Living organisms are made up of hundreds of thousands of cells that cooperate to create the organs and systems that breathe, eat, move, and think. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a new way to track how and when cells touch each other to work together in these ways. In a study published in January in Cell Reports Methods, researchers from The University of Osaka reported the development of fluorescent markers for monitoring cell communication under a microscope.
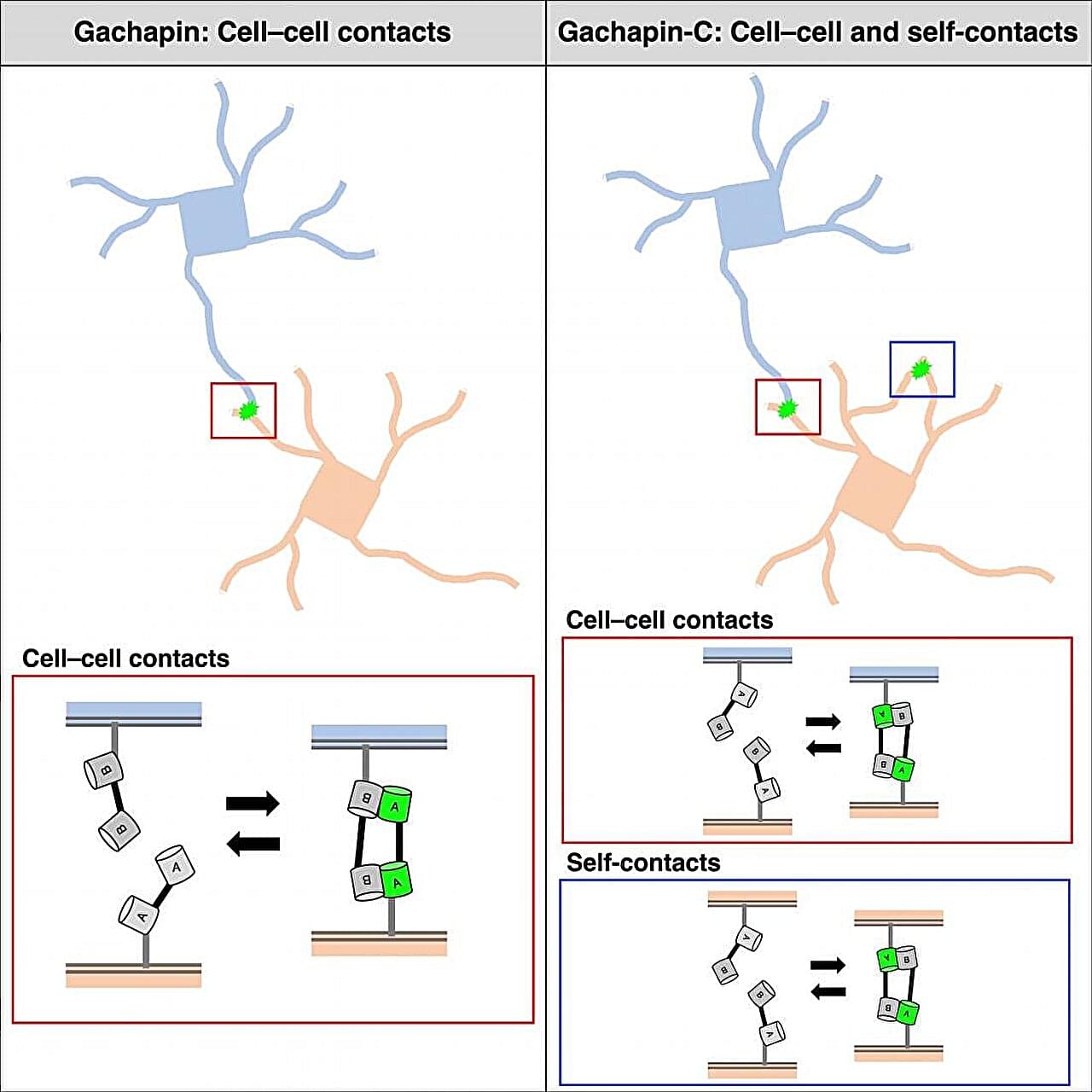
Cells communicate with each other by making cell-to-cell contacts, and fluorescent markers are often used to visualize these contacts. The most commonly used marker for this purpose is green fluorescent protein (GFP). GFP can be divided into two halves that are expressed on different cells. When the cells touch, the two halves come together to form a complete GFP, letting off a fluorescent signal.
“Split GFP is useful for detecting the formation of stable connections between cells,” says lead author of the study Takashi Kanadome. “But because it takes time for the rejoined GFP to emit its signal and the association is irreversible, this approach cannot be used to detect dynamic cell–cell interactions in real-time.”