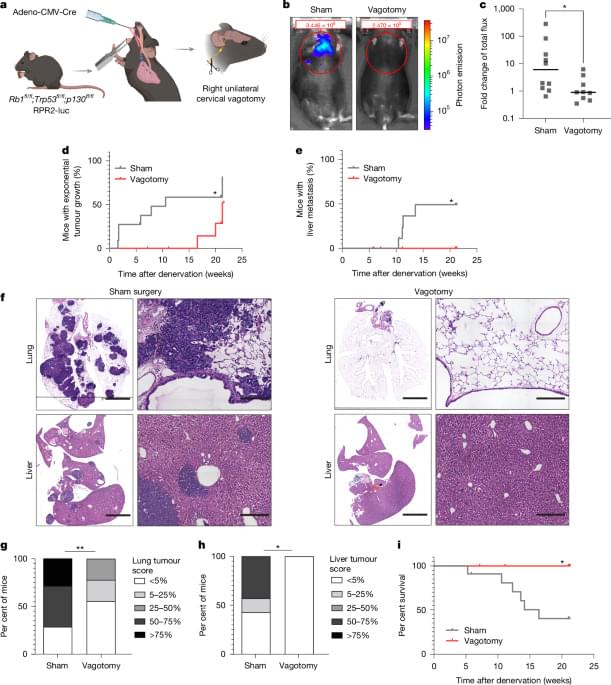
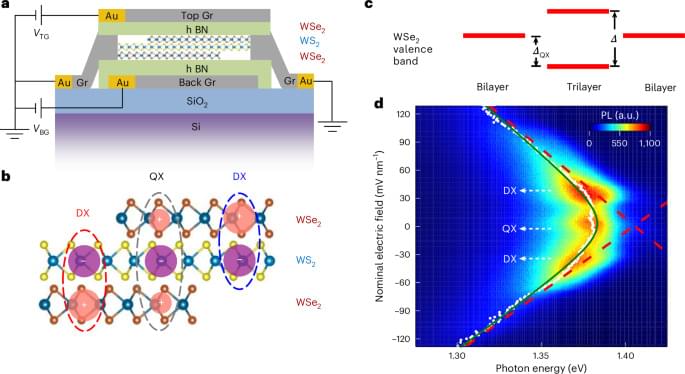
Glutamatergic and GABAergic (γ-aminobutyric acid-producing) cortical neuronal activity drives proliferation of small lung cell cancer via paracrine interactions and through synapses formed with tumour cells.


One of the biggest quests in biology is understanding how every cell in an animal’s body carries an identical genome yet still gives rise to a kaleidoscope of different cell types and tissues. A neuron doesn’t look nor behave like a muscle cell but has the same DNA.
Researchers think it comes down to how cells allow different parts of the genome to be read. Controlling these permissions are regulatory elements, regions of the genome which switch genes on or off. A detailed overview of how they do this is largely restricted to a handful of classic model organisms like mice and fruit flies.
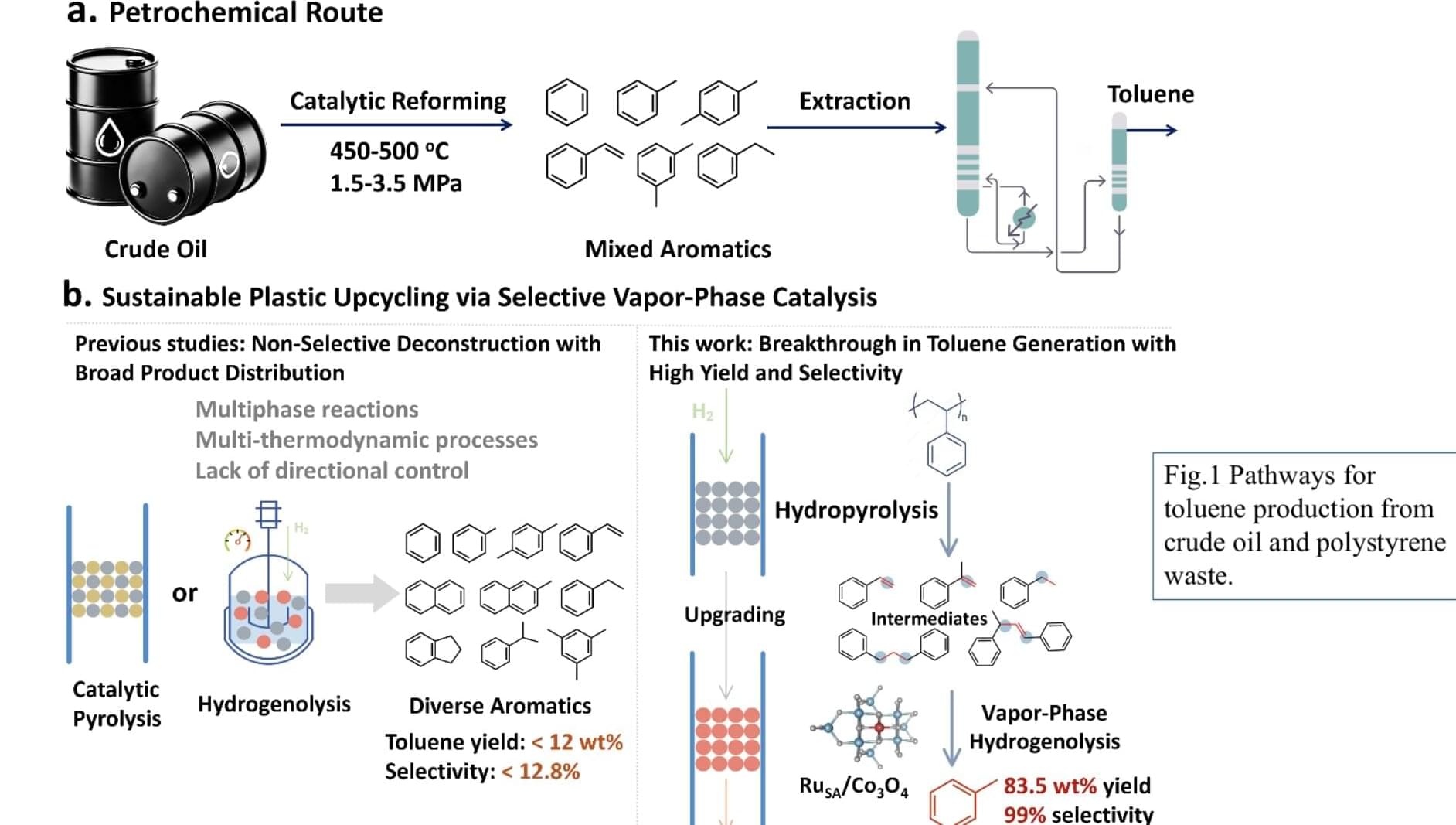
The rapid accumulation of plastic waste is currently posing significant risks for both human health and the environment on Earth. A possible solution to this problem would be to recycle plastic waste, breaking it into smaller molecules that can be used to produce valuable chemicals.
Researchers at Nanjing Forestry University and Tsinghua University recently introduced a new approach to convert polystyrene (PS), a plastic widely used to pack some foods and other products, into toluene, a hydrocarbon that is of value in industrial and manufacturing settings. Their proposed strategy, outlined in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, entails heating polystyrene waste in hydrogen and breaking it down into smaller vapor molecules, a process known as hydro-pyrolysis.
Life-cycle and techno-economic analyses performed by the team showed that the newly introduced process could reduce the carbon footprint of toluene production by 53%, producing toluene at an estimated cost of $0.61/kg, which is below the current industry benchmark.
Attention disorders such as ADHD involve a breakdown in our ability to separate signal from noise. The brain is constantly bombarded with information, and focus depends on its ability to filter out distractions and detect what matters.
Stimulant medications improve attention by boosting activity in circuits known to govern attention, such as the prefrontal cortex. But a new study reveals a surprising alternative: reduce background activity as a way of turning down extraneous noise.
In a paper published in Nature Neuroscience, researchers show that the Homer1 gene plays a critical role in shaping attention in just that way. Mice with lower levels of two specific versions of the gene enjoyed quieter brain activity and improved ability to focus.

Stra8 links neuronal activity to inhibitory circuit protection in the adult mouse brain.
Huang et al. show that Stra8, a gene previously thought to be germline specific, is expressed in the adult mouse hippocampus in an activity-dependent manner. Stra8 protects neuronal integrity and cognition by regulating neuromodulator genes and preserving inhibitory circuit function.
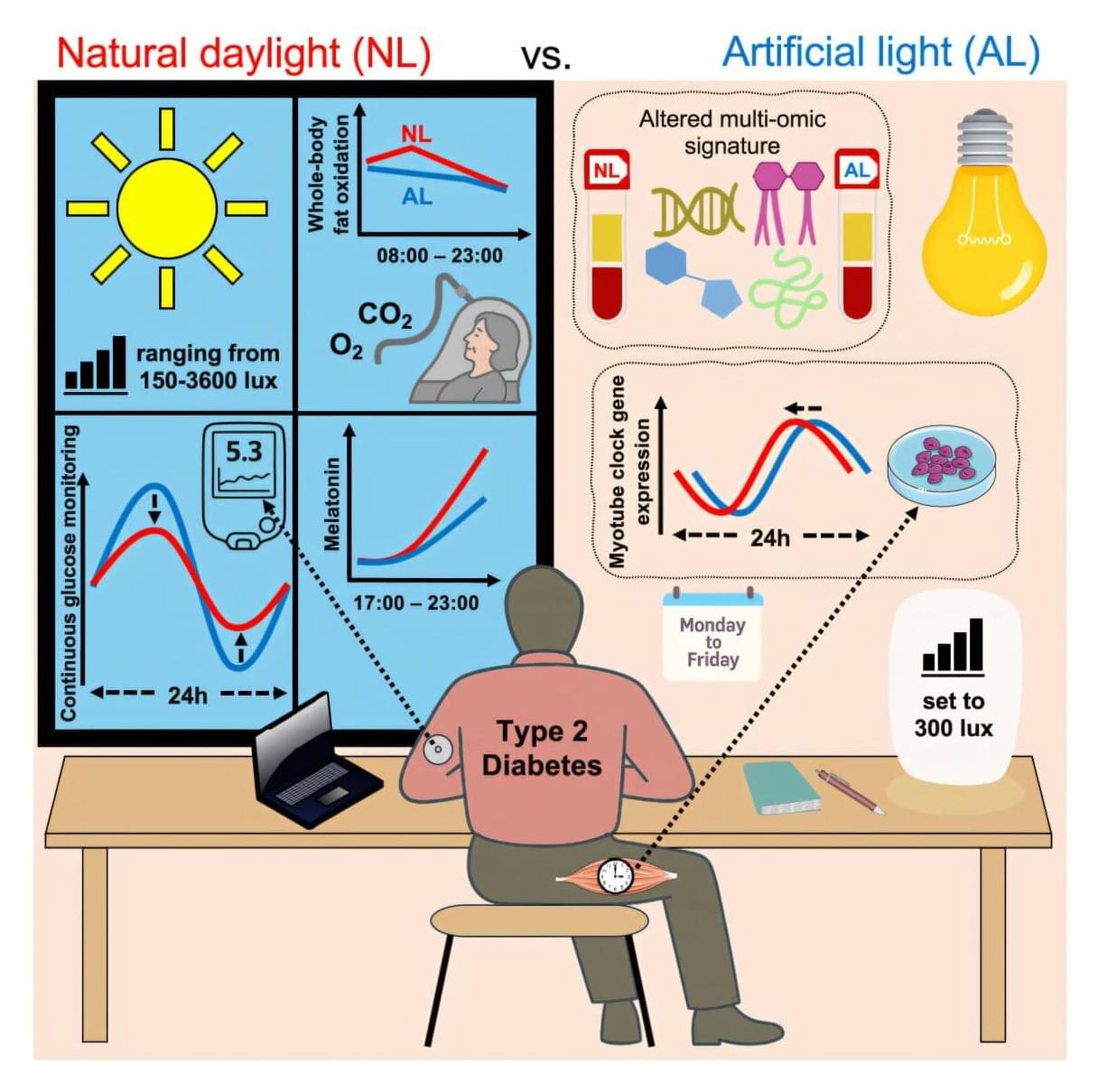
People with type 2 diabetes may be able to improve their blood sugar by doing something as simple as sitting by a window for a few hours each day. In a study published in Cell Metabolism, scientists showed that natural daylight helps maintain healthy glucose levels.
Daylight is known to be a mood enhancer and also beneficial for our health. However, according to the research team, most people living in Western societies typically stay indoors around 80% to 90% of the time under artificial light, which is not as bright or dynamic as sunlight. This is important because the human body operates on circadian rhythms, internal 24-hour clocks that orchestrate a range of biological processes, such as digestion and temperature regulation. These are synchronized by light, and a lack of natural light is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Previous studies have shown that artificial light at night disrupts these rhythms and that daylight outdoors can improve the body’s response to insulin, which helps control blood sugar levels. But no prior research examined how natural light entering a window affects people with diabetes.
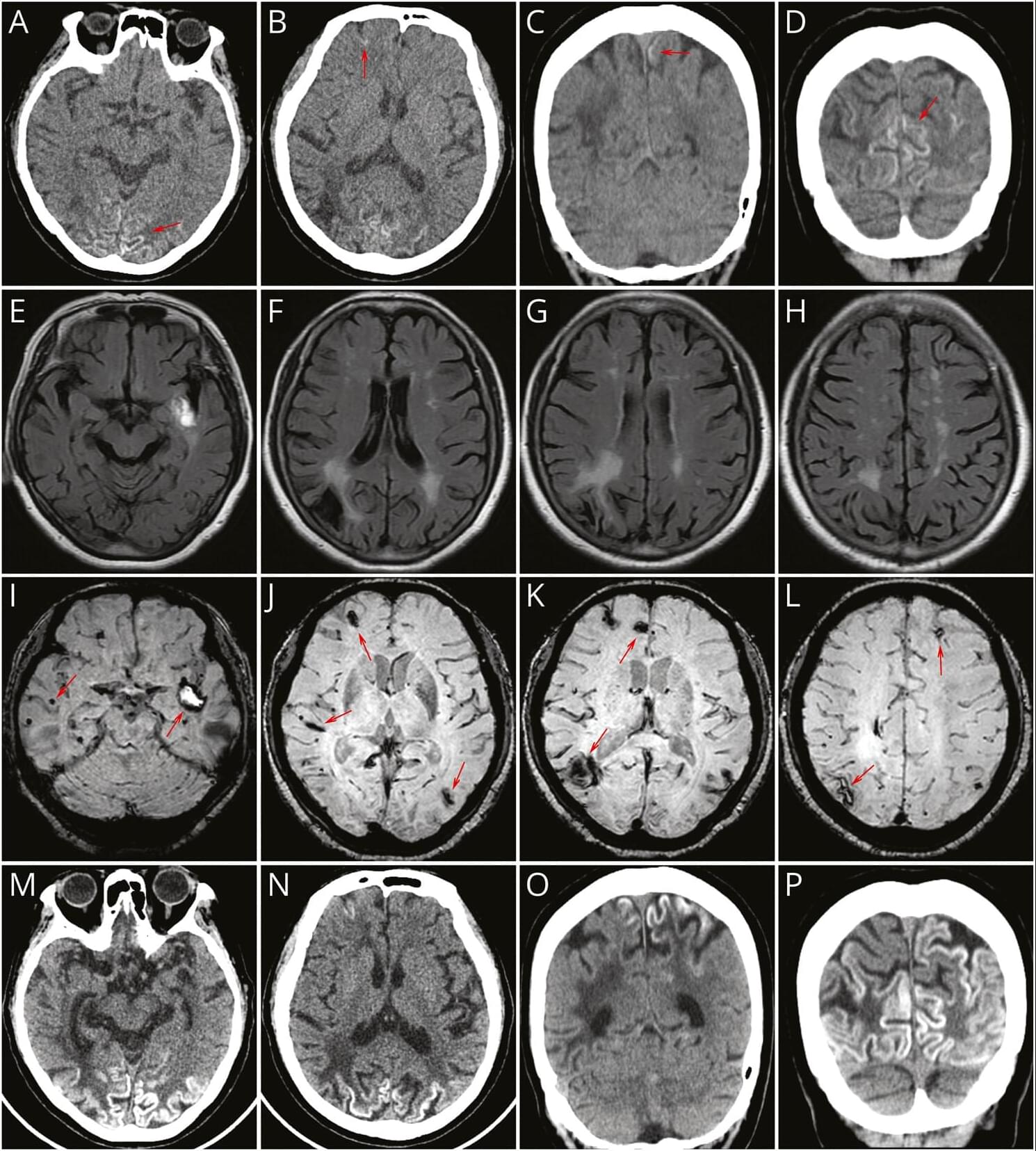
The Letters section represents an opportunity for ongoing author debate and post-publication peer review. View our submission guidelines for Letters to the Editor before submitting your comment.
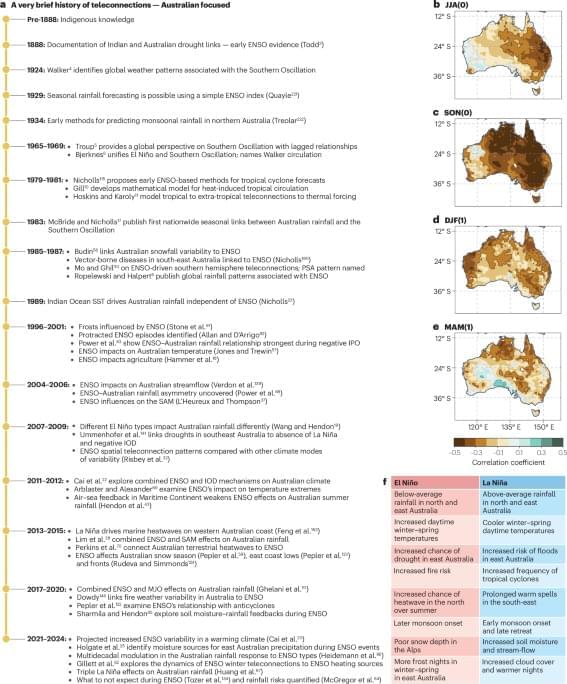
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) profoundly affects Australian weather, climate, ecosystems and socio-economic sectors. This Review presents the progress made in understanding ENSO teleconnections to Australian weather over the past 40 years, describing the atmospheric dynamics, complexities and impacts of this climate phenomenon.
