News from Cambridge businesses. Network members upload news here about their products, services and achievements.


The fast-advancing fields of neuroscience and computer science are on a collision course. David Cox, Assistant Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Computer Science at Harvard, explains how his lab is working with others to reverse engineer how brains learn, starting with rats. By shedding light on what our machine learning algorithms are currently missing, this work promises to improve the capabilities of robots – with implications for jobs, laws and ethics.
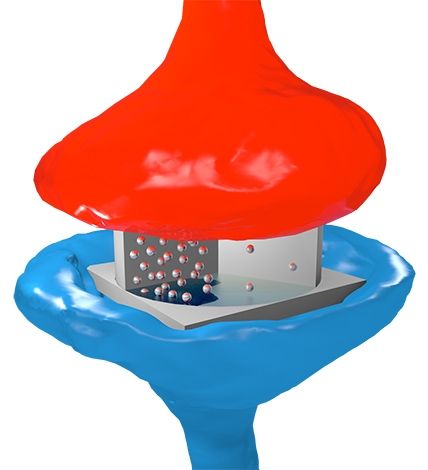
© Sören Boyn / CNRS/Thales physics joint research unit.
Artist’s impression of the electronic synapse: the particles represent electrons circulating through oxide, by analogy with neurotransmitters in biological synapses. The flow of electrons depends on the oxide’s ferroelectric domain structure, which is controlled by electric voltage pulses.
Thanks for your interest!
Thanks to SAP Italia for making this video available, the original video is at https://youtu.be/PLS5wGAM3R8 You can download all my slides at www.gerdcloud.net; direct link to the slides used here is gerd.fm/sapitaliagerd
In this talk, I address the opportunities and challenges of exponential transformation, the coming convergence of man and machine, the changes coming to society, work and jobs, the 10 megashifts, and what it takes to lead into this future responsible and openly.
If you enjoy my videos and talks, please take a look at my new book “Technology vs Humanity” http://www.techvshuman.com or buy it via Amazon http://gerd.fm/globalTVHamazon
Gerd Leonhard Futurist, Humanist, Author / Keynote Speaker.
CEO of The Futures Agency
Zürich / Switzerland
http://www.futuristgerd.com or www.gerdleonhard.de
Download all of my videos and PDFs at http://www.gerdcloud.net
About my new book: are you ready for the greatest changes in recent human history? Futurism meets humanism in Gerd Leonhard’s ground-breaking new work of critical observation, discussing the multiple Megashifts that will radically alter not just our society and economy but our values and our biology. Wherever you stand on the scale between technomania and nostalgia for a lost world, this is a book to challenge, provoke, warn and inspire.


SpaceX and Tesla CEO Elon Musk is backing a brain-computer interface venture called Neuralink, according to The Wall Street Journal. The company, which is still in the earliest stages of existence and has no public presence whatsoever, is centered on creating devices that can be implanted in the human brain, with the eventual purpose of helping human beings merge with software and keep pace with advancements in artificial intelligence. These enhancements could improve memory or allow for more direct interfacing with computing devices.
Musk has hinted at the existence of Neuralink a few times over the last six months or so. More recently, Musk told a crowd in Dubai, “Over time I think we will probably see a closer merger of biological intelligence and digital intelligence.” He added that “it’s mostly about the bandwidth, the speed of the connection between your brain and the digital version of yourself, particularly output.” On Twitter, Musk has responded to inquiring fans about his progress on a so-called “neural lace,” which is sci-fi shorthand for a brain-computer interface humans could use to improve themselves.

A group of prominent researchers is calling for changes to scientific-research guidelines to address a range of new biological entities created in labs that may share similar characteristics to embryos.
These entities, created through a variety of techniques, have been studied at only the earliest stages of development. In some cases, scientists have taken cells from an embryo and manipulated them to generate another embryo-like…

From AlphaGo’s historic victory against world champion Lee Sedol to DeepStack’s sweeping win against professional poker players, artificial intelligence is clearly on a roll.
Part of the momentum comes from breakthroughs in artificial neural networks, which loosely mimic the multi-layer structure of the human brain. But that’s where the similarity ends. While the brain can hum along on energy only enough to power a light bulb, AlphaGo’s neural network runs on a whopping 1,920 CPUs and 280 GPUs, with a total power consumption of roughly one million watts—50,000 times more than its biological counterpart.
Extrapolate those numbers, and it’s easy to see that artificial neural networks have a serious problem—even if scientists design powerfully intelligent machines, they may demand too much energy to be practical for everyday use.
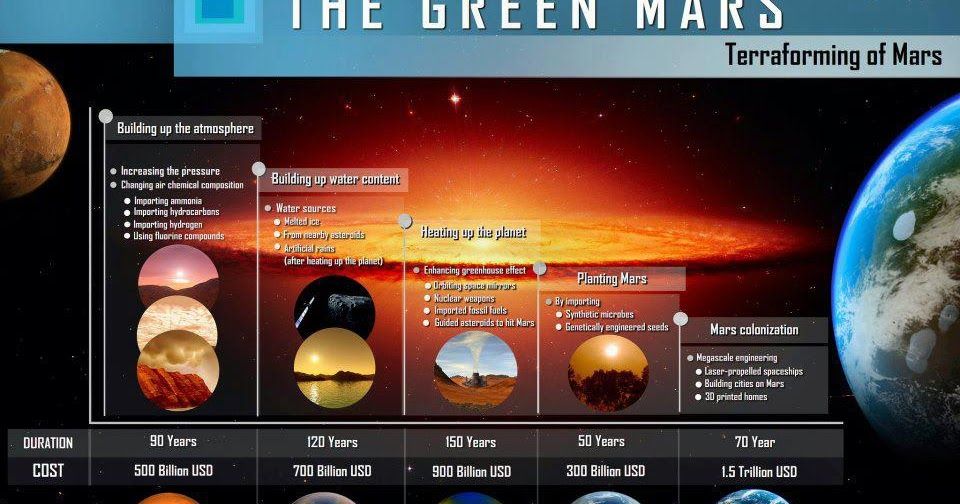
If all the solar incident on Mars were to be captured with 100% efficiency, then Mars would warm to Earth-like temperatures in about 10 years. However, the efficiency of the greenhouse effect is plausibly about 10%, thus the time it would take to warm Mars would be ~100 years. This assumes, of course, adequate production of super greenhouse gases over that entire time. The super greenhouse gases desired for use on Mars would be per fluorinated compounds (PFCs) as these are not toxic, do not destroy ozone, will resist degradation by ultraviolet life, and are composed of elements (C, S, and F) that are present on Mars. Fluorine has been detected on Mars by Curiosity.
The Warming Phase of a terraforming project on Mars results in a planet with a thick CO2 atmosphere. The thickness is determined by the total releasable CO2 present on Mars.
The temperatures would become well above freezing and liquid water is common. An Earth-like hydrological cycle is maintained. Photosynthetic organisms can be introduced as conditions warm and organic biomass is thus produced. A rich flora and fauna are present. A natural result of this is the biological consumption of the nitrate and perchlorate in the.
Would you like to know more? http://pdxint.at/2mvFVSx
Stellaris: Utopia brings even greater depth and variety to a game already celebrated for its story-telling power and near endless possibilities. Are you ready for perfection?
One of the core improvements in Utopia is the introduction of Ascension Perks. As your species advances and gains new traditions, it can choose how it wants to evolve as it is further enlightened. You can choose between a biological path, a psionic path or a synthetic path, with various options within these broad categories. Body, Mind or Machine — how will your species challenge the future?
Utopia Also Includes:
Megastructures: Build wondrous structures in your systems including Dyson Spheres and ring worlds, bringing both prestige and major advantages to your race.
Habitat Stations: Build “tall” and establish space stations that will house more population, serving the role of planets in a small and confined empire.
Rights and Privileges: Set specific policies for which of the many species under your thumb will have the rights and privileges of full citizenship. Build an egalitarian paradise or follow a caste system.
And even more improvements and updates, including (as is traditional with all of our paid content releases) free updates for every Stellaris owner!