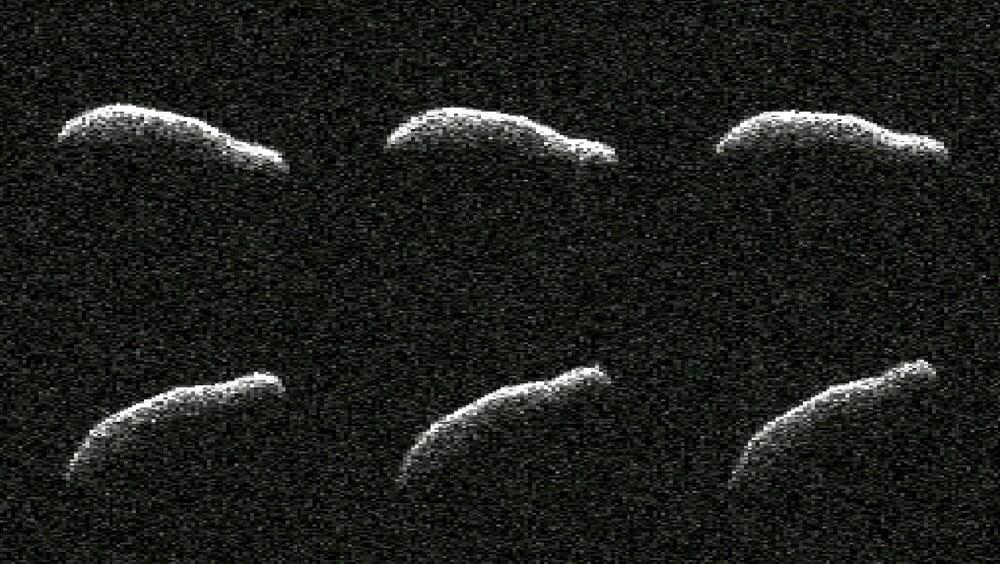
On Feb. 3, an asteroid more than three times as long as it is wide safely flew past Earth at a distance of about 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers, or a little under five times the distance between the Moon and Earth). While there was no risk of the asteroid—called 2011 AG5—impacting our planet, scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California closely tracked the object, making invaluable observations to help determine its size, rotation, surface details, and, most notably, shape.
This close approach provided the first opportunity to take a detailed look at the asteroid since it was discovered in 2011, revealing an object about 1,600 feet (500 meters) long and about 500 feet (150 meters) wide—dimensions comparable to the Empire State Building. The powerful 230-foot (70-meter) Goldstone Solar System Radar antenna dish at the Deep Space Network’s facility near Barstow, California, revealed the dimensions of this extremely elongated asteroid.
“Of the 1,040 near-Earth objects observed by planetary radar to date, this is one of the most elongated we’ve seen,” said Lance Benner, principal scientist at JPL who helped lead the observations.