Modern computer models—for example for complex, potent AI applications—push traditional digital computer processes to their limits. New types of computing architecture, which emulate the working principles of biological neural networks, hold the promise of faster, more energy-efficient data processing.
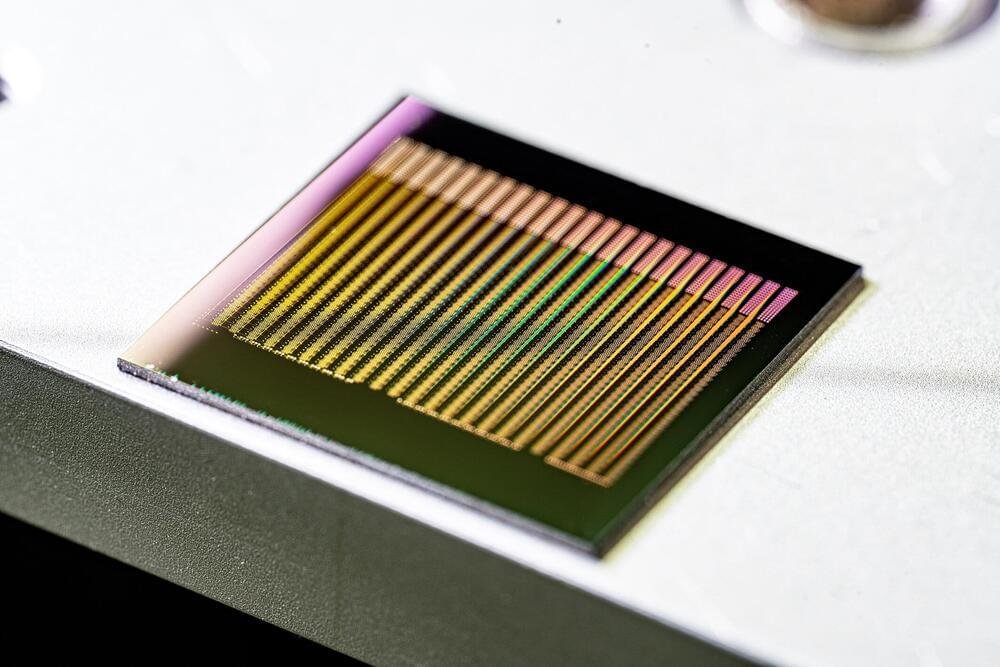
A team of researchers has now developed a so-called event-based architecture, using photonic processors with which data are transported and processed by means of light. In a similar way to the brain, this makes possible the continuous adaptation of the connections within the neural network. This changeable connections are the basis for learning processes.
For the purposes of the study, a team working at Collaborative Research Center 1,459 (Intelligent Matter)—headed by physicists Prof. Wolfram Pernice and Prof. Martin Salinga and computer specialist Prof. Benjamin Risse, all from the University of Münster—joined forces with researchers from the Universities of Exeter and Oxford in the UK. The study has been published in the journal Science Advances.