The (changing) belief distribution over possible environmental states may be represented in ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC). Several lines of evidence point to a general function of this brain region in maintaining a compact internal model of the environment (ie state belief) by extracting information across individual experiences to guide goal-directed behavior, such as the value of different choice options (Levy and Glimcher 2012; Averbeck and O’Doherty 2022; Klein-Flügge et al. 2022), cognitive maps (Boorman et al. 2021; Klein-Flügge et al. 2022; Schuck et al. 2016; Wilson et al. 2014), or schemas (Gilboa and Marlatte 2017; Bein and Niv 2025). Studies employing probabilistic learning tasks furthermore show that neural activity in vmPFC also reflects uncertainty about external states, which were linked to adaptive exploration behavior and learning-rate adjustments (Karlsson et al. 2012; McGuire et al. 2014; Starkweather et al. 2018; Domenech et al. 2020; Trudel et al. 2021). Notably, Karlsson et al. (2012) found that trial-to-trial neural population spiking variability in the medial PFC of mice peaked around transitions from exploitation to exploration periods following changes in reward structure when state uncertainty is highest, which may reflect more variable belief states. While ours is the first study to link human brain signal variability to belief precision, a previous study by Grady and Garrett (2018) observed increased BOLD signal variability while subjects performed externally-versus internally-oriented tasks; an effect spanning the vmPFC and other nodes of the canonical default mode network (DMN; Yeo et al. 2011). Since learning an abstract world model reflects a shift towards an internal cognitive mode, we tentatively expected brain signal variability compression over the course of learning to be (partly) expressed in the vmPFC.
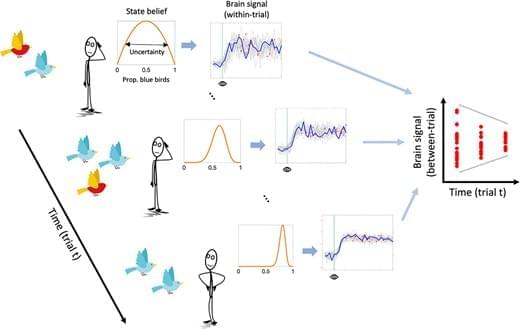
We assume that uncertainty-related neural dynamics unfold on a fast temporal scale, as suggested by electrophysiological evidence in human and nonhuman animals (Berkes et al. 2011; Palva et al. 2011; Rouhinen et al. 2013; Honkanen et al. 2015; Orbán et al. 2016; Grundy et al. 2019). However, within-trial dynamics should also affect neural variability across independent learning trials (see Fig. 1). A more variable system should have a higher probability of being in a different state every time it is (sparsely) sampled. Conversely, when a system is in a less stochastic state, the within-trial variance is expected to reduce, yielding less across-trial variance at the same time. This argument aligns with work by Orbán et al. (2016), who showed that a computational model of the sampling account of sensory uncertainty captures empirically observed across-trial variability of neural population responses in primary visual cortex. In the case of human research, this means that neuroimaging methods with slower sampling rates, such as functional MRI (fMRI), may be able to approximate within-trial neural variability from variability observed across trials. Indeed, the majority of previous fMRI studies reporting within-region, within-subject modulation of brain signal variability by task demand have exclusively employed block designs, necessitating that the main source of variability be between-rather than within-trial (Garrett et al. 2013; Grady and Garrett 2014; Garrett et al. 2015; Armbruster-Genç et al. 2016).
In the current study, we acquired fMRI while participants performed a “marble task”. In this task, participants had to learn the probability of drawing a blue marble from an unseen jar (ie urn) based on five samples (ie draws from the urn with replacement). In a Bayesian inference framework, the jar marble ratio can be considered a latent state that participants must infer. We hypothesized that (i) across-trial variability in the BOLD response (SDBOLD) would compress over the sampling period, thus mirroring the reduction in state uncertainty, and that (ii) subjects with greater SDBOLD compression would show smaller estimation errors of the jars’ marble ratios as an index of more efficient belief updating. A secondary aim of the current study was to directly compare the effect of uncertainty on SDBOLD with a more standard General Linear Modeling (GLM) approach, which looks for correlations between average BOLD activity and uncertainty. This links our findings directly to previous investigations of neural uncertainty correlates, which disregarded the magnitude of BOLD variability (Huettel et al. 2005; Grinband et al. 2006; Behrens et al. 2007; Bach et al. 2011; Bach and Dolan 2012; Badre et al. 2012; Vilares et al. 2012; Payzan-LeNestour et al. 2013; McGuire et al. 2014; Michael et al. 2015; Meyniel and Dehaene 2017; Nassar et al. 2019; Meyniel 2020; Tomov et al. 2020; Trudel et al. 2021; Walker et al. 2023). We hypothesized (iii) that SDBOLD would uniquely predict inference accuracy compared to these standard neural uncertainty correlates.