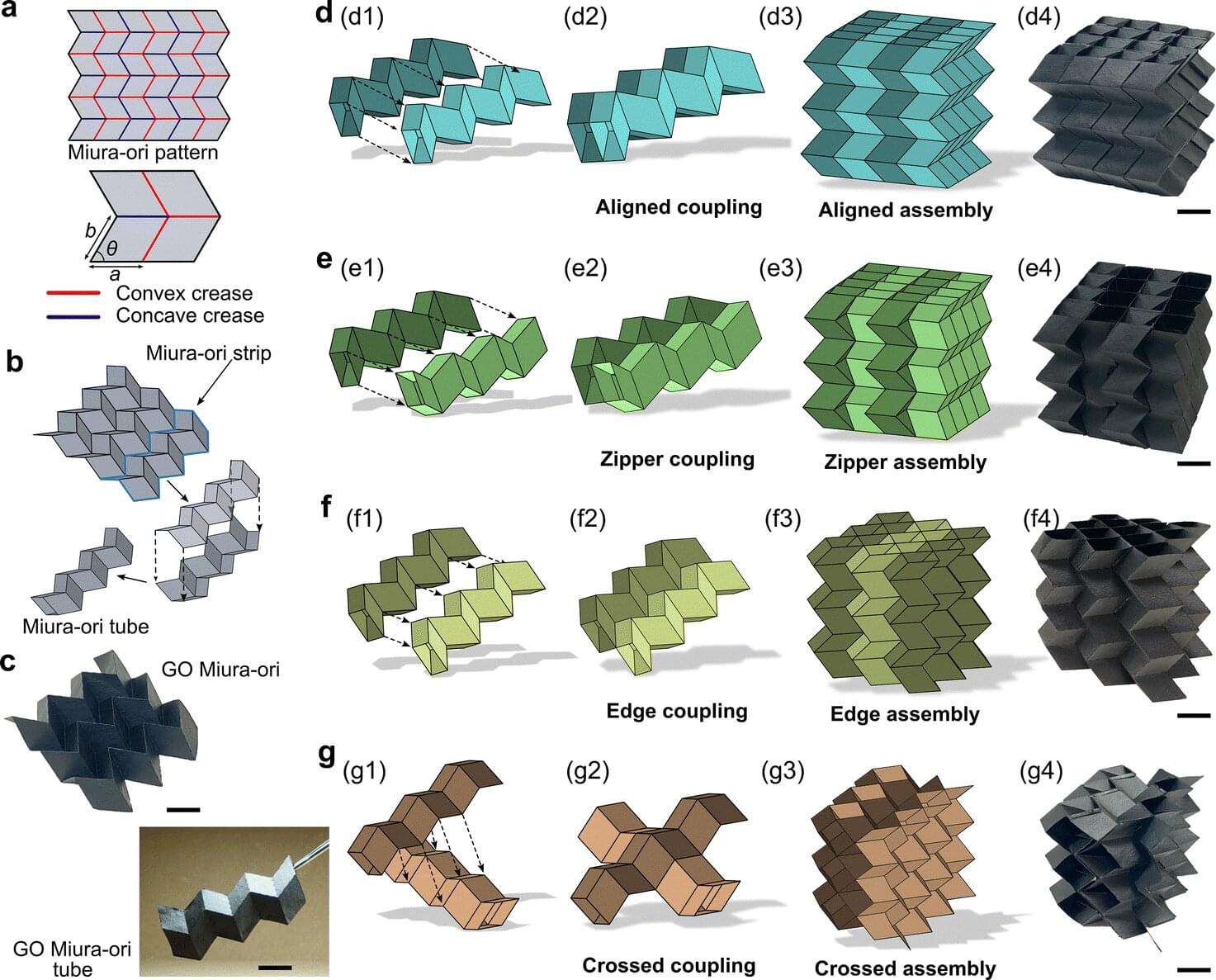
McGill University engineers have developed new ultra-thin materials that can be programmed to move, fold and reshape themselves, much like animated origami. They open the door to softer, safer and more adaptable robots that could be used in medical tools that gently move inside the body, wearable devices that change shape on the skin or smart packaging that reacts to its environment.
The research, jointly led by the laboratories of Hamid Akbarzadeh in the Department of Bioresource Engineering and Marta Cerruti in the Department of Mining and Material Engineering, shows how simple, paper-like sheets made from folded graphene oxide (GO) can be turned into tiny devices that walk, twist, flip and sense their own motion. Two related studies demonstrate how these materials can be made at scale, programmed to change shape and controlled either by humidity or magnetic fields.
The studies are published in Materials Horizons and Advanced Science.