Stars scattered throughout the cosmos look different, but they may be more alike than once thought, according to Rice University researchers.
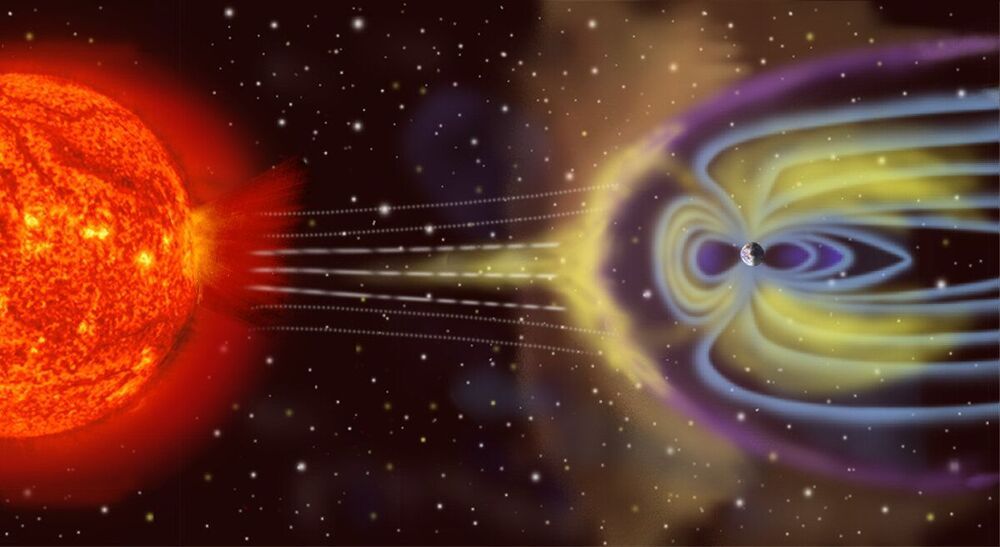
New modeling work by Rice scientists shows that “cool” stars like the sun share the dynamic surface behaviors that influence their energetic and magnetic environments. This stellar magnetic activity is key to whether a given star hosts planets that could support life.
The work by Rice postdoctoral researcher Alison Farrish and astrophysicists David Alexander and Christopher Johns-Krull appears in a published study in The Astrophysical Journal. The research links the rotation of cool stars with the behavior of their surface magnetic flux, which in turn drives the star’s coronal X-ray luminosity, in a way that could help predict how magnetic activity affects any exoplanets in their systems.