The Japanese have created an uncanny AI model that can estimate your true age from the looks of your chest X-ray. It can help doctors in the early detection of chronic disorders.
Have you ever wondered why some people look much older than their chronological age? A new study from Japan’s Osaka Metropolitan University (OMU) suggests this could be a sign of a disease they don’t know yet.
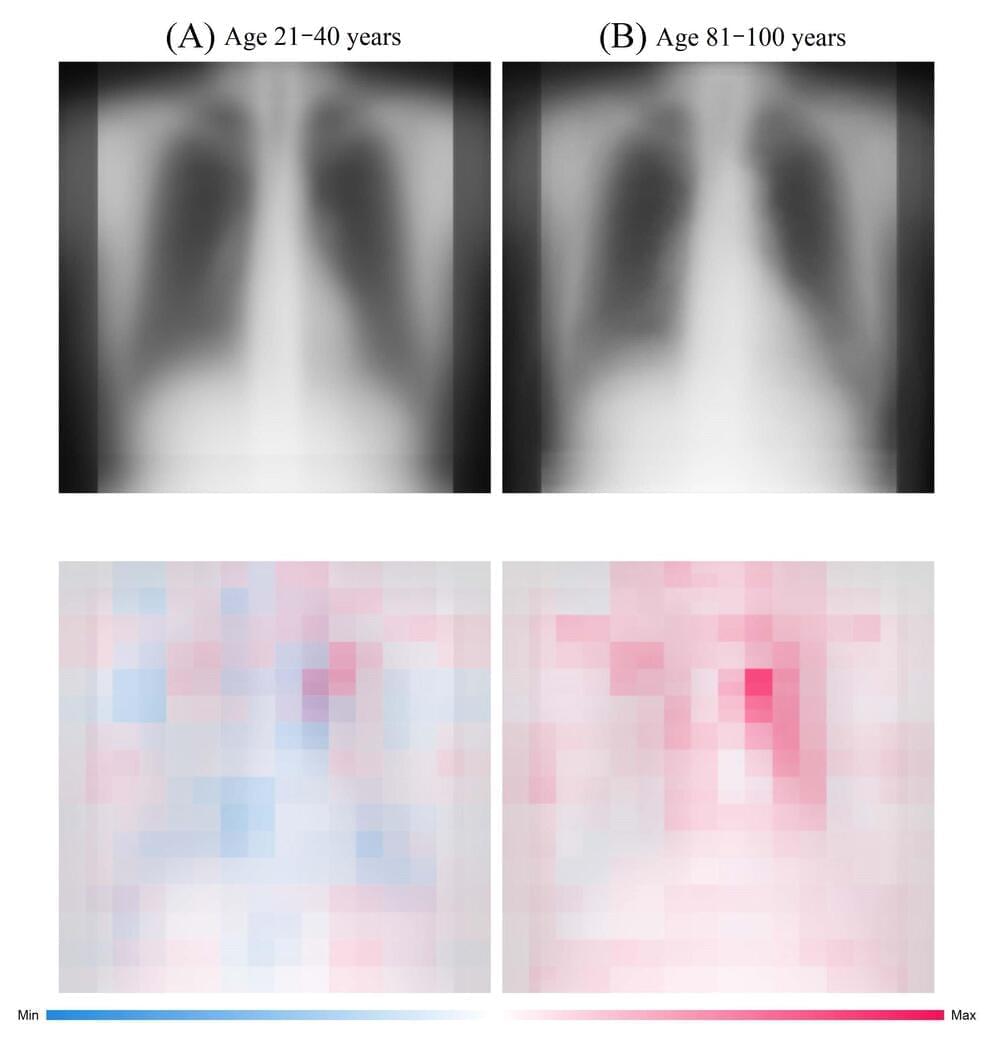
The study authors have developed an AI program that can accurately calculate an individual’s age by reading their chest X-ray. This model estimates age, unlike various previously reported AI programs that examine radiographs to detect lung anomalies. Then researchers use this information to predict body ailments further.