Tropical mosquitoes are increasingly widespread across the planet, and their leap to new continents could be incubating the next global human pandemic.
Read more ❯.
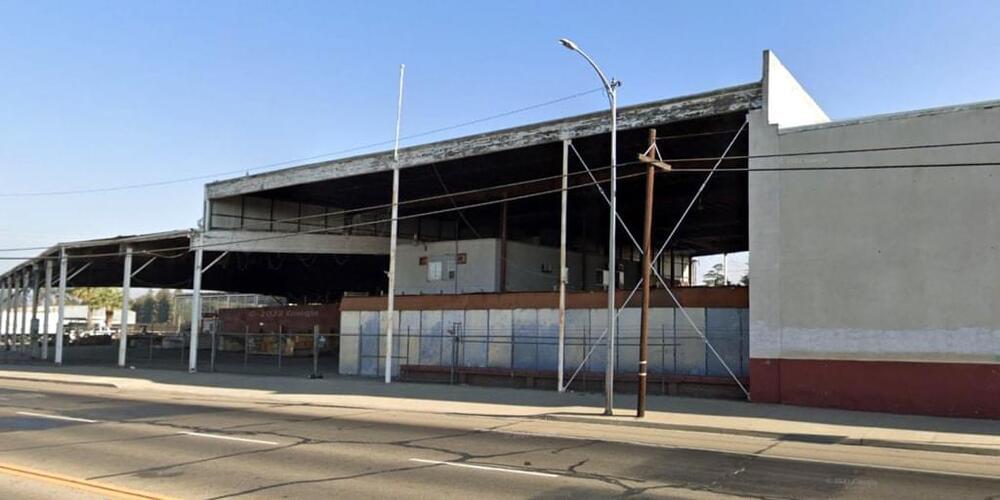

Local and federal authorities spent months investigating a warehouse in Fresno County, California, that they suspect was home to an illegal, unlicensed laboratory full of lab mice, medical waste and hazardous materials.
The Fresno County Public Health Department has been “evaluating and assessing the activities of an unlicensed laboratory” in Reedley, the health department’s assistant director, Joe Prado, said in a statement Thursday. All of the biological agents were destroyed by July 7 following a legal abatement process by the agency.
“The evaluation required coordination and collaboration with multiple federal and state agencies to determine and classify biological and chemical contents onsite, in addition to assessing jurisdictional authority under this unique situation,” Prado said.

When Samuel Peralta contacts artists about putting their work on the moon, they don’t always believe him.
“I say, ‘I’d like to put your art on the moon,’ and they think this is some sort of a scam,” the semiretired physicist and author tells the New York Times’ J. D. Biersdorfer.
But it’s true. Peralta is the mastermind behind the Lunar Codex, a series of time capsules containing the work of 30,000 artists from 157 countries that will journey to the lunar surface. Peralta wants the project to honor artists after the difficulties they faced during the pandemic, he tells the Toronto Star’s Kevin Jiang.
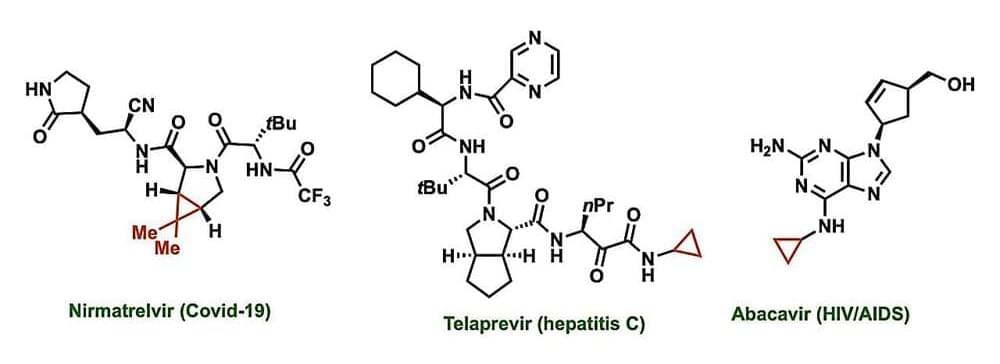
Chemical structures called cyclopropanes can increase the potency and fine-tune the properties of many drugs, but traditional methods to create this structure only work with certain molecules and require highly reactive—potentially explosive—ingredients.
Now, a team of researchers from Penn State has identified and demonstrated a safe, efficient and practical way to create cyclopropanes on a wide variety of molecules using a previously undescribed chemical process. With additional development, the new method—described in a paper publishing Aug. 4 in the journal Science —could transform how this important process occurs during drug development and creation.
Cyclopropanes are a key feature in many drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including those used to treat COVID-19, asthma, hepatitis C, and HIV/AIDs. These structures can increase a drug’s potency, alter its ability to dissolve in the body, minimize its interactions with unintended targets, and otherwise fine-tune performance. Cyclopropanes are a ring of three connected carbon atoms, with one carbon attached to the rest of the drug molecule and the other two each attached to two hydrogen atoms.
A research team led by Prof. Yossi Paltiel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem with groups from HUJI, Weizmann and IST Austria has published a new study that reveals the influence of nuclear spin on biological processes. This discovery challenges long-held assumptions and opens up exciting possibilities for advancements in biotechnology and quantum biology.
Scientists have long believed that nuclear spin had no impact on biological processes. However, recent research has shown that certain isotopes behave differently due to their nuclear spin. The team focused on stable oxygen isotopes (16 O, 17 O, 18 O) and found that nuclear spin significantly affects oxygen dynamics in chiral environments, particularly in its transport.
The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), have potential implications for controlled isotope separation and could revolutionize nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology.
It’s one of the mysteries of nature: How does the axolotl, a small salamander, boast a superhero-like ability to regrow nearly any part of its body? For years, scientists have studied the amazing regenerative properties of the axolotl to inform wound healing in humans.
Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have made a leap forward in understanding what sets the axolotl apart from other animals. Axolotls, they discovered, have an ultra-sensitive version of mTOR, a molecule that acts as an on-off switch for protein production. And, like survivalists who fill their basements with non-perishable food for hard times, axolotl cells stockpile messenger RNA molecules, which contain genetic instructions for producing proteins. The combination of an easily activated mTOR molecule and a repository of ready-to-use mRNAs means that after an injury, axolotl cells can quickly produce the proteins needed for tissue regeneration.
The new findings were published July 26 in Nature.

A rising in the number of cases in Florida of Hansen’s disease, commonly known as leprosy, highlights the increase in tropical disease infections found in the US. The World’s Marco Werman speaks with professor Peter Hotez, co-director of the Texas Children’s Hospital Center for Vaccine Development and dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, about the conditions driving the uptick in tropical illnesses more commonly found in the global south.
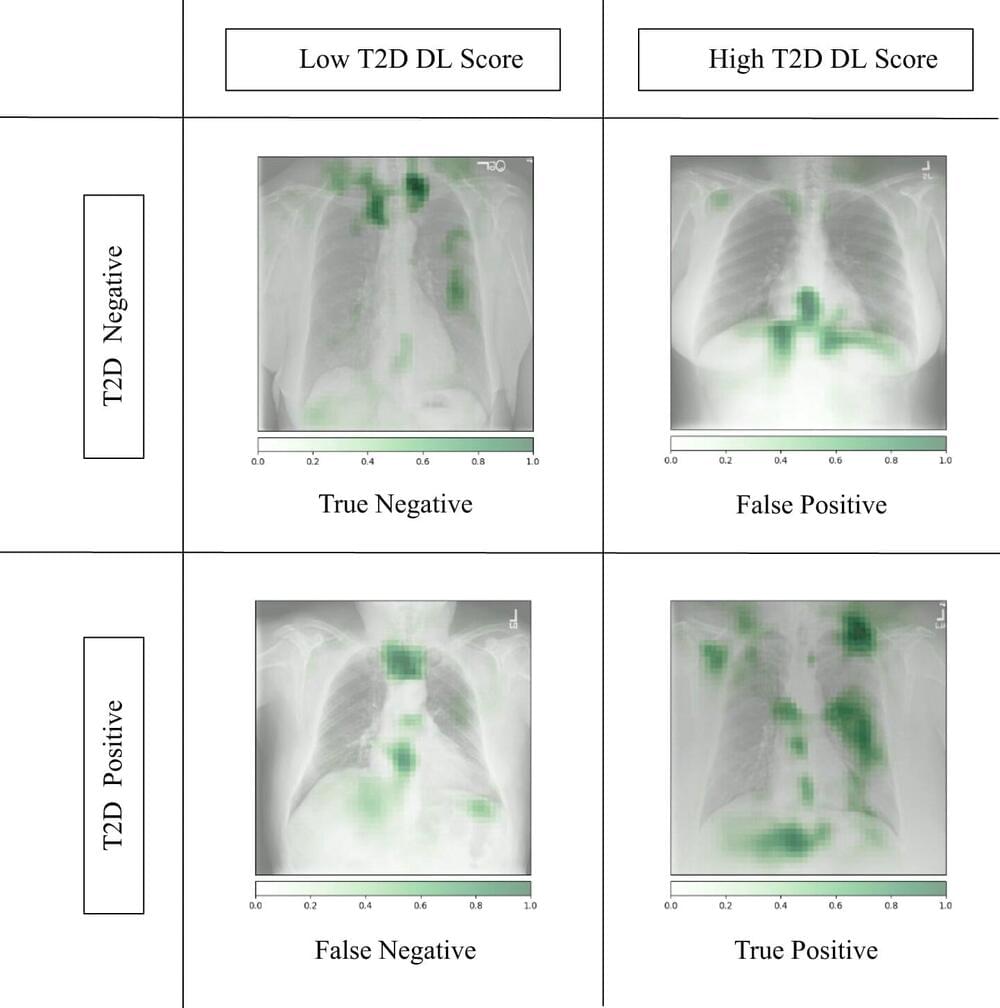
A new artificial intelligence model finds that X-ray images collected during routine medical care can provide warning signs for diabetes, even in patients who don’t meet the guidelines for elevated risk. The model could help physicians detect the disease earlier and prevent complications, says a multi-institutional team which published the findings in Nature Communications.
Applying the computational method known as deep learning to images and electronic health record data, the researchers developed a model that successfully flagged elevated diabetes risk in a retrospective analysis, often years before patients were diagnosed with the disease. That’s significant, the researchers say, given the prevalence of diabetes in the U.S. has more than doubled over the past 35 years.
Current guidelines suggest screening patients for type 2 diabetes if they are between 35 and 70 years old and have a body mass index (BMI) in the overweight to obese range.
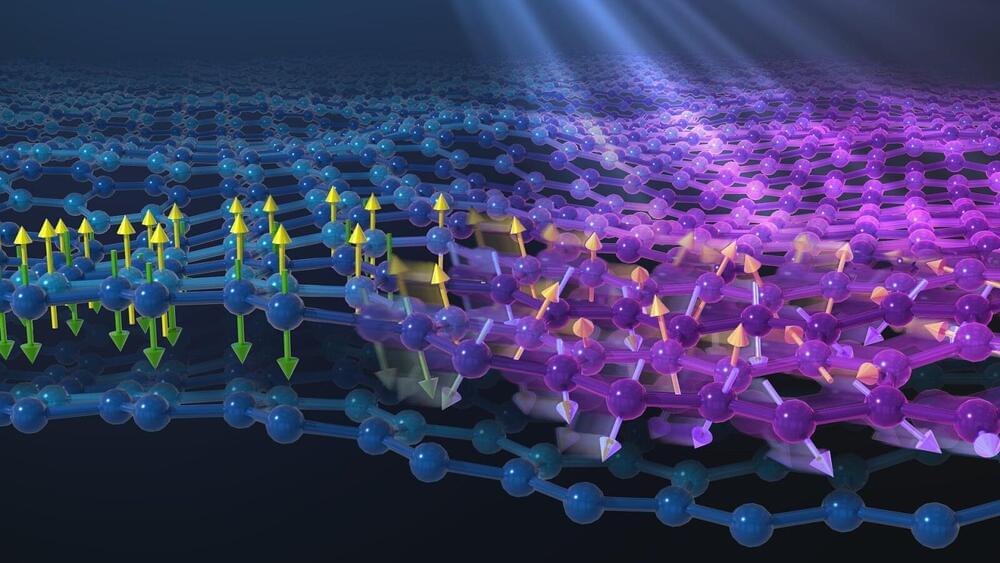
A common metal paper clip will stick to a magnet. Scientists classify such iron-containing materials as ferromagnets. A little over a century ago, physicists Albert Einstein and Wander de Haas reported a surprising effect with a ferromagnet. If you suspend an iron cylinder from a wire and expose it to a magnetic field, it will start rotating if you simply reverse the direction of the magnetic field.
“Einstein and de Haas’s experiment is almost like a magic show,” said Haidan Wen, a physicist in the Materials Science and X-ray Science divisions of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory. “You can cause a cylinder to rotate without ever touching it.”
In Nature, a team of researchers from Argonne and other U.S. national laboratories and universities now report an analogous yet different effect in an “anti”-ferromagnet. This could have important applications in devices requiring ultra-precise and ultrafast motion control. One example is high-speed nanomotors for biomedical applications, such as use in nanorobots for minimally invasive diagnosis and surgery.
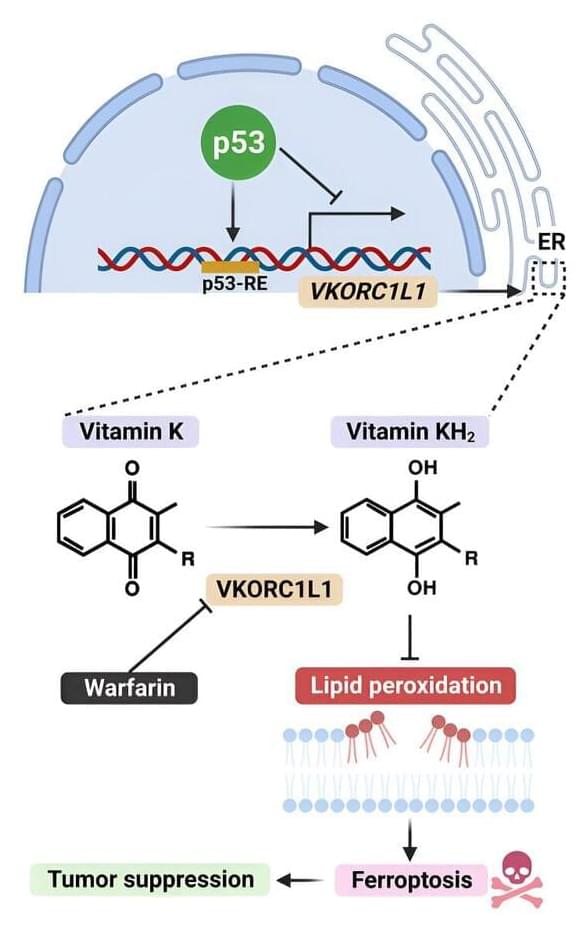
Warfarin, a widely used blood thinner, appears to have potent anti-cancer properties, according to a study by Columbia University researchers. The study, conducted in human cells and in mice, found that warfarin stops tumors from interfering with a self-destruct mechanism that cells initiate when they detect mutations or other abnormalities.
“Our findings suggest that warfarin, which is already approved by the FDA, could be repurposed to treat a variety of cancers, including pancreatic cancer,” says study leader Wei Gu, Ph.D., the Abraham and Mildred Goldstein Professor of Pathology & Cell Biology (in the Institute for Cancer Genetics) at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
The study is titled “Regulation of VKORC1L1 is critical for p53-mediated tumor suppression through vitamin K metabolism,” and it was published July 18 in Cell Metabolism. Postdoctoral researcher scientists Xin Yang, Ph.D., and Zhe Wang, Ph.D., contributed equally as first authors.