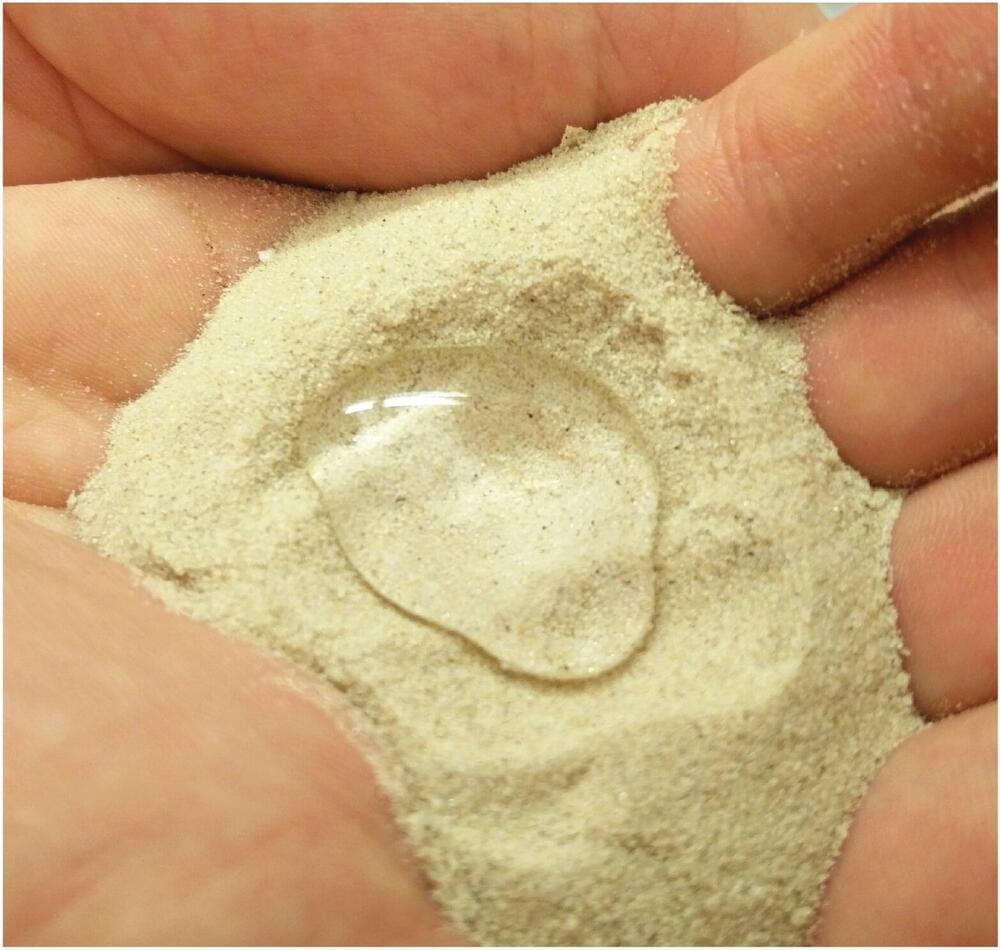
Dry, hot regions are difficult places to grow plants because the soil dries out quickly. As a result, farmers in arid and semi-arid regions irrigate their fields with buried networks of irrigation tubing and cover the ground with plastic sheets. But plastic sheets are expensive and create waste. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Agricultural Science & Technology have developed a simple, biodegradable ground cover—wax-coated sand—which keeps soil wet and increases crop yields.
To irrigate crops, farmers usually get water from nearby waterways or underground aquifers. These supplies can be rapidly depleted when growing plants in arid regions, where the soil is comprised mostly of sand and can’t hold onto water well. One way to improve irrigated water’s efficiency is to make sure it stays in the soil long enough so that plants’ roots can take it up. Previous studies have shown that ground cover barriers, such as plastic sheets and engineered nanomaterials, can slow evaporation and enhance plant growth and crop yields. However, both could leach unwanted compounds into the soil with unknown long-term impacts. Some plants and animals naturally produce waxy substances that trap and pool water from fog or condensation so that they can access these moisture sources. Taking inspiration from nature, Himanshu Mishra and colleagues wanted to see if they could coat sand with wax, creating an environmentally benign ground cover to control soil evaporation.
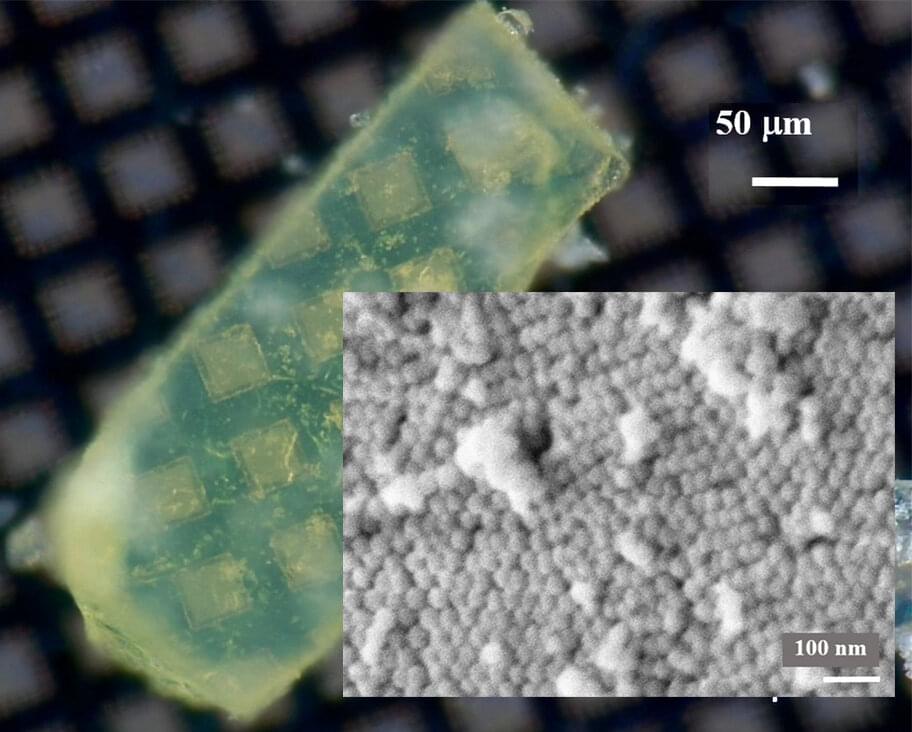
The researchers chose purified paraffin wax, a biodegradable substance available in large quantities, for their experiments. They dissolved the wax in hexane and poured silica sand into the mixture. As the solvent evaporated, a 20-nm-thick coating of wax was left behind on the grains. When the team applied the wax-coated sand in a thin layer on an open field in Saudi Arabia, it decreased the loss of soil moisture up to 50–80%. Field trials revealed that tomato, barley and wheat plants mulched with the new material produced substantially more fruit and grain than those grown in uncovered soil. In addition, the microbial community around the plants’ roots and in the soil wasn’t negatively impacted by the waxy mulch, which could have acted as a food source for some of the microbes. This simple nature-inspired technology could make water use more efficient in arid regions, the researchers say.