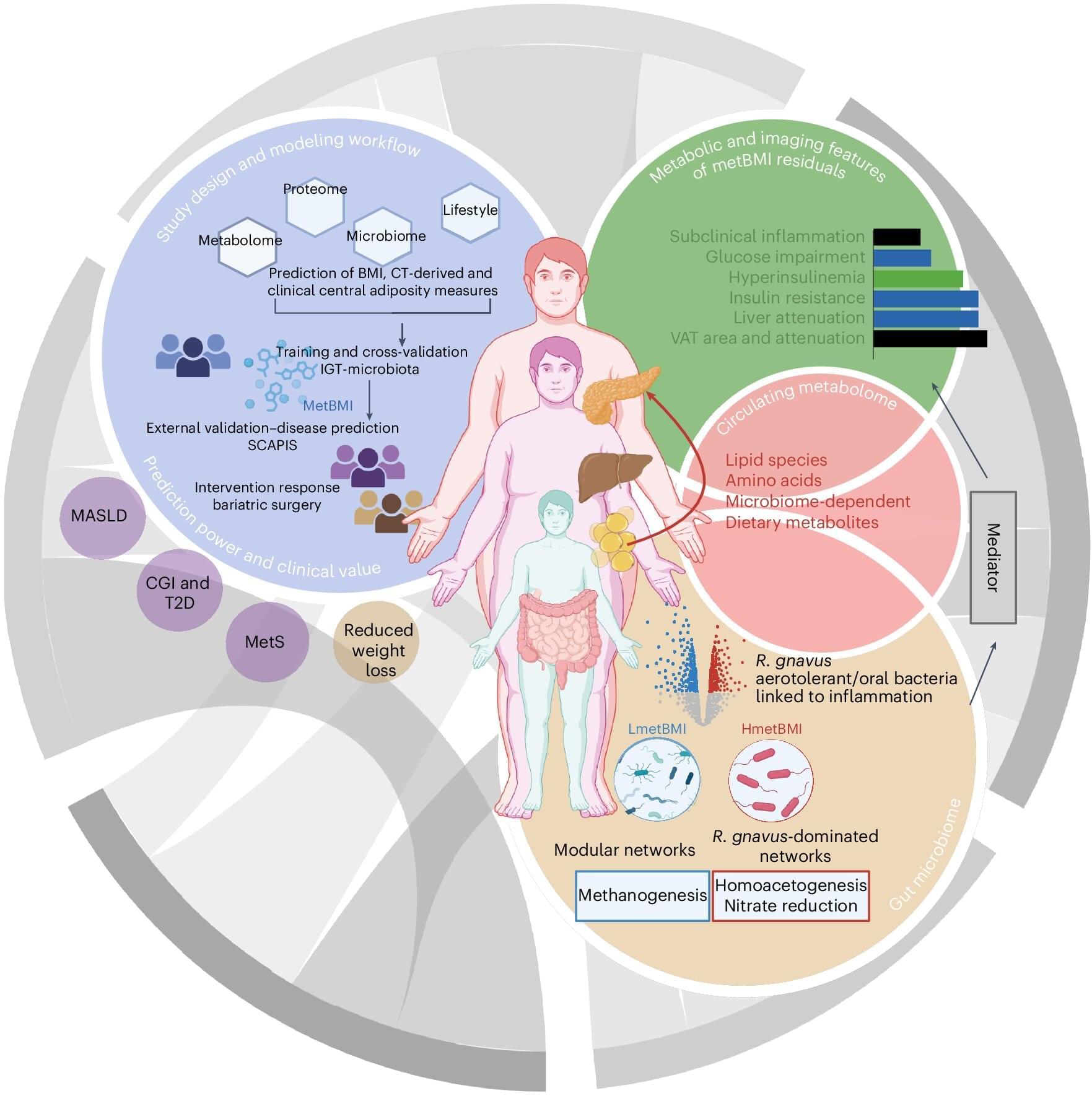
Researchers at Leipzig University and the University of Gothenburg have developed a novel approach to assessing an individual’s risk of metabolic diseases such as diabetes or fatty liver disease more precisely. Instead of relying solely on the widely used body mass index (BMI), the team developed an AI-based computational model using metabolic measurements. This so-called metabolic BMI shows that people of normal weight with a high metabolic BMI have up to a fivefold higher risk of metabolic disease. The findings have been published in the journal Nature Medicine.
The conventional body mass index, calculated using height and weight, may indicate overweight but does not reflect how healthy or unhealthy body fat actually is. According to BMI classifications, up to 30% of people are considered to be of normal weight but already show dangerous metabolic changes. Conversely, there are individuals with an elevated BMI whose metabolism remains largely unremarkable. This discrepancy can lead to at-risk patients being identified and treated too late.
For the current scientific study, the international research team analyzed data from two large Swedish population studies involving a total of almost 2,000 participants. In addition to standard health and lifestyle parameters, extensive laboratory data from blood samples and analyses of the gut microbiome were collected. Based on this dataset, the researchers developed a computational model that predicts metabolic BMI.