We’re about to revolutionize how drugs are developed in the United States.


A group of neuroscientists developed a test to detect a novel marker of Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer’s disease is a disease that attacks the brain, causing a decline in mental ability that worsens over time. It is the most common form of dementia and accounts for 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. There is no current cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are medications that can help ease the symptoms.
Oto_feja/iStock.
John DeLong and his colleagues at the University of Nebraska have discovered that a species of Halteria—microscopic ciliates prevalent in freshwater habitats worldwide—can consume a sizable number of infectious chloroviruses. For the first time, the team’s laboratory tests have also demonstrated that a virus-only diet, or “virovory,” can support an organism’s physiological growth and even population increase.
Transhuman brains are the melding of hyper-advanced electronics and super-artificial intelligence (AI) with neurobiological tissue. The goal is not only to repair injury and mitigate disease, but also to enhance brain capacity and boost mental function. What is the big vision, the end goal — how far can transhuman brains go? What does it mean for individual consciousness and personal identity? Is virtual immortality possible? What are the ethics, the morality, of transhuman brains? What are the dangers?
Free access to Closer to Truth’s library of 5,000 videos: http://bit.ly/376lkKN
Support the show with Closer To Truth merchandise: https://bit.ly/3P2ogje.
Watch more interviews on transhuman brains: https://bit.ly/3Wb7yRm.
Max Tegmark is Professor of Physics at Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He holds a BS in Physics and a BA in Economics from the Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden. He also earned a MA and PhD in physics from University of California, Berkeley.
Register for free at CTT.com for subscriber-only exclusives: http://bit.ly/2GXmFsP
India’s space program is still in its early stages but has been making global headlines in recent years after ISRO’s launch vehicle launched a record-breaking 104 satellites in one go a few years ago. More recently, a private space tech company test-fired the world’s first 3D-printed rocket engine, which has a turnaround of just four days.
The next phase of the country’s space story includes human space flight, which was announced in 2018 and expected to be launched this year, coinciding with the 75th year of Indian independence. However, the COVID-19 pandemic threw a spanner in the works delaying the project by two years.
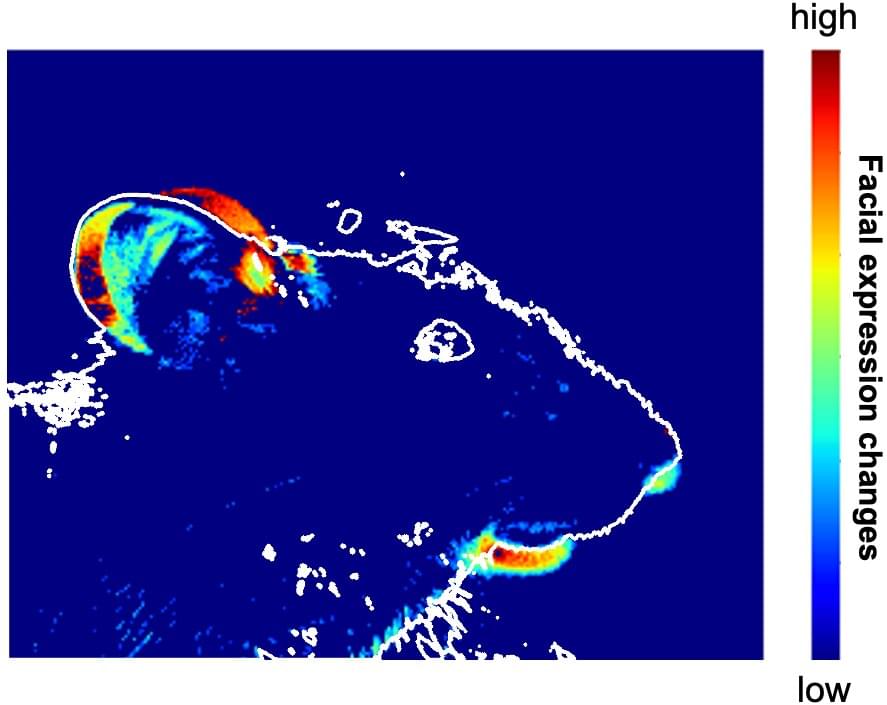
New insights into the opposing actions of serotonin-producing nerve fibers in mice could lead to drugs for treating addiction and major depression.
Scientists in Japan have identified a nerve pathway involved in the processing of rewarding and distressing stimuli and situations in mice.
The new pathway, originating in a bundle of brain stem nerve fibers called the median raphe nucleus, acts in opposition to a previously identified reward/aversion pathway that originates in the nearby dorsal raphe nucleus. The findings, published by scientists at Hokkaido University and Kyoto University with their colleagues in the journal Nature Communications, could have implications for developing drug treatments for various mental disorders, including addiction and major depression.
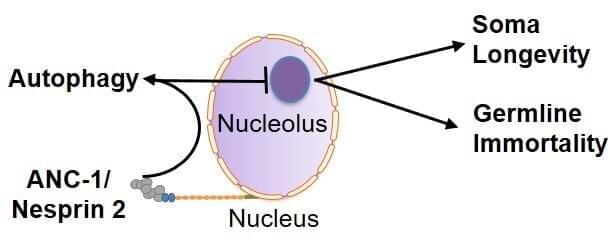
Research at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) of the Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), published today in the journal Nature Aging, reveals a fundamental quality control mechanism that operates in cells to safeguard the integrity and function of the nucleus. By maintaining nuclear homeostasis, this molecular mechanism contributes critically to promote longevity and fertility.
IMBB researchers Dr. Margarita-Elena Papandreou and Dr. Georgios Konstantinidis, headed by Dr. Nektarios Tavernarakis (Professor at the Medical School, University of Crete, and Chairman of the Board at FORTH), discovered that recycling of nuclear and nucleolar components via autophagy delays aging of somatic cells, and sustains the immortality of germ cells, which are required for reproduction.
The nucleus is the central organelle of all eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material (DNA), which determines cellular identity and function. During aging and in cancer cells, the ultrastructure of the nucleus is dramatically altered. Moreover, progressive and pronounced deterioration of the nuclear architecture is a common and conserved feature of progeria and numerous other disorders associated with aging.
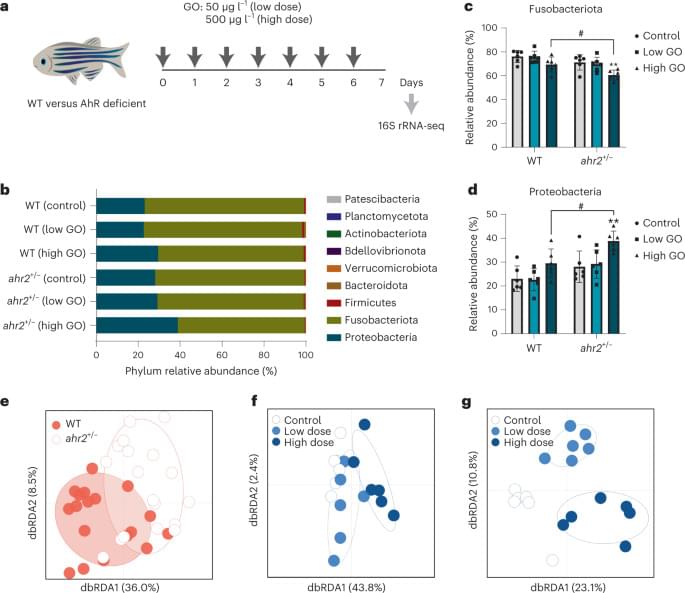
Although the toxicity of graphene‐based nanomaterials on human health has been extensively studied, their impact on the microbiome remains poorly understood. Using zebrafish as a model, we show that graphene oxide modulates the immune system in a microbiome‐dependent manner through a mechanism mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. The study suggests an interplay among graphene‐based nanomaterials, microbiome and innate immune system.

For nearly two decades, astrophysicists have believed that long gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) resulted solely from the collapse of massive stars. Now, a new study upends that long-established and long-accepted belief.
Led by Northwestern University.
Established in 1,851, Northwestern University (NU) is a private research university based in Evanston, Illinois, United States. Northwestern is known for its McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science, Kellogg School of Management, Feinberg School of Medicine, Pritzker School of Law, Bienen School of Music, and Medill School of Journalism.
Scientists have discovered that an inflammatory cytokine known as LIGHT is a major factor in the deadly airway damage that can affect people with severe asthma. This research has suggested that such airway damage could be reversed by therapeutics that halt LIGHT, and the molecule could offer a way to treat asthma. The study, which used a mouse model and human tissue, has been reported in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
“This is a very, very significant finding,” said senior study author and LJI Professor Michael Croft, Ph.D. “This research gives us a better understanding of the potential of therapeutic targeting of LIGHT and what we might do to relieve some of the symptoms and some of the inflammatory features seen in patients who have severe asthma.”