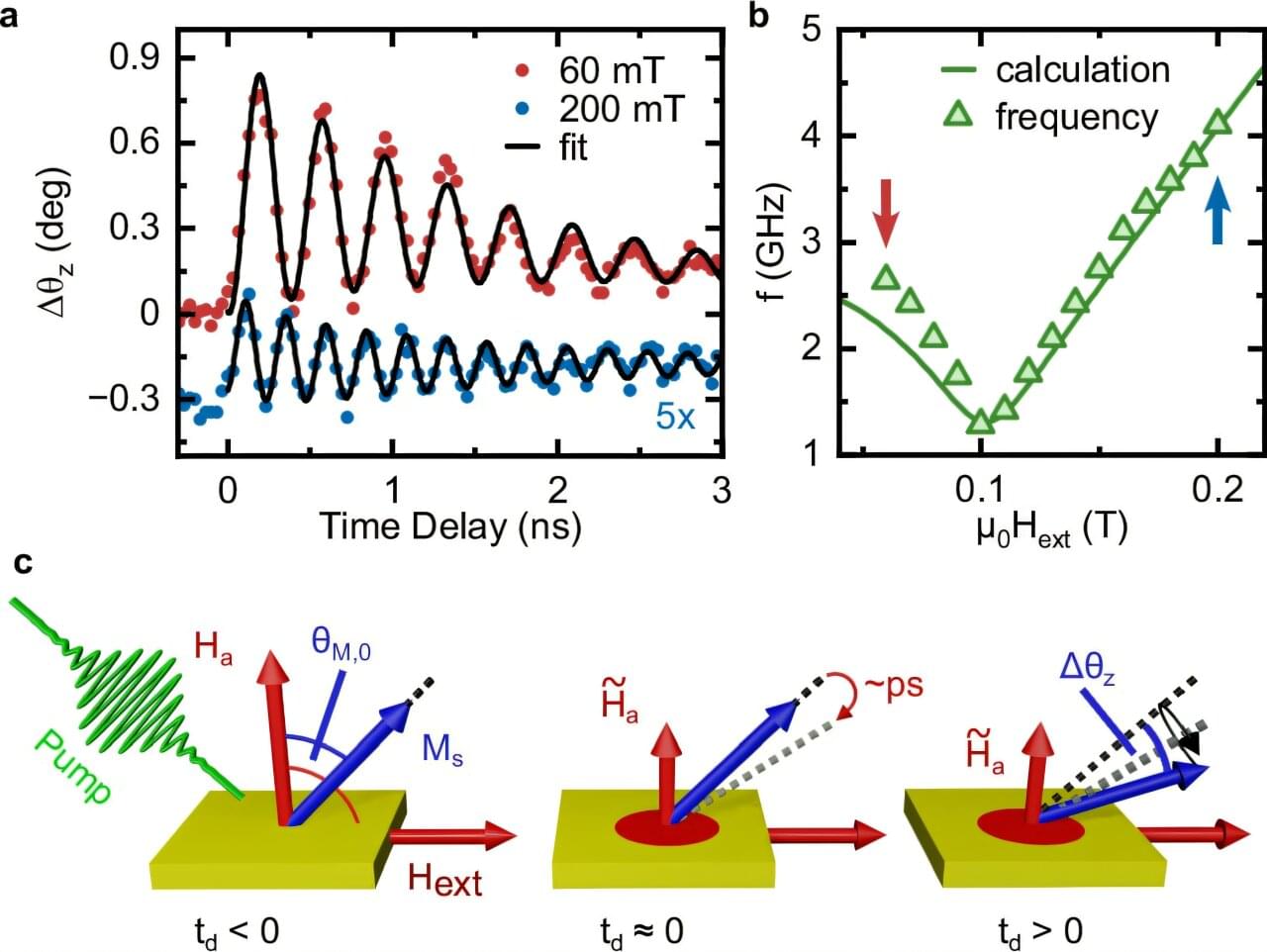
Physicist Davide Bossini from the University of Konstanz has recently demonstrated how to change the frequency of the collective magnetic oscillations of a material by up to 40%—using commercially available devices at room temperature.
“We now have a full picture,” Bossini says. For years, the physicist from the University of Konstanz has studied how to use light to control the collective magnetic oscillations of a material—known as magnons. In the summer of 2025, he was finally able to show how to change the “magnetic DNA” of a material via the interaction between light and magnons.
He now demonstrates how the frequency of oscillations can be controlled quasi instantly and on demand by means of a weak magnetic field and intense laser pulses. In this way, he can increase or decrease frequencies by up to 40%. The effect is due to the interaction of the optical excitation, magnetic anisotropy (directional dependence) and the external magnetic field.