Supports high-speed transfer between USB-A and USB-C devices
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Can We Actually Regrow Teeth? The Science Behind the Tooth Regeneration Shot
In this video, Whitney, a registered dental hygienist, breaks down the viral headlines about a “tooth regrowth shot” being tested in Japan. She explains the real science behind the drug — how it targets the USAG-1 protein to potentially reactivate dormant tooth buds — and clears up common misconceptions about tooth regeneration research. From animal trials to current human safety studies, Whitney dives into what’s fact, what’s hype, and what this breakthrough could mean for the future of dentistry.
https://bit.ly/free-oral-hygiene-rout… SHOP MY STOREFRONT: https://bit.ly/4jgJPdG • Born With Missing Teeth? (Hypodontia)
• What Happens If You Don’t Replace Your Mis…
• Regrowing vs Remineralizing Tooth Enamel 🦷 WANT MORE TEETH TALK? ▶ newsletter: https://bit.ly/ttg-subscribe ▶ bettermouth app: https://www.bettermouth.com/ ▶ website: https://teethtalkgirl.com ▶ shop happyteeth: https://givehappyteeth.com/ ▶ amazon storefront: https://www.amazon.com/shop/teethtalk?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20 🦷 SUPPORT THIS CONTENT: ▶ patreon:
/ teethtalkgirl ▶ youtube:
/ @teethtalkhttps://www.france24.com/en/live-news… https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33579… https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en/research… https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/stor… https://trial.medpath.com/news/7c38d8… https://theweek.com/health/the-scienc… 🦷 BACKGROUND MUSIC: artlist.io 🦷 NOTE: This video does not provide medical advice and is intended for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your dentist or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical or dental condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have heard or seen on social media. ☮️ ❤️ 🦷
https://bit.ly/4jgJPdG
• Born With Missing Teeth? (Hypodontia)
• What Happens If You Don’t Replace Your Mis…
• Regrowing vs Remineralizing Tooth Enamel.
▶ newsletter: https://bit.ly/ttg-subscribe.
▶ bettermouth app: https://www.bettermouth.com/
▶ website: https://teethtalkgirl.com.
▶ shop happyteeth: https://givehappyteeth.com/
▶ amazon storefront: https://www.amazon.com/shop/teethtalk?tag=lifeboatfound-20?tag=lifeboatfound-20.
▶ patreon: / teethtalkgirl.
▶ youtube: / @teethtalk.

String Theory Inspires a Brilliant, Baffling New Math Proof
When the team posted their proof in August, many mathematicians were excited. It was the biggest advance in the classification project in decades, and hinted at a new way to tackle the classification of polynomial equations well beyond four-folds.
But other mathematicians weren’t so sure. Six years had passed since the lecture in Moscow. Had Kontsevich finally made good on his promise, or were there still details to fill in?
And how could they assuage their doubts, when the proof’s techniques were so completely foreign — the stuff of string theory, not polynomial classification? “They say, ‘This is black magic, what is this machinery?’” Kontsevich said.
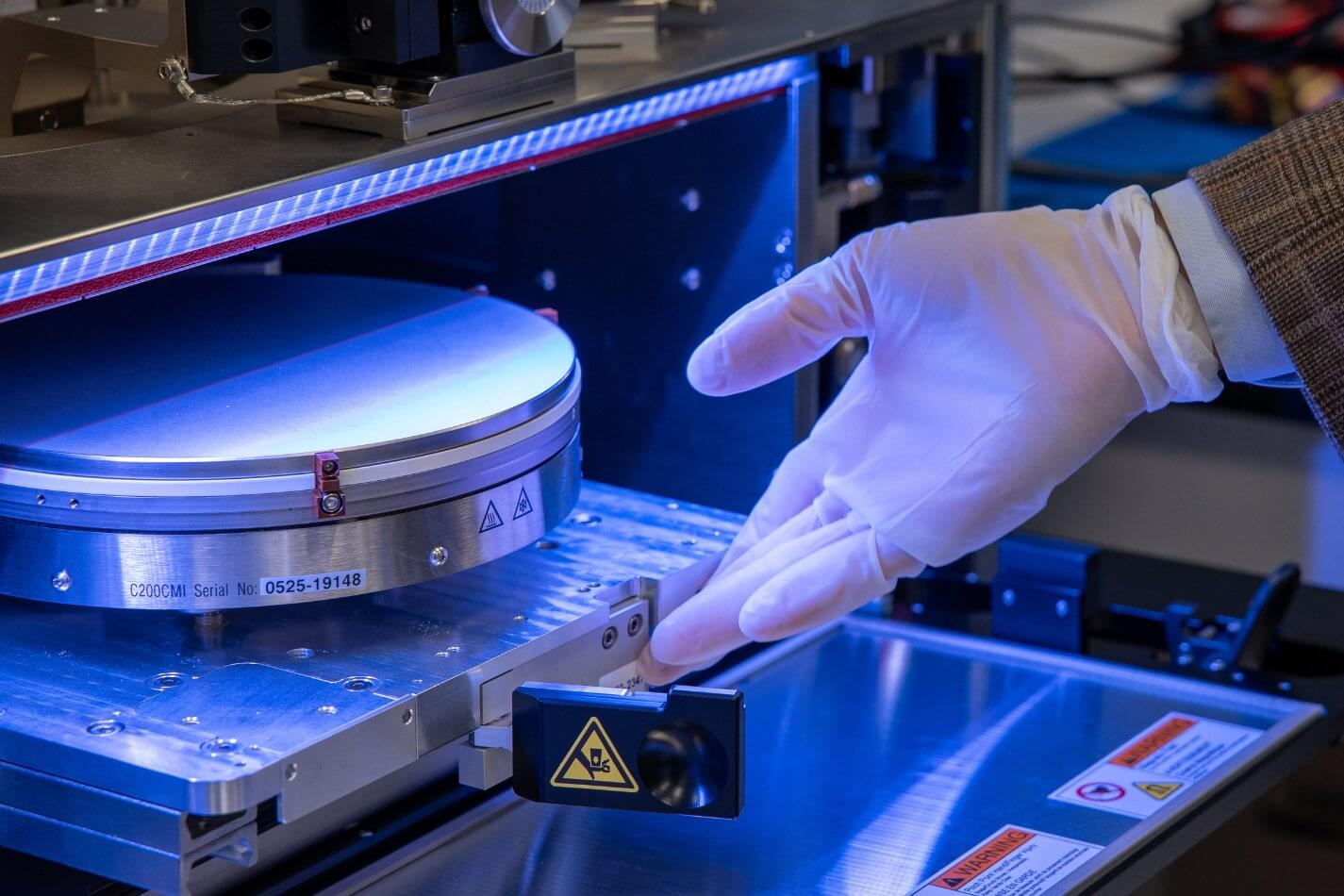

First monolithic 3D chip built in U.S. foundry delivers major AI speed gains
A collaborative team has achieved the first monolithic 3D chip built in a U.S. foundry, delivering the densest 3D chip wiring and order-of-magnitude speed gains.
Engineers at Stanford University, Carnegie Mellon University, University of Pennsylvania, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have collaborated with SkyWater Technology, the largest exclusively U.S.-based pure-play semiconductor foundry, to develop a novel multilayer computer chip whose architecture could help usher in a new era of AI hardware and domestic semiconductor innovation.
Unlike today’s largely flat, 2D chips, the new prototype’s key ultra-thin components rise like stories in a tall building, with vertical wiring acting like numerous high-speed elevators that enable fast, massive data movement. Its record-setting density of vertical connections and carefully interwoven mix of memory and computing units help the chip bypass the bottlenecks that have long slowed improvement in flat designs. In hardware tests and simulations, the new 3D chip outperforms 2D chips by roughly an order of magnitude.

Atmosphere Detected on Ultra-Hot Rocky World
“What really sets this planet apart is its anomalously low density. It is less dense than you would expect if it had an Earth-like composition,” said Dr. Johanna Teske.
What can a rocky molten exoplanet with an atmosphere teach astronomers about planetary formation and evolution? This is what a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated a thick atmosphere enveloping an exoplanet where previous hypotheses state it shouldn’t exist. This study has the potential to help scientists not only challenge longstanding hypotheses regarding exoplanets but also gain new insight into planetary formation and evolution.
For the study, the researchers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to observe TOI-561 b, which is located approximately 86 parsecs (280 light-years) from Earth and whose radius is 1.4 times of Earth. What makes TOI-561 unique is its orbit is only 11 hours long, resulting in an equilibrium temperature of approximately 2,500 Kelvin (2,227 degrees Celsius/4,040 degrees Fahrenheit).
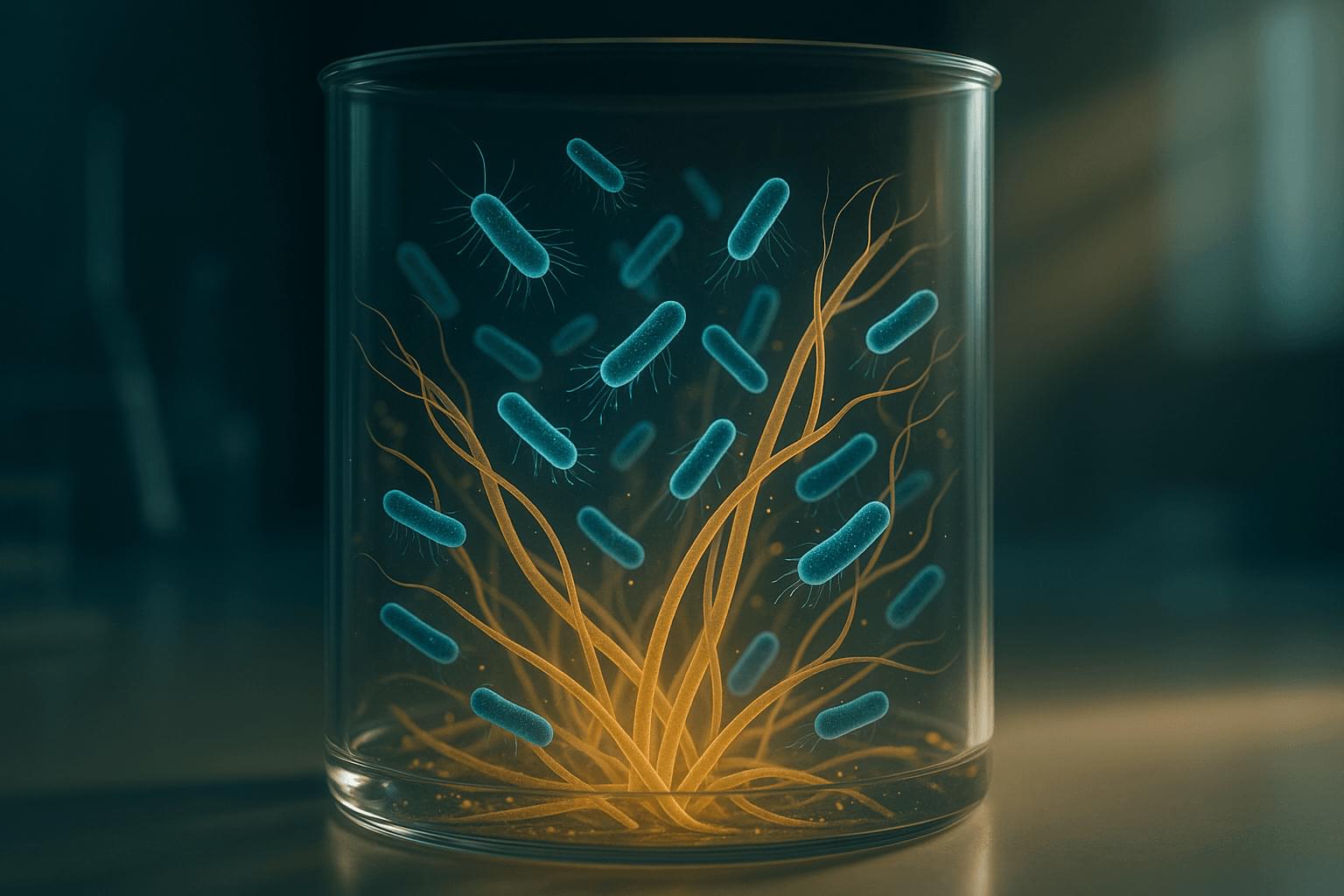
Scientists Uncover How Tiny “Nanopores” Learn Like the Brain
Scientists found that nanopores’ electrical charges control how ions flow and when pores temporarily shut down. The discovery could allow engineers to design nanopores that “learn” like synapses for next-generation computing.
Pore-forming proteins appear across many forms of life. In humans, they help protect the body by supporting immune defenses. In bacteria, they often function as toxins that create openings in cell membranes. These natural pores regulate the movement of ions and molecules, and their precise control over molecular transport has made them valuable in biotechnology, including DNA sequencing and molecular sensing.
Unpredictable Behavior in Ion Flow.
Time might not exist — and we’re starting to understand why
Consider two events, A and B, such as flashes of light made by two sources in different places.
Cause and effect means there are three possibilities: 1) Flash A happened before flash B, and via some mechanism, could have triggered B; 2) Flash B happened before Flash A and could have triggered it; 3) Neither one could have triggered the other because they are too far apart in space and too close in time for a triggering signal to have been sent from one location to the other.
Now, Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity states that all observers, no matter how fast they’re moving relative to each other, see light travelling at the same constant speed.
This strange but simple fact can lead to observers seeing events happening in different orders.
For option above, two observers moving relative to each other close to the speed of light might disagree on the ordering of flashes.
Thankfully, there’s no danger of an effect coming before its cause (known as a ‘violation of causality’) since the events are too far apart for either to cause the other.
However, what if options and coexisted in a quantum superposition? The causal order of the two events would no longer be fixed.
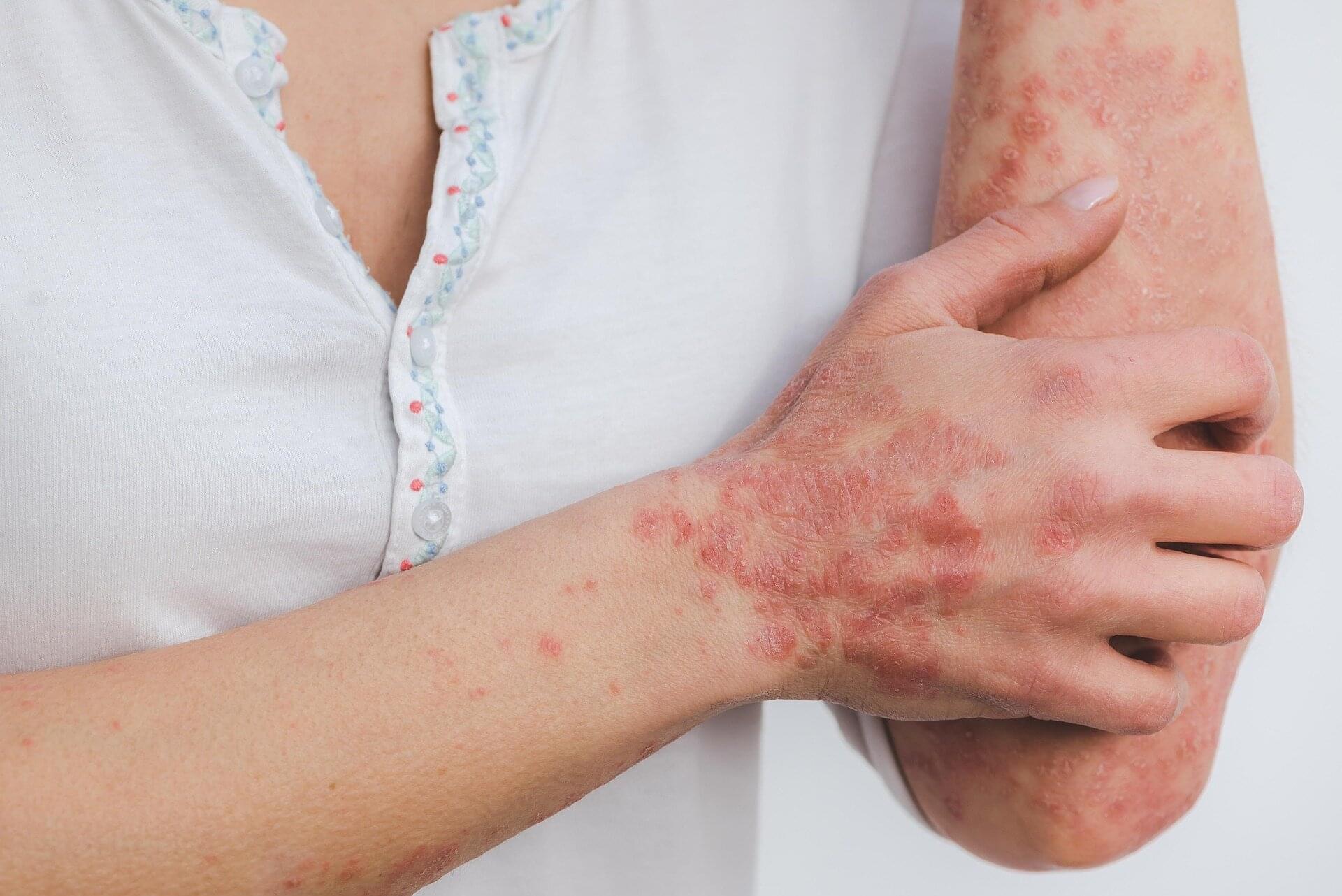
Psoriasis rates rise globally, with highest burden in wealthier regions
Researchers in China report that global incidence rates of psoriasis rose slightly from 1990 to 2021 and are projected to continue rising for both men and women through 2050.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that continues to impose a growing global burden. Understanding the rate of increase is critical for informing public health strategies, improving health care access, and supporting early diagnosis worldwide.
In the study, “Global Psoriasis Burden and Forecasts to 2050,” published as a Research Letter in JAMA Dermatology, researchers used a time-series forecasting analysis to project global psoriasis incidence through 2050 and to address age, sex, and regional differences in burden.
Where does Everything come from?
Sharpen your logic skills with Brilliant! Start learning for free at https://brilliant.org/sabine/ and get 20% off a premium subscription, which includes daily unlimited access!
The universe is full of a seemingly unending number of different things, from subatomic particles to plants and animals to gas giants and supernovae. But where did all of this stuff (for lack of a better word) come from? Let’s take a look.
👕T-shirts, mugs, posters and more: ➜ https://sabines-store.dashery.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜ / @sabinehossenfelder 📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW #science #physics #philosophy.
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW
#science #physics #philosophy
