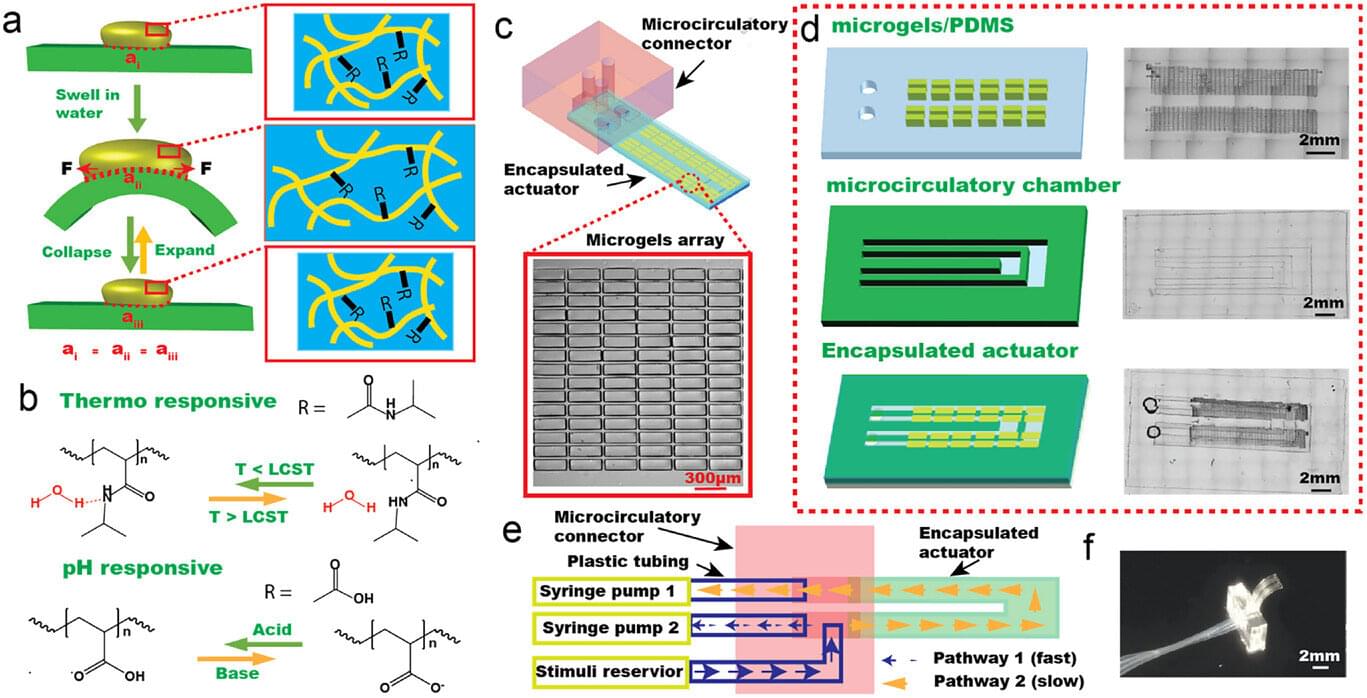
Researchers are continuing to make progress on developing a new synthetic material that behaves like biological muscle, an advancement that could provide a path to soft robotics, prosthetic devices and advanced human-machine interfaces. Their research, recently published in Advanced Functional Materials, demonstrates a hydrogel-based actuator system that combines movement, control and fuel delivery in a single integrated platform.
Biological muscle is one of nature’s marvels, said Stephen Morin, associate professor of chemistry at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln. It can generate impressive force, move quickly and adapt to many different tasks. It is also remarkable in its flexibility in terms of energy use and can draw on sugars, fats and other chemical stores, converting them into usable energy exactly when and where they are needed to make muscles move.
A synthetic version of muscle is one of the Holy Grails of material science.