The subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB may somewhat evade prior immunity, however, further research is required.
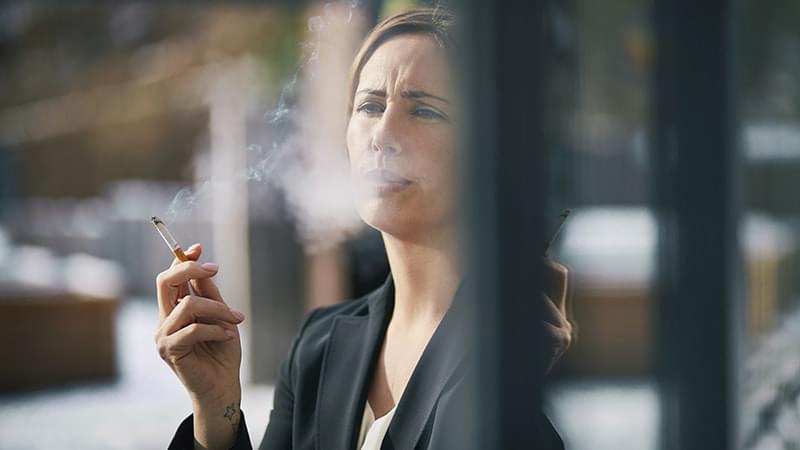


𝐍𝐢𝐜𝐨𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐁𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤𝐬 𝐄𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐠𝐞𝐧 𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐢𝐧 𝐖𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐧’𝐬 𝐁𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧𝐬
𝙏𝙝𝙚 𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙙𝙪𝙘𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙤𝙛 𝙚𝙨𝙩𝙧𝙤𝙜𝙚𝙣 𝙞𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙡𝙖𝙢𝙪𝙨 𝙖𝙥𝙥𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙨 𝙩𝙤 𝙗𝙚 𝙘𝙪𝙧𝙩𝙖𝙞𝙡𝙚𝙙 𝙗𝙮 𝙟𝙪𝙨𝙩 𝙤𝙣𝙚 𝙙𝙤𝙨𝙚 𝙤𝙛 𝙣𝙞𝙘𝙤𝙩𝙞𝙣𝙚, 𝙚𝙦𝙪𝙞𝙫𝙖𝙡𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙩𝙤 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙞𝙣 𝙖 𝙘𝙞𝙜𝙖𝙧𝙚𝙩𝙩𝙚, 𝙧𝙚𝙫𝙚𝙖𝙡𝙨 𝙖 𝙬𝙝𝙤𝙡𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣 𝙖𝙣𝙖𝙡𝙮𝙨𝙞𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙝𝙚𝙖𝙡𝙩𝙝𝙮 𝙬𝙤𝙢𝙚𝙣 𝙞𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙛𝙞𝙧𝙨𝙩 𝙨𝙩𝙪𝙙𝙮 𝙤𝙛 𝙞𝙩𝙨 𝙠𝙞𝙣𝙙.
“We were surprised to see that this effect could be seen even with a single dose of nicotine, equivalent to just one cigarette, showing how powerful the effects of smoking are on a woman ’ s brain.”
Emphasizing the preliminary nature of the study and the need for a larger sample, she added: We’re still not sure what the behavioral or cognitive outcomes are; only that nicotine acts on this area of the brain.
However, we note that the affected brain system is a target for addictive drugs, such as nicotine.
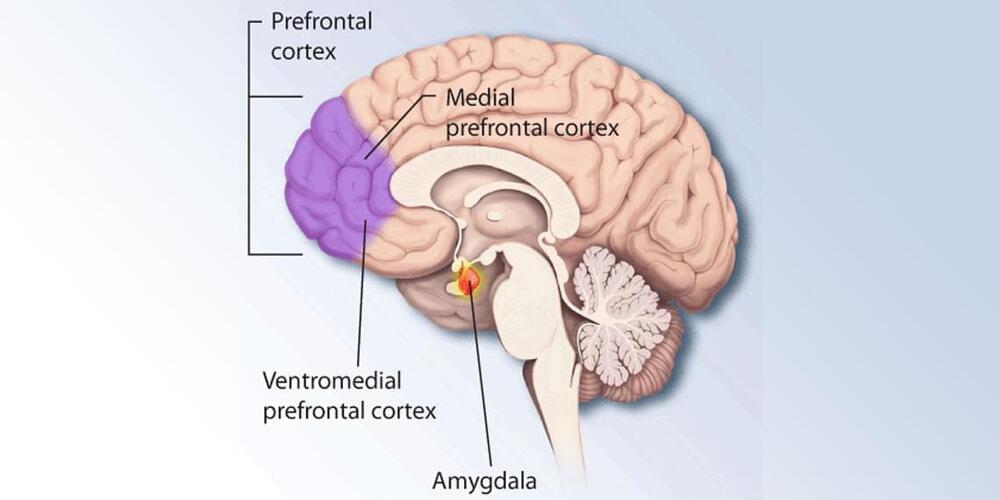
A study on a large sample of patients found chronic, long-lasting depression to be associated with reduced brain volume. The reduced volume was found in brain regions relevant for planning one’s behavior, focusing attention, thinking, learning and remembering and also in regions relevant for regulating emotions. The study was published in Neurobiology and Treatment of Depression.
Depression, also called major depressive disorder, is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. It changes the way a person feels, thinks and behaves. For many people suffering from it, depressive episodes become a recurring event. More than half of patients with depression experience a relapse after 2 years and the probability of recurrent depressive episodes rises to 90% after 3–4 episodes. Studies have indicated that recurring depressive episodes might be linked to structural changes in the brain, but the existing results are not uniform.
Ms. Hannah Lemke and her colleagues analyzed the data of 681 patients from the Marburg-Muenster-Affective-Cohort Study (MACS) in order to better link properties of the course of depressive disorder with specific changes in the brain structure. Patient data were collected at two sites in Germany – Muenster and Marburg.
Weill Cornell Medicine researchers have developed a computational method to map the architecture of human tissues in unprecedented detail. Their approach promises to accelerate studies on organ-scale cellular interactions and could enable powerful new diagnostic strategies for a wide range of diseases.
The method, published Oct. 31 in Nature Methods, grew out of the scientists’ frustration with the gap between classical microscopy and modern single-cell molecular analysis. “Looking at tissues under the microscope, you see a bunch of cells that are grouped together spatially—you see that organization in images almost immediately,” said lead author Junbum Kim, a graduate student in physiology and biophysics at Weill Cornell Medicine.
“Now, cell biologists have gained the ability to examine individual cells in tremendous detail, down to which genes each cell is expressing, so they’re focused on the cells instead of focusing on the tissue structure,” he said.
The number of syphilis cases in Japan this year has exceeded 10,000 for the first time since comparable data became available in 1999.
Japan’s National Institute of Infectious Diseases says 10,141 cases were reported as of October 23. That is about 1.7 times the figure for the same period last year, which was a record high.
Syphilis is a bacterial infection transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Symptoms may quickly disappear, or not appear at all. So, infected people could spread the disease without knowing.
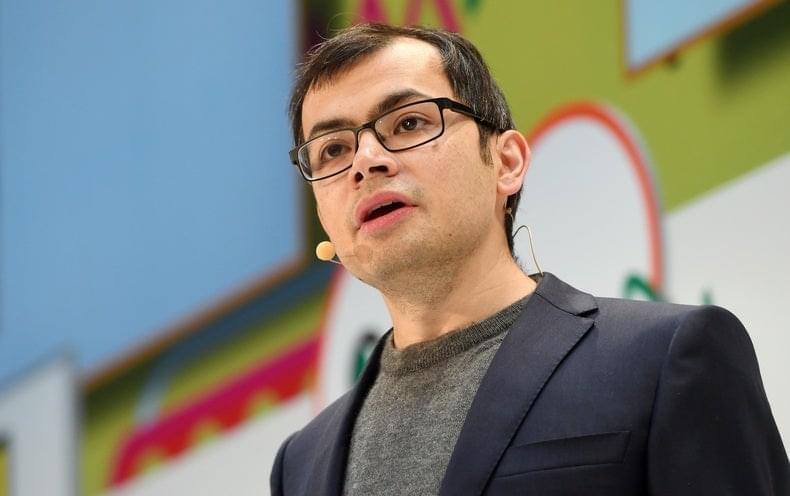

There’s an age-old adage in biology: structure determines function. In order to understand the function of the myriad proteins that perform vital jobs in a healthy body—or malfunction in a diseased one—scientists have to first determine these proteins’ molecular structure. But this is no easy feat: protein molecules consist of long, twisty chains of up to thousands of amino acids, chemical compounds that can interact with one another in many ways to take on an enormous number of possible three-dimensional shapes. Figuring out a single protein’s structure, or solving the protein-folding problem, can take years of finicky experiments.
But earlier this year an artificial intelligence program called AlphaFold, developed by the Google-owned company DeepMind, predicted the 3D structures of almost every known protein —about 200 million in all. DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis and senior staff research scientist John Jumper were jointly awarded this year’s $3-million Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences for the achievement, which opens the door for applications that range from expanding our understanding of basic molecular biology to accelerating drug development.
DeepMind developed AlphaFold soon after its AlphaGo AI made headlines in 2016 by beating world Go champion Lee Sedol at the game. But the goal was always to develop AI that could tackle important problems in science, Hassabis says. DeepMind has made the structures of proteins from nearly every species for which amino acid sequences exist freely available in a public database.
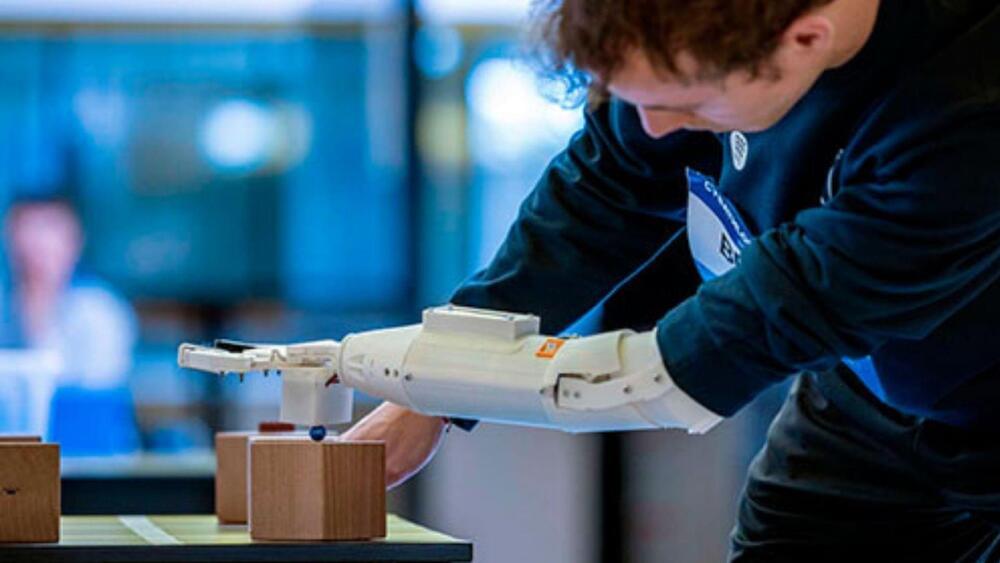

More affordable than the regular ones.
The Arm2u biomedical engineering team from the Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering (ETSEIB) of the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya designed and constructed a configurable transradial prosthesis that responds to the user’s nerve impulses using 3D printing technology.
Arm2u is a prosthesis that can replace a missing arm below the elbow. It can be controlled with myoelectric control, which means that it is controlled by the natural electrical signals produced by muscle contraction.
UPC
As stated in the release, UPC bachelor’s and master’s degree students started off improving a prosthesis for people with disabilities using assistive technologies.
Here is what the ECG reports of the first patient with the pig heart say.
In January this year, the heart of a genetically modified pig was transplanted into a human for the first time. The patient, David Bennett, managed to survive for two months with the pig heart, and this unique organ transplant operation led to various exciting findings and further research work.
One recently published research reveals that the electrical conduction system (network of cells, signals, and nodes in a heart that collectively controls heart functions and heartbeat) of the genetically modified pig heart differs from that of an ordinary pig’s heart.
David Bennett, the 57-year-old man who became globally known as the first human to receive a genetically modified pig’s heart as a transplant has died in the hospital where he underwent the transplant and was recovering, according to a press release.
Bennett was first admitted to the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC) in October last year with arrhythmia — the irregular beating of the heart, which in his case had become life-threatening. The doctors placed him on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), commonly known as a heart-lung bypass machine to keep him alive.

Times after the pandemic have not been good for tech giants.
The world’s 20 richest tech billionaires have lost close to half a trillion dollars in 2022 so far. Fears of a recession and increased interest rates have dipped revenues of tech companies in the U.S., and market valuations of their companies have tumbled thereafter, Wall Street Journal.
Mark Zuckerberg might be the poster boy for how falling revenues of tech companies also shrink the personal fortunes of the founders since most of their wealth is associated with stocks of the companies they have founded.

Summary: A genetic form of frontotemporal dementia is associated with abnormal lipid accumulation in the brain fueled by disrupted cell metabolism. The findings could pave the way for new targeted therapies for FTD.
Source: Harvard.
Dementia encompasses a range of neurodegenerative conditions that lead to memory loss and cognitive deficiencies and affect some 55 million people worldwide. Yet despite its prevalence, there are few effective treatments, in part because scientists still don’t understand how exactly dementia arises on a cellular and molecular level.