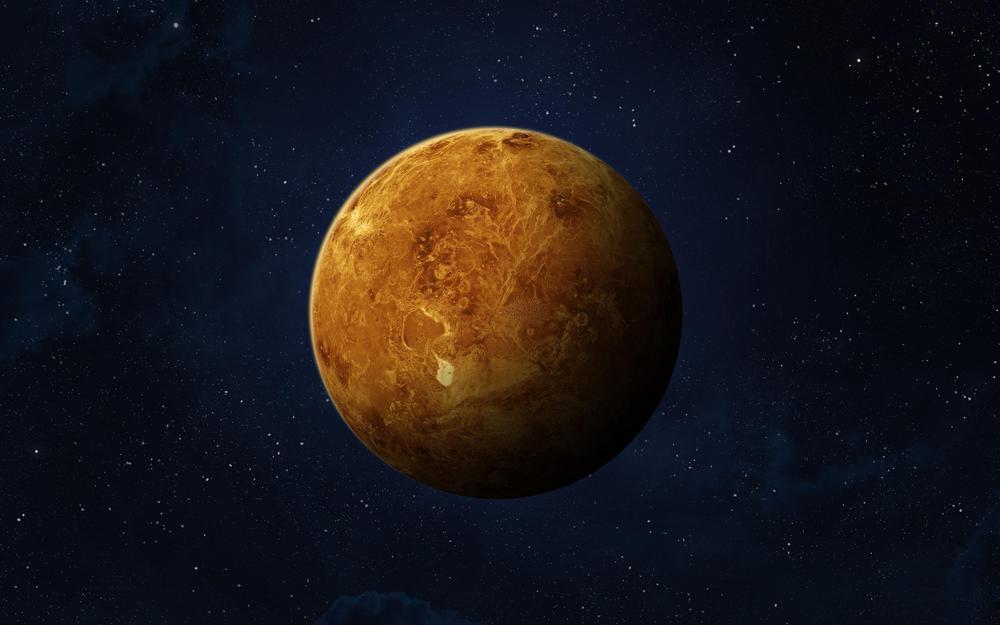
Millions of space nerds reacted with joy Monday to a study showing the atmosphere of Venus contains phosphine, a chemical byproduct of biological life. But none would have been more thrilled or less surprised by the discovery than the late, great Carl Sagan — who said this day might come more than 50 years ago.
Now best remembered as the presenter of the most-viewed-ever PBS series Cosmos, the author of the book behind the movie Contact, and the guy who put gold disks of Earth music on NASA’s Voyager missions, Sagan actually got his start studying our closest two planets. He became an astronomer after being inspired as a kid by Edgar Rice Burroughs’ space fantasies, set on Mars and Venus.
‘Cosmos’ presenter Carl Sagan was one of the world’s top experts on Venus, and he saw first what scientists have just announced: possible life on Venus.