Quintavalle, C., Ingenito, F., Roscigno, G. et al. Ex.50.T aptamer impairs tumor–stroma cross-talk in breast cancer by targeting gremlin-1. Cell Death Discov. 11, 94 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-025-02363-6
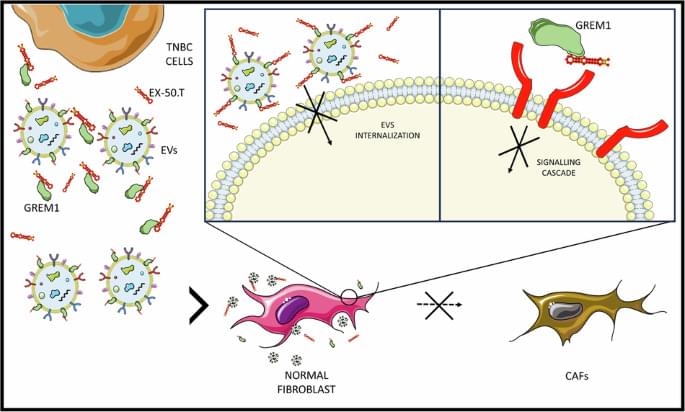

Quintavalle, C., Ingenito, F., Roscigno, G. et al. Ex.50.T aptamer impairs tumor–stroma cross-talk in breast cancer by targeting gremlin-1. Cell Death Discov. 11, 94 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-025-02363-6

Isaac Asimov’s The Last Answer is a chilling dive into what happens after death — not heaven, not hell, but an eternity trapped with a godlike entity that’s impossibly bored. This breakdown reveals the unsettling conversation between a dead physicist and the cosmic intelligence that wants him to think forever. It’s dark, smart, and brutally honest about existence, purpose, and the terrifying possibility that the afterlife isn’t salvation… it’s a job you can’t quit.
#IsaacAsimov #TheLastAnswer #AsimovExplained #SciFiStories #StoryAnalysis #Existential #Afterlife #Philosophy #ShortStory #HorrorSciFi.
#EducationSystemExposed #SchoolMindset #SuccessWithoutSchool #UnlearnSchool #LifeAfterEducation #RedefineSuccess #BreakTheRules #AdultingStruggles #BoredomIsPower #SchoolTrauma #ThinkForYourself #EducationReform #SelfDiscoveryJourney #QuestionAuthority #LifeHacksTheyNeverTaughtYou.
#USA #SuperBowl2025 #Shorts #Viral #Trending #TechNewsUSA #NYCFoodie #LAFashion #CrossFitUSA #HollywoodUpdates #TravelUSA #StartupNation #Motivation #MadeInUSA #Oscars2025 #Healthylifestyle #ShortsMagic #GamingUSA #SmallBusinessUS #TrendingBytes #FitnessJourney #TexasTravel #CaliforniaAdventures #Thanksgiving2025 #BlackFriday2025 #USATech #AITrends2025 #PelotonWorkout #HomeWorkout #July4thRecipes #NYCMakeup #MiamiNightlife #ChicagoEats #FortniteUSA #CallOfDuty2025 #VeganRecipes #LaughInShorts #TikTokDanceChallenge #Coachella2025 #NBAFinals2025 #USATravelVlog
An exploration of whether when a civilization develops AI, it convinces or compels them to not attempt interstellar travel for its own reasons and motives.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Music:
An exploration of the idea of building a Dyson Sphere or Swarm around a black hole.
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/eventhorizonshow.
Music:


The FDA’s December 2025 expert panel signals a major shift in how testosterone decline, aging, and treatment access are viewed in men’s health.
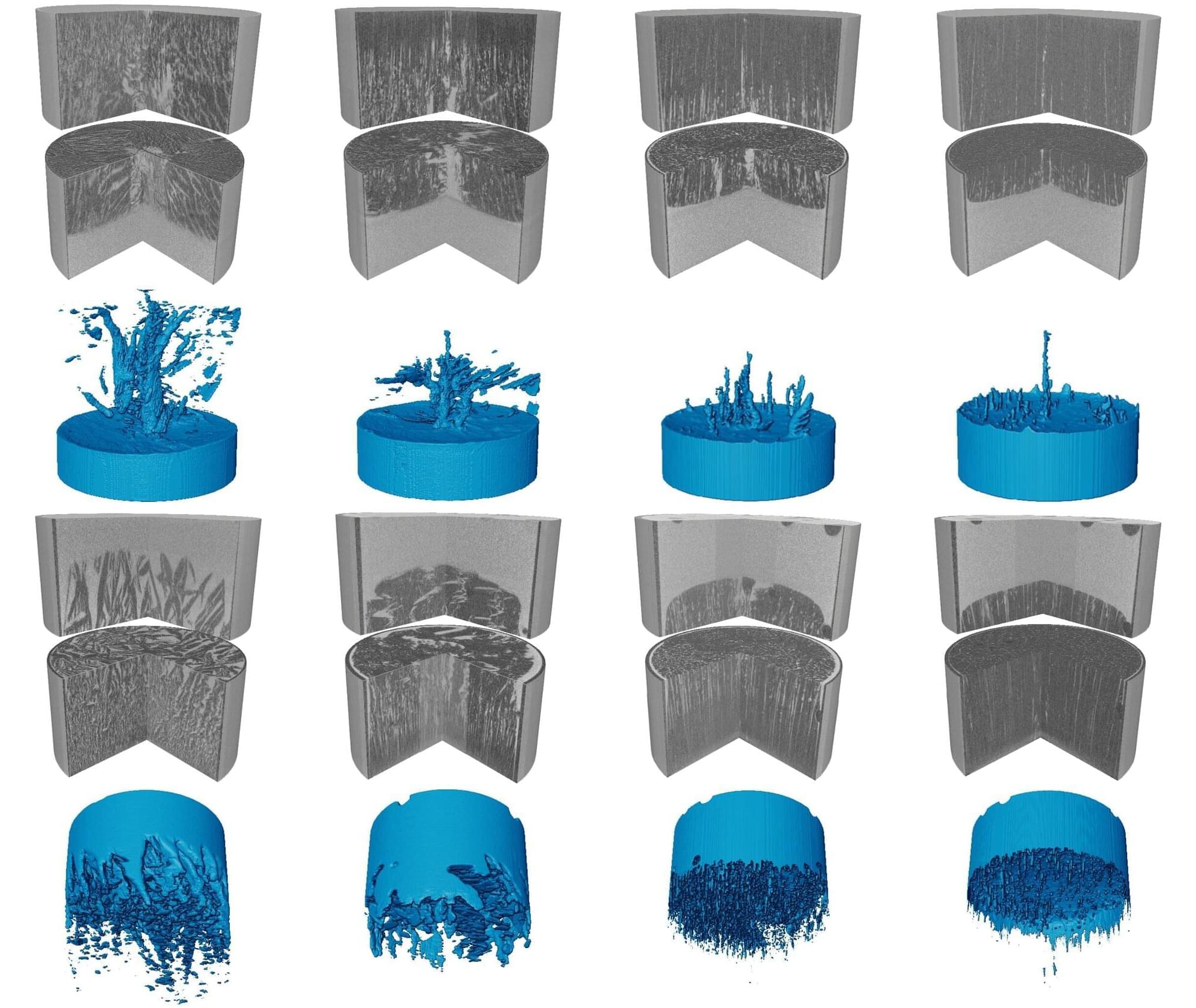
Imagine holding a narrow tube filled with salty water and watching it begin to freeze from one end. You might expect the ice to advance steadily and push the salt aside in a simple and predictable way. Yet the scene that unfolded was unexpectedly vivid.
Based on X-ray computed tomography (Micro-CT), our study, published in the Journal of Fluid Mechanics, realized the 4D (3D + time) dynamic observation and modeling of the whole process of ice crystal growth and salt exclusion.
When we monitored brine as it froze, the microstructure evolved far more dynamically than expected. Immediately after nucleation, ice crystals (dark areas) formed rapidly and trapped brine (bright areas) within a porous network. As freezing progressed, this network reorganized into striped patterns that moved either downward or upward depending on boundary conditions.