Previous research has implicated fungi in chronic neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there is limited understanding of how these common microbes could be involved in the development of these conditions.
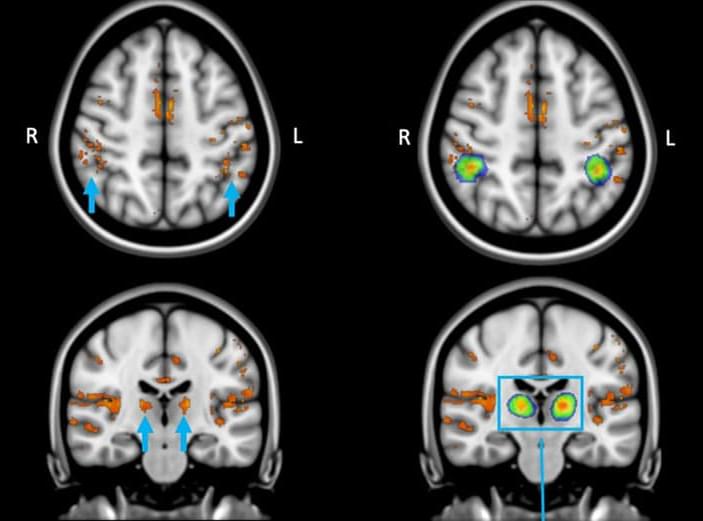
Working with animal models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions discovered how the fungus Candida albicans enters the brain, activates two separate mechanisms in brain cells that promote its clearance, and, important for the understanding of Alzheimer’s disease development, generates amyloid beta (Ab)-like peptides, toxic protein fragments from the amyloid precursor protein that are considered to be at the center of the development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study appears in the journal Cell Reports.
“Our lab has years of experience studying fungi, so we embarked on the study of the connection between C. albicans and Alzheimer’s disease in animal models,” said corresponding author Dr. David Corry, Fulbright Endowed Chair in Pathology and professor of pathology and immunology and medicine at Baylor. He also is a member of Baylor’s Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center. “In 2019, we reported that C. albicans does get into the brain where it produces changes that are very similar to what is seen in Alzheimer’s disease. The current study extends that work to understand the molecular mechanisms.”