An excellent and inspiring writeup of the story of Dyno Therapeutics, one of the most exciting startups in the gene therapy world.
How AI can accelerate gene therapy.
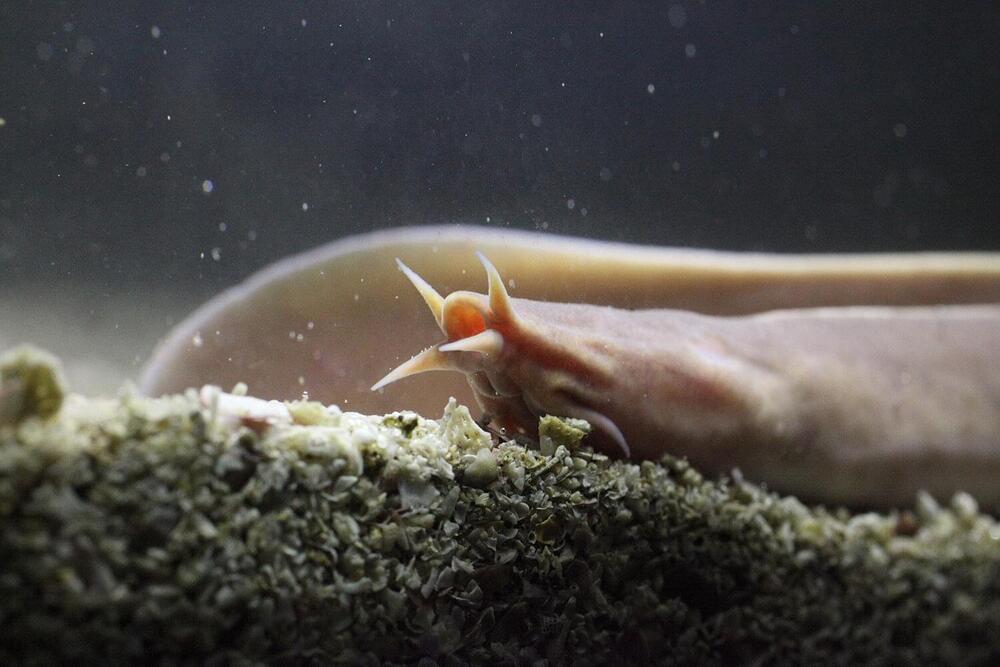


An international scientific team including more than 40 authors from seven different countries, led by a researcher at the University of Malaga Juan Pascual Anaya, has managed to sequence the first genome of the myxini, also known as hagfish, the only large group of vertebrates for which there has been no reference genome of any of its species yet.
This finding, published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution, has allowed for deciphering the evolutionary history of genome duplications that occurred in the ancestors of vertebrates, a group that includes humans.
“This study has important implications in the evolutionary and molecular field, as it helps us understand the changes in the genome that accompanied the origin of vertebrates and their most unique structures, such as the complex brain, the jaw and the limbs,” explains the scientist of the Department of Animal Biology of the UMA Pascual Anaya, who has coordinated the research.

(BRLS), formerly known as Life Extension Foundation, Inc., is one of the world’s leading providers of financial support for otherwise unfunded research in the areas of cryobiology, interventive gerontology and cryonics. During the last decade alone, BRLS awarded more than $100 million in grants to highly-specialized cryogenic research organizations.
BRLS is exempt from taxation under Internal Revenue Service code Section 501©(4)1, and is operated exclusively to promote social welfare through scientific research and education. BRLS was founded in 1977, and since then, we have awarded hundreds of grants to scientists throughout the United States who are personally committed to our mission. These dedicated professionals take extraordinary steps to make their research as cost-effective as possible. We are careful to commit our research dollars to projects that are difficult or impossible to fund through government and institutional grants or other sources.

Nonprofit organization, whose goal is the extension of the healthy human lifespan
Biomedical Research and Longevity Society, Inc. (BRLS), formerly known as Life Extension Foundation, Inc., is one of the world’s leading providers of financial support for otherwise unfunded research in the areas of cryobiology, interventive gerontology and cryonics. During the last decade alone, BRLS awarded more than $100 million in grants to highly-specialized cryogenic research organizations.
Visit website: https://www.brlsociety.org/.
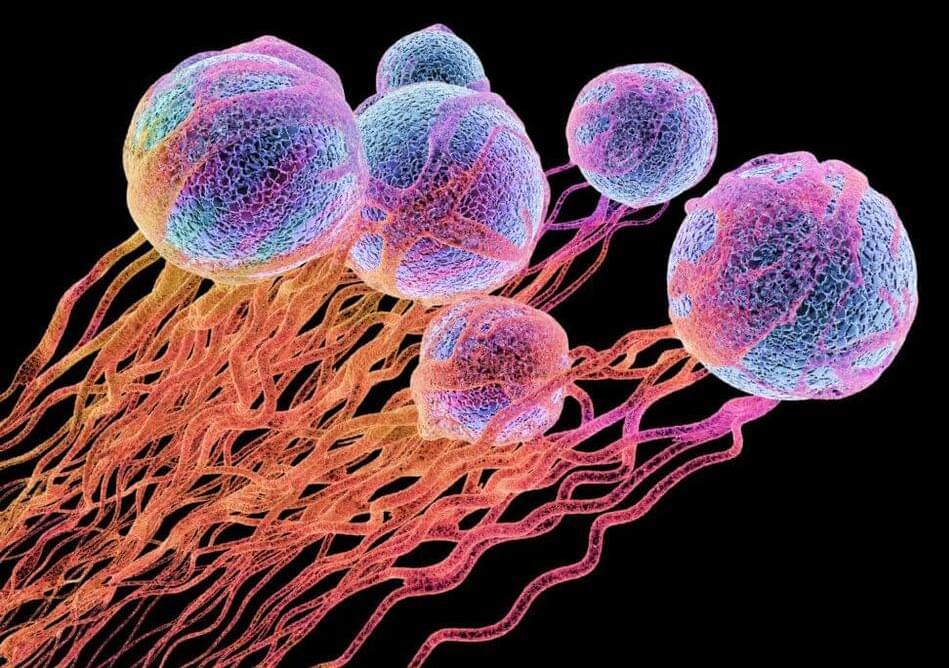
In a preclinical study, researchers led by City of Hope have discovered that a type of immune cell in the human body, known to be important for allergy and other immune responses, can also attack cancer. The cells, called human type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), can be expanded outside of the body and applied in larger numbers to overpower a tumor’s defenses and eliminate malignant cells in mouse models with cancer.
The findings are published in Cell in an article titled, “Therapeutic application of human type 2 innate lymphoid cells via induction of granzyme B-mediated tumor cell death.”
“The City of Hope team has identified human ILC2 cells as a new member of the cell family capable of directly killing all types of cancers, including blood cancers and solid tumors,” said Jianhua Yu, PhD, a professor in the department of hematology and hematopoietic cell transplantation at City of Hope and the study’s senior author. “In the future, these cells could be manufactured, preserved by freezing, and then administered to patients. Unlike T cell-based therapies, such as CAR T cells, which necessitate using the patient’s own cells due to their specific characteristics, ILC2s might be sourced from healthy donors, presenting a distinct potential therapeutic approach as an allogeneic and ‘off-the-shelf’ product.”
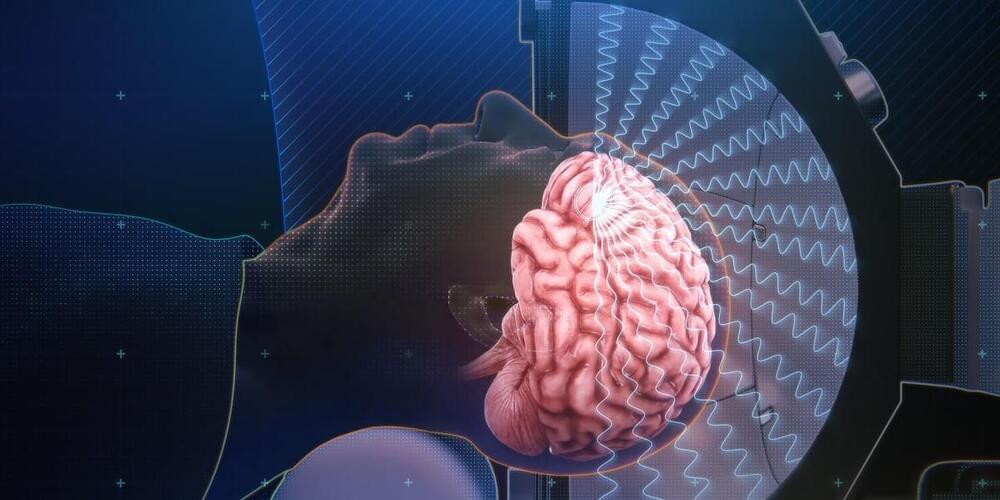
Last week, researchers at the West Virginia University Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute reported that by using focused ultrasound to open the blood-brain barrier, they improved delivery of a new Alzheimer’s treatment and sped up clearance of the sticky plaques that are thought to contribute to some of the cognitive and memory problems in people with Alzheimer’s by 32%.
For this issue of The Checkup, we’ll explore some of the ways scientists are trying to disrupt the blood-brain barrier.
In the West Virginia study, three people with mild Alzheimer’s received monthly doses of aducanumab, a lab-made antibody that is delivered via IV. This drug, first approved in 2021, helps clear away beta-amyloid, a protein fragment that clumps up in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease. (The drug’s approval was controversial, and it’s still not clear whether it actually slows progression of the disease.) After the infusion, the researchers treated specific regions of the patients’ brains with focused ultrasound, but just on one side. That allowed them to use the other half of the brain as a control. PET scans revealed a greater reduction in amyloid plaques in the ultrasound-treated regions than in those same regions on the untreated side of the brain, suggesting that more of the antibody was getting into the brain on the treated side.



One approach to AI uses a process called machine learning. In machine learning, a computer model is built to predict what may happen in the real world. The model is taught to analyze and recognize patterns in a data set. This training enables the model to then make predictions about new data. Some AI programs can also teach themselves to ask new questions and make novel connections between pieces of information.
“Computer models and humans can really work well together to improve human health,” explains Dr. Grace C.Y. Peng, an NIH expert on AI in medicine. “Computers are very good at doing calculations at a large scale, but they don’t have the intuitive capability that we have. They’re powerful, but how helpful they’re going to be lies in our hands.”
Researchers are exploring ways to harness the power of AI to improve health care. These include assisting with diagnosing and treating medical conditions and delivering care.

Part 3: This is the last of a three-part series on how Stanford Medicine researchers are designing vaccines that protect people from not merely individual viral strains but broad ranges of them. The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
Until now, vaccine efforts have mainly focused on stimulating B cells, described and discussed in Part 1 and Part 2. These antibody-producing immune cells’ virtue of being highly specific in what they target is also a vice. An antibody against influenza is unlikely to ever bind to, say, a coronavirus or a rabies virus.
Even when a virus mutates in some small way that distorts or disguises one of its biochemical bull’s-eyes, antibodies that worked before (because they aimed at that particular bull’s-eye) are now unemployed.