3. Pathology as Network Dysregulation.
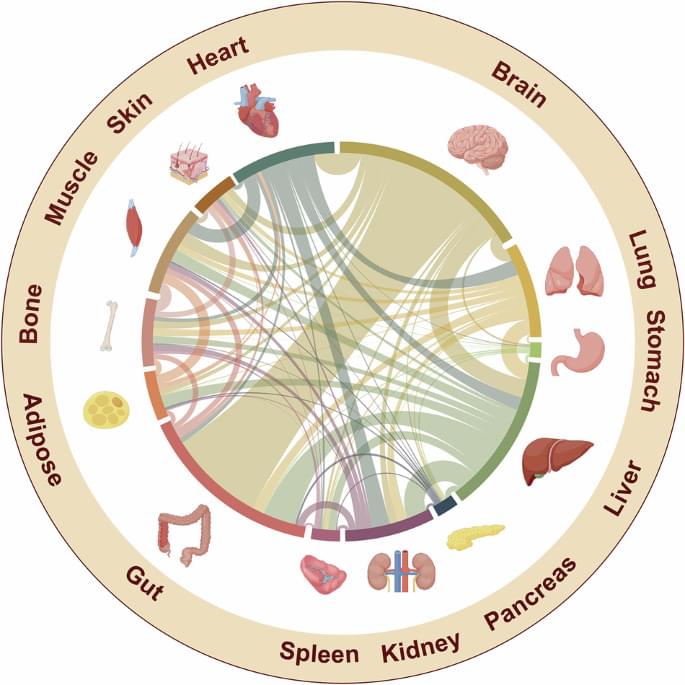
In recent years, a transformative view of physiology has emerged: the body operates not as isolated organs, but as an integrated communication network in which signals flow bidirectionally between the brain, the immune system, the gut, and peripheral organs. This comprehensive review synthesizes current mechanistic insights into this “organ cross-talk” and frames them within systems biology and neuroscience.
At its core, organ cross-talk encompasses neural, endocrine, metabolic, and immune signaling between organs that coordinate homeostasis and orchestrate responses to stress and disease. From a neuroscience vantage point, three themes stand out:
1. The Brain as a Communication Hub.
2. Peripheral Feedback to the CNS.