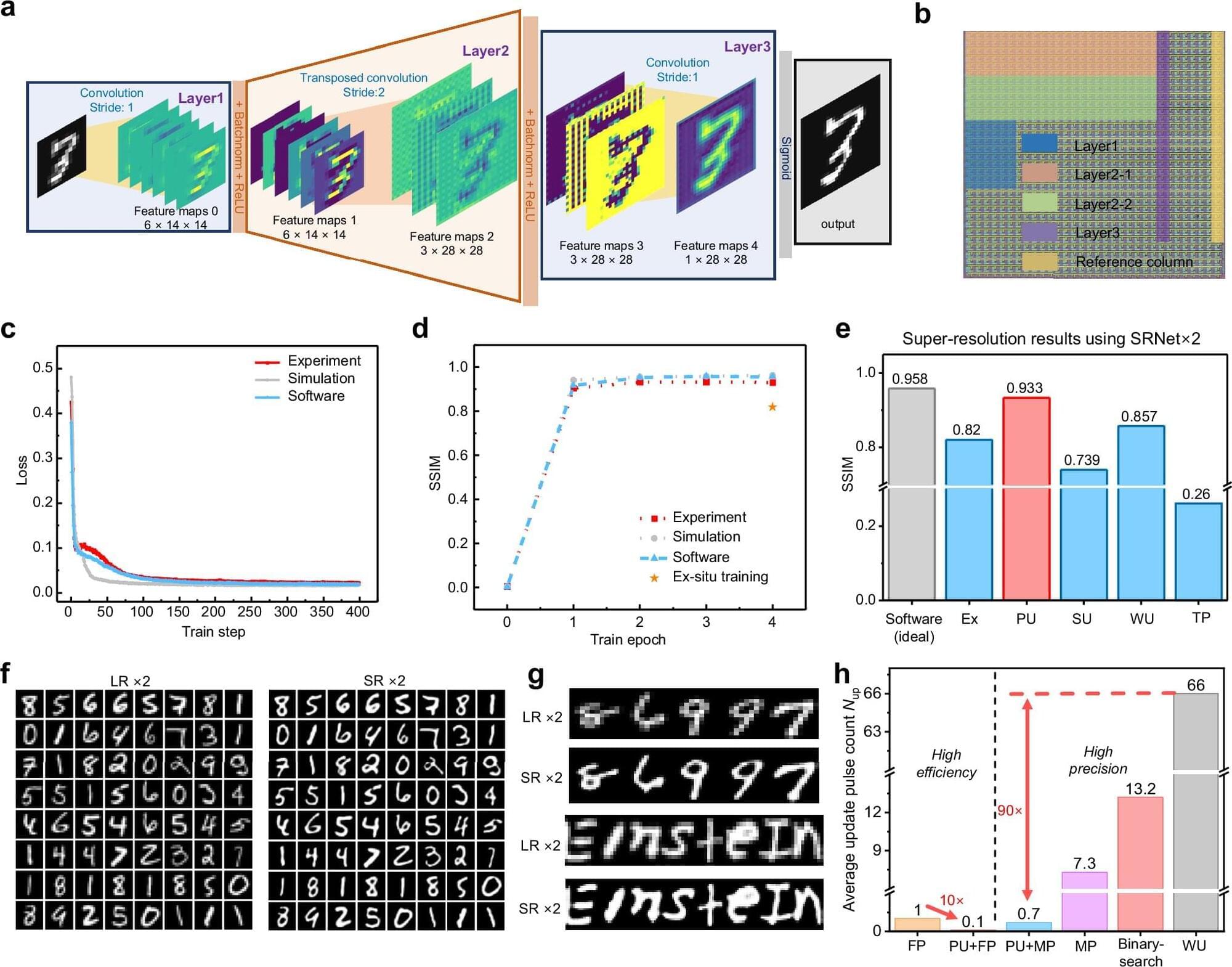
In a Nature Communications study, researchers from China have developed an error-aware probabilistic update (EaPU) method that aligns memristor hardware’s noisy updates with neural network training, slashing energy use by nearly six orders of magnitude versus GPUs while boosting accuracy on vision tasks. The study validates EaPU on 180 nm memristor arrays and large-scale simulations.
Analog in-memory computing with memristors promises to overcome digital chips’ energy bottlenecks by performing matrix operations via physical laws. Memristors are devices that combine memory and processing like brain synapses.
Inference on these systems works well, as shown by IBM and Stanford chips. But training deep neural networks hits a snag: “writing” errors when setting memristor weights.