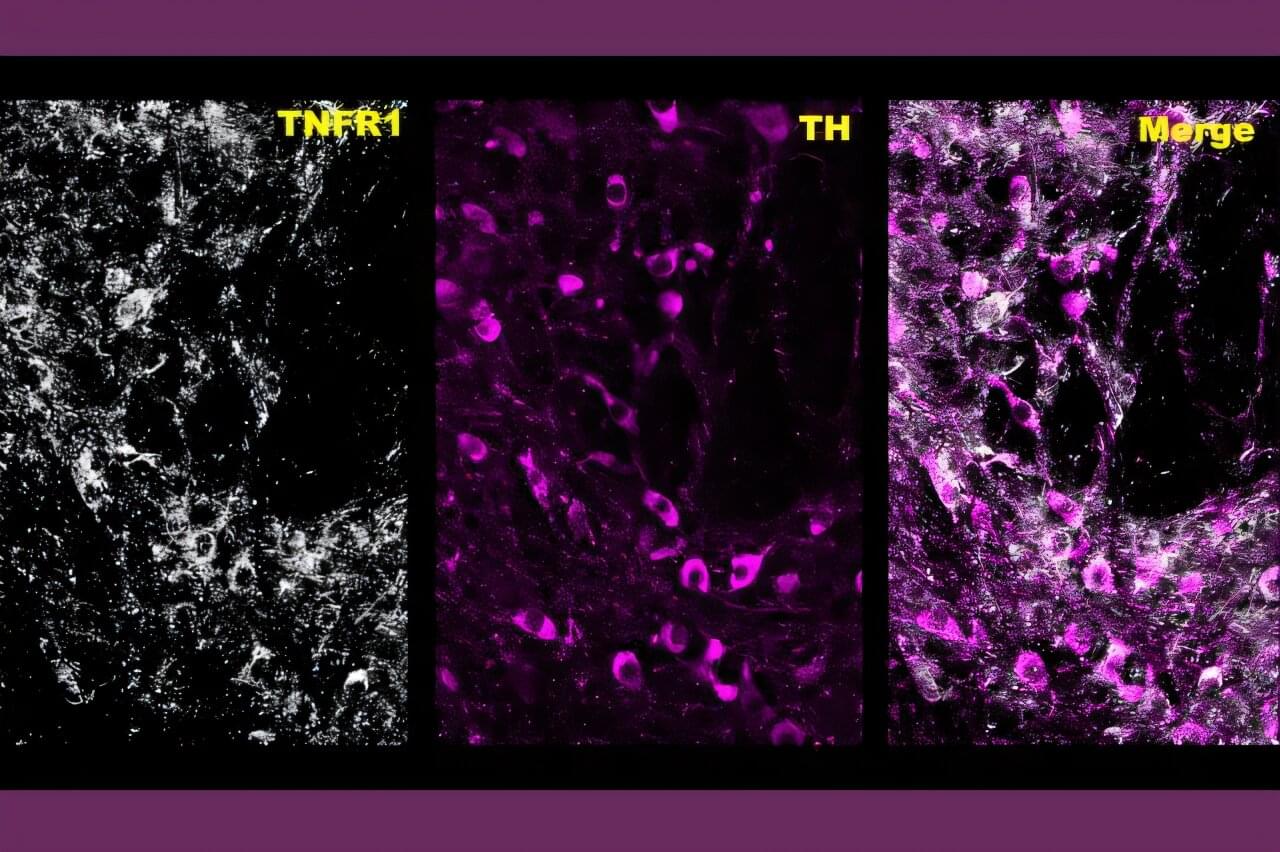
University of Florida neuroscientists have made a mechanistic discovery that paves the way to test immune-modulating medicines as a potential tool to break the cycle of methamphetamine addiction.
In a new preclinical study, a McKnight Brain Institute team led by Habibeh Khoshbouei, Ph.D., Pharm. D., examined the role of neuroinflammation in meth addiction to provide a deeper understanding of the mechanisms at work.
“Unlike alcohol or opioids, there currently is no medicinal therapeutic approach for methamphetamine addiction,” said Khoshbouei, a professor of neuroscience and psychiatry. “So this is an important societal issue.”