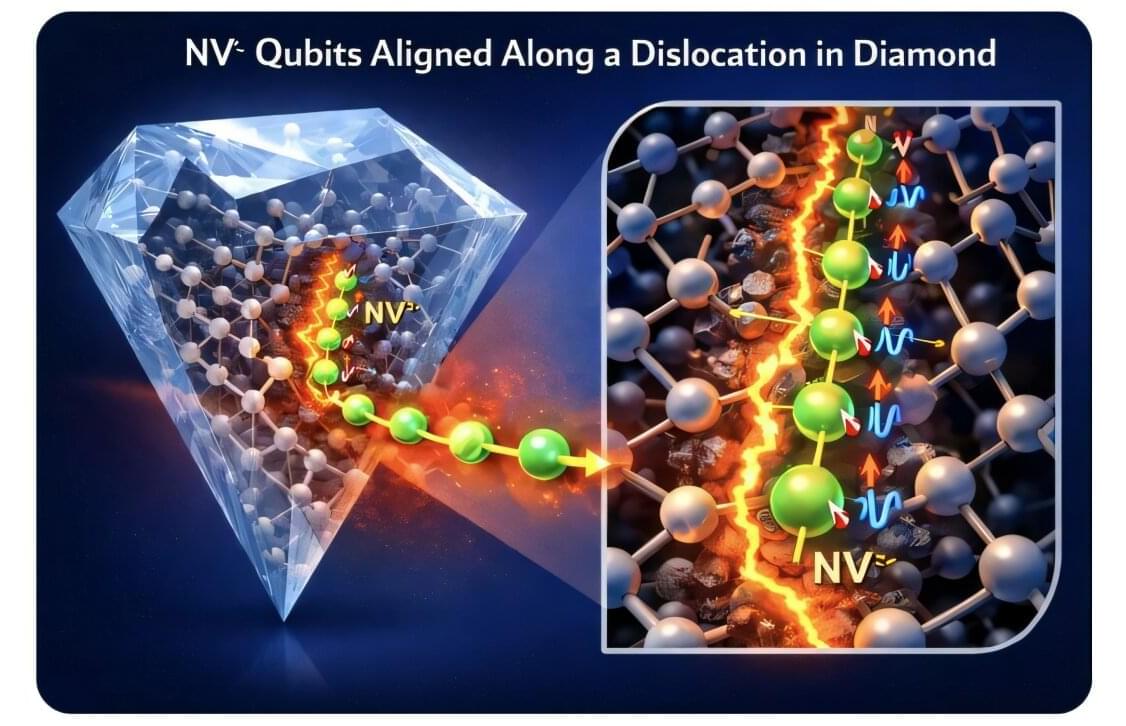
Building large-scale quantum technologies requires reliable ways to connect individual quantum bits (qubits) without destroying their fragile quantum states. In a new theoretical study, published in npj Computational Materials, researchers show that crystal dislocations—line defects long regarded as imperfections—can instead serve as powerful building blocks for quantum interconnects.
Using advanced first-principles simulations, a team led by Prof. Maryam Ghazisaeidi at The Ohio State University and Prof. Giulia Galli at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) and Chemistry Department demonstrated that nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond, a leading solid-state qubit platform, can be attracted to dislocations and retain—and in some cases improve—their quantum properties when positioned near these line defects.
“Because dislocations form quasi-one-dimensional (1D) structures extending through a crystal, they provide a natural scaffold for arranging qubits into ordered arrays,” said co-first author Cunzhi Zhang, a UChicago PME staff scientist in the Galli Group.