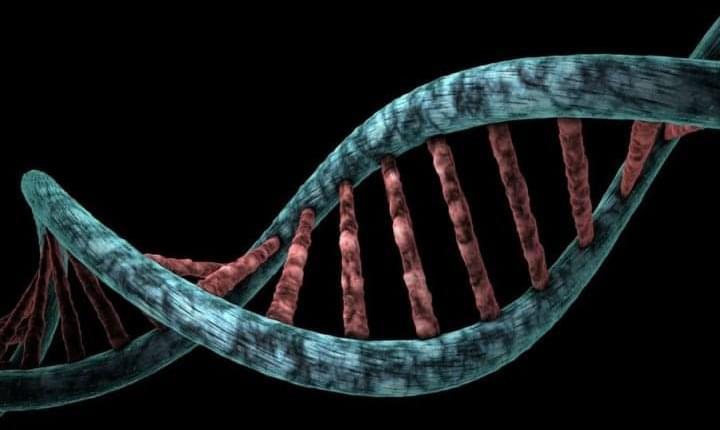
A fundamental discovery concerning a driver of healthy development in embryos might rewrite our understanding of what we can inherit from our parents and how their life experiences shape us. The new study reveals that epigenetic information, which sits on top of DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
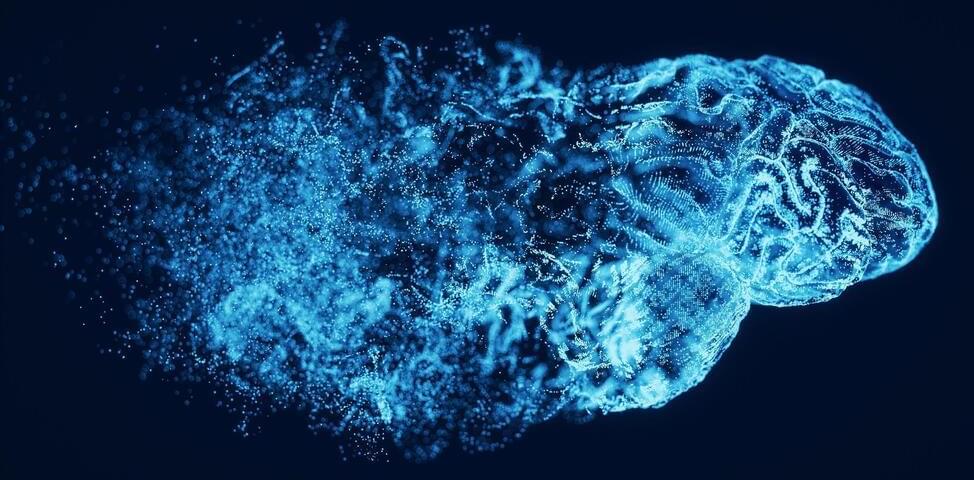

Before the first clinical symptoms appear, Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer’s disease is a disease that attacks the brain, causing a decline in mental ability that worsens over time. It is the most common form of dementia and accounts for 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. There is no current cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are medications that can help ease the symptoms.
The findings also point to possible directions for treatment of the disease.
The results are published Sept. 6 in the journal Neuron.
Almost half the human genome is comprised of transposable elements, long and short stretches of DNA called “jumping genes” for their ability to move from one location of the genome to others. Once called “junk” DNA, these transposable sequences have been shown to play crucial regulatory roles in many biological functions. Once they fulfill these myriad roles, molecular regulators usually silence their expression.
Along the way, they discuss the early days of David’s HedWeb, the Abolitionist Project, the Three Supers of Transhumanism (Superhappiness, Superintelligence, and Superlongevity), philosophy and history of science, the nature of intelligence, field theories of consciousness, anesthesia, empathogens, anti-tolerance drugs, and much more.
Some of the key essays discussed:
Utopian Pharmacology — “Mental Health in the Third Millennium — MDMA and Beyond” — https://mdma.net/
Future Opioids: The Quest for a Drug-Free Society — https://www.opioids.com/
The Biointelligence Explosion — “How recursively self-improving organic robots will modify their own source code and bootstrap our way to full-spectrum superintelligence” — https://www.biointelligence-explosion.com/
👉For business inquiries: [email protected].
✅ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/pro_robots.
You’re on the PRO Robots channel, and today we’re bringing you some high-tech news. Robots from Boston Dynamics will get advanced artificial intelligence, neural networks will be able to translate the language of all animals, incredibly fast nanorobots will travel inside the human body, a robot-surgeon will perform an operation on the ISS. See these and other technology news in one video right now!
0:00 Intro.
0:28 Robots from Boston Dynamics get advanced artificial intelligence.
1:52 AI will never be intelligent.
2:50 Earth Species Project hopes to develop a neural network that can decipher animal language.
3:16 Species Project decides to go around and create an algorithm.
4:07 A gadget to control your smart home with your mind.
5:04 Nanobots.
5:19 The world’s fastest bowel robot.
6:10 Robots will join the U.S. space forces.
6:47 Surgical robot to be tested on ISS
7:37 GITAI News.
7:59 The first launch in NASA’s Artemis lunar mission.
8:34 Super Heavy rocket successfully passes first static firing test.
8:57 Gigafactory in Canada.
9:22 Baidu says its Jidu robot car autopilot will be a generation ahead of Tesla’s autopilot.
10:02 A system that can calculate the optimal end design and calculate the best trajectory for grabbing objects of any shape.
10:25 A drone to search for gold and jewelry.
11:22 Engineers have trained a drone with 12 rotary screws to manipulate objects.
#prorobots #robots #robot #futuretechnologies #robotics.
More interesting and useful content:
✅ Elon Musk Innovation https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLcyYMmVvkTuQ-8LO6CwGWbSCpWI2jJqCQ
✅Future Technologies Reviews https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLcyYMmVvkTuTgL98RdT8-z-9a2CGeoBQF
✅ Technology news.
https://www.facebook.com/PRO.Robots.Info.
#prorobots #technology #roboticsnews.
PRO Robots is not just a channel about robots and future technologies, we are interested in science, technology, new technologies and robotics in all its manifestations, science news, technology news today, science and technology news 2022, so that in the future it will be possible to expand future release topics. Today, our vlog just talks about complex things, follows the tech news, makes reviews of exhibitions, conferences and events, where the main characters are best robots in the world! Subscribe to the channel, like the video and join us!