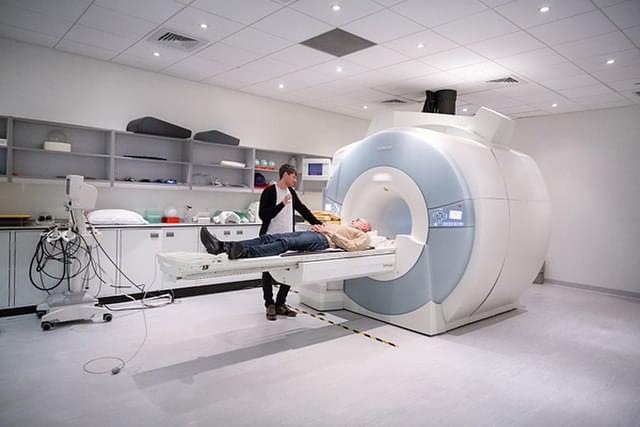
When some materials are cooled to a certain temperature, they lose electric resistance, becoming superconductors.
In this state, an electric charge can course through the material indefinitely, making superconductors a valuable resource for transmitting high volumes of electricity and other applications. Superconductors ferry electricity between Long Island and Manhattan. They’re used in medical imaging devices such as MRI machines, in particle accelerators and in magnets such as those used in maglev trains. Even unexpected materials, such as certain ceramic materials, can become superconductors when cooled sufficiently.
But scientists previously have not understood what occurs in a material to make it a superconductor. Specifically, how high-temperature superconductivity, which occurs in some copper-oxide materials, works hasn’t been previously understood. A 1966 theory examining a different type of superconductors posited that electrons which spin in opposite directions bind together to form what’s called a Cooper pair and allow electric current to pass through the material freely.