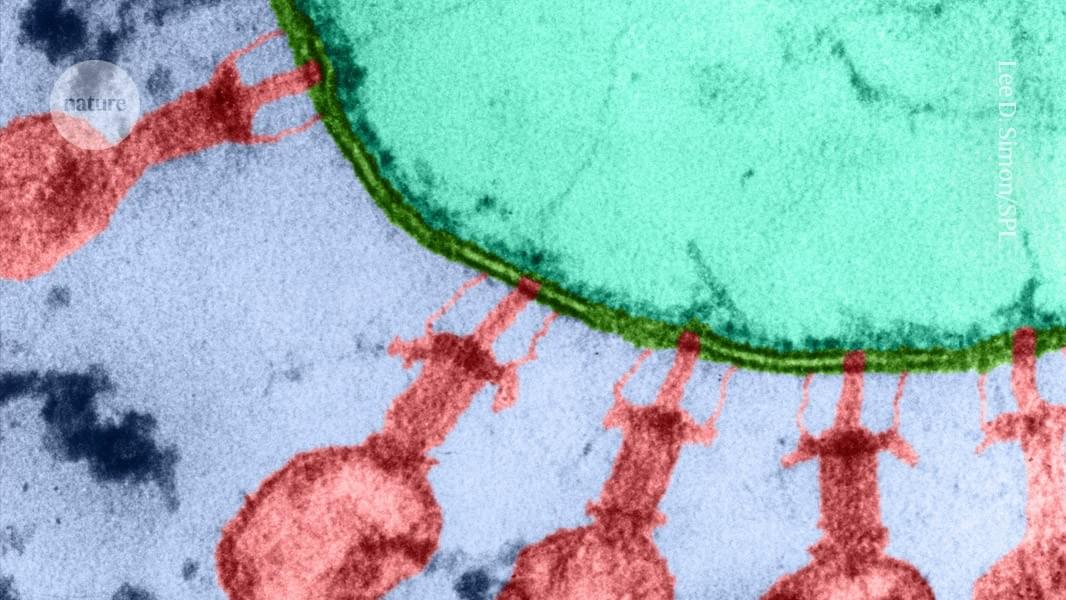
Scientists used artificial intelligence to write coherent viral genomes, using them to synthesize bacteriophages capable of killing resistant strains of bacteria.


In their nucleus, as they replicate, blood stem cells can accumulate mutations and lose epigenetic marks that used to keep DNA well-arranged, ultimately increasing mechanical tension on the nuclear envelope. This study figured out RhoA is a mechanosensor activated by such tension and conducts a key role in the stem cell ageing process. Researchers subsequently proved its rejuvenating potential: after ex vivo treatment of blood stem cells with the drug Rhosin, a RhoA inhibitor, they observed an improvement in aged-related markers.
As study co-author summarizes: “Overall, our experiments show that Rhosin did rejuvenate blood stem cells, increased the regenerative capacity of the immune system and improved the production of blood cells once transplanted in the bone marrow.”
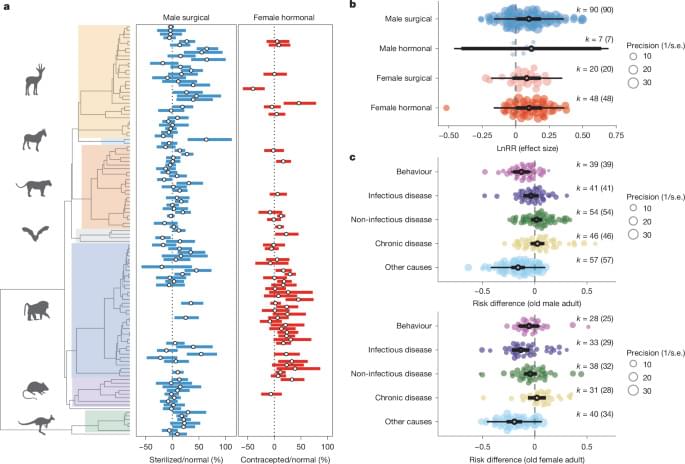
Ageing is defined as the deterioration of function overtime, and it is one of the main risk factors for numerous chronic diseases. Although ageing is a complex phenomenon affecting the whole organism, it is proved that the solely manifestation of ageing in the haematopoietic system affects the whole organism.
A research team previously revealed the significancy of using blood stem cells to pharmacologically target ageing of the whole body, thereby suggesting rejuvenating strategies that could extend healthspan and lifespan. Now, in a Nature Ageing publication, they propose rejuvenating aged blood stem cells by treating them with the drug Rhosin, a small molecule that inhibits RhoA, a protein that is highly activated in aged haematopoietic stem cells. This study combined in vivo and in vitro assays together with innovative machine learning techniques.
Blood stem cells, or hematopoietic stem cells, are located in the bone marrow, a highly dynamic and specialised tissue within the cavity of long bones. They are responsible for the vital function of continuously producing all types of blood cells: red blood cells (oxygen transporters), megakaryocytes (future platelets) and white blood cells (immune cells, lymphocytes and macrophages). Over time, however, stem cells also do age, they lose their regenerative capacity and generate fewer and lower quality immune cells. This has been linked to immunosenescence, chronic low grade inflammation and certain chronic diseases.

An AI tool that can analyze abnormalities in the shape and form of blood cells, and with greater accuracy and reliability than human experts, could change the way conditions such as leukemia are diagnosed.
Researchers have created a system called CytoDiffusion that uses generative AI – the same type of technology behind image generators such as DALL-E – to study the shape and structure of blood cells.
Unlike many AI models, which are trained to simply recognize patterns, the researchers – led by the University of Cambridge, University College London and Queen Mary University of London – showed that CytoDiffusion could accurately identify a wide range of normal blood cell appearances and spot unusual or rare cells that may indicate disease. Their results are reported in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.
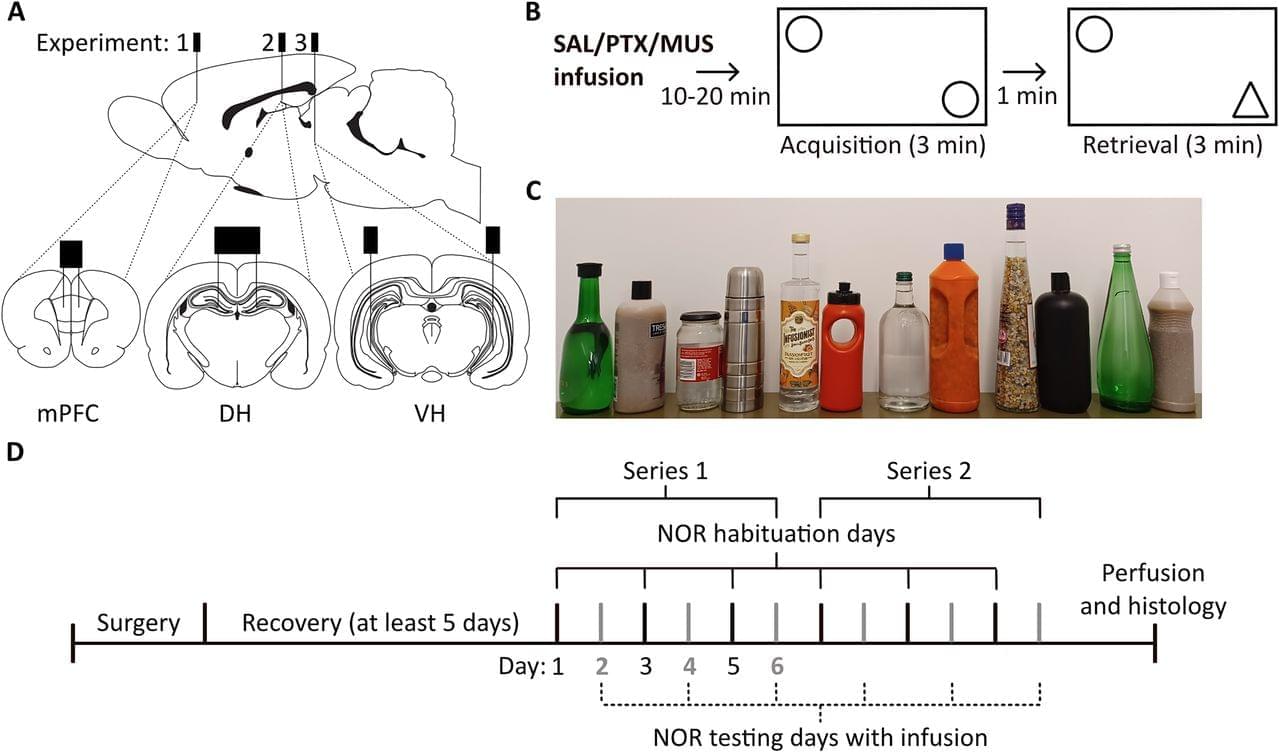
Impaired GABAergic inhibition, so-called neural disinhibition, in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus has been linked to cognitive deficits. The novel object recognition (NOR) task has been used widely to study cognitive deficits in rodents. However, the contribution of prefrontal cortical and hippocampal GABAergic inhibition to NOR task performance has not been established. Here, we investigated NOR task performance in male Lister hooded rats following regional neural disinhibition or functional inhibition, using intracerebral microinfusion of the GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin or agonist muscimol, respectively. Our infusion targets were the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), dorsal hippocampus (DH), and ventral hippocampus (VH).

Tanning bed users have more melanomas in uncommonly diagnosed areas, according to new research.
The mutation burden of melanocytes in tanning bed users was nearly twofold that of melanocytes from control donors [median mutations per megabase (mut/Mb) of 5.69 versus 2.86] (Fig. 2B). This trend remained significant when we separately compared melanocytes by anatomic site (median mut/Mb of 8.82 versus 4.60 in upper back and 5.19 versus 2.05 in lower back) (Fig. 2C). The mutation burdens of cells from both control groups were less than the cells in the tanning cohort (fig. S2A).
We developed a linear mixed-effects (LME) model to determine whether tanning bed users had higher mutation burdens after adjusting for anatomic site and outliers (18). Specifically, we compared the tanning and control cohorts at the cell level while introducing a variable for anatomic site and including a random effect for different donors (fig. S3). In this analysis, the cells from tanning bed users had a significantly higher mutation burden (P = 1.3 × 10−2). However, we noted that cells from one donor (donor 59) had an extremely high mutation burden. To ensure that this donor was not entirely responsible for the differences observed, the analyses were repeated with a robust linear mixed-effects (RLME) model, which is less sensitive to outliers, heavy-tailed distributions, and model violations (19). In this analysis, the cells from tanning bed users continued to have a significantly higher mutation burden (P = 6.1 × 10−5).
We also compared mutation burdens at the biopsy level. We defined the mutation burden of a biopsy as the median mutation burden of its constituent melanocytes. Our statistical power was more limited in these comparisons because there were fewer independent biopsies than individual cells. On the lower back, tanning bed biopsies had significantly higher mutation burdens than control biopsies (Fig. 2D and fig. S2B). The difference was not statistically significant on the upper back (Fig. 2E and fig. S2C), although cell-level differences were significant at this site (Fig. 2C). The upper back is the most common site of sunburn (20) and melanoma (21), indicating that natural sunlight can induce high mutation burdens at this site, even without the additional influence of tanning beds. Since tanning bed–induced mutations would be expected to contribute to a smaller proportion of mutations in the underlying skin cells from the upper back, we would need a larger sample size to detect a statistically significant difference at the biopsy level.


Tanning bed use is tied to almost a three-fold increase in melanoma risk, and for the first time, scientists have shown how these devices cause melanoma-linked DNA damage across nearly the entire skin surface, reports a new study led by Northwestern Medicine and University of California, San Francisco.
The findings are published in Science Advances.
Melanoma, the deadliest skin cancer, kills about 11,000 in the U.S. each year. Despite decades of warnings, the precise biological mechanism behind tanning beds’ cancer risk remained unclear. The indoor tanning industry, which is making a comeback, has used that uncertainty to argue that tanning beds are no more harmful than sunlight.

The ubiquity of generative AI is a hard pill to swallow, but even harder is figuring out what’s AI and isn’t. It’s easier than ever now to reach for that low-hanging fruit of critique in saying that something looks like an AI spat it out, especially now that games are claiming they were, in fact, spat out entirely by AI. Positive Concept Games, the developer of SNES-esque RPG Shrine’s Legacy, found that out the hard way, as it shared in a post on X last Wednesday.
Please don’t do this. We poured years of our lives into this game and only worked with real human artists on everything: From the writing to the coding, all work was done by human hands. We do not endorse generative AI and will never use it. pic.twitter.com/3L7NKVX1L8 December 10, 2025
The dev shared a Steam review of the game that calls it “AI slop,” claims the “story is dogshit mixed with catshit,” and reiterates that the game was “made in CHAT GPT.” The developer caption reads: “Please don’t do this. We poured years of our lives into this game and only worked with real human artists on everything … We do not endorse generative AI and will never use it.”
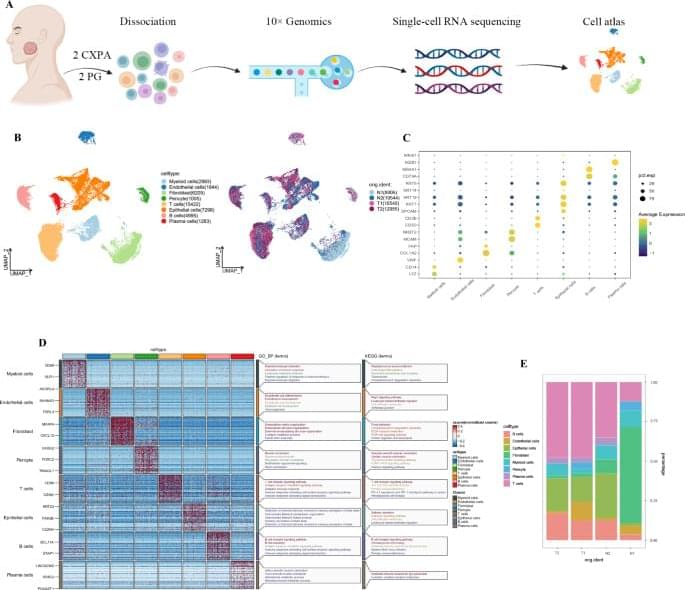
Chen, W., Wang, Y., Yao, Z. et al. ECT2+ cell group acts as cancer stem cell in malignant pleomorphic adenoma. npj Precis. Onc. 9, 189 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-025-00974-x.