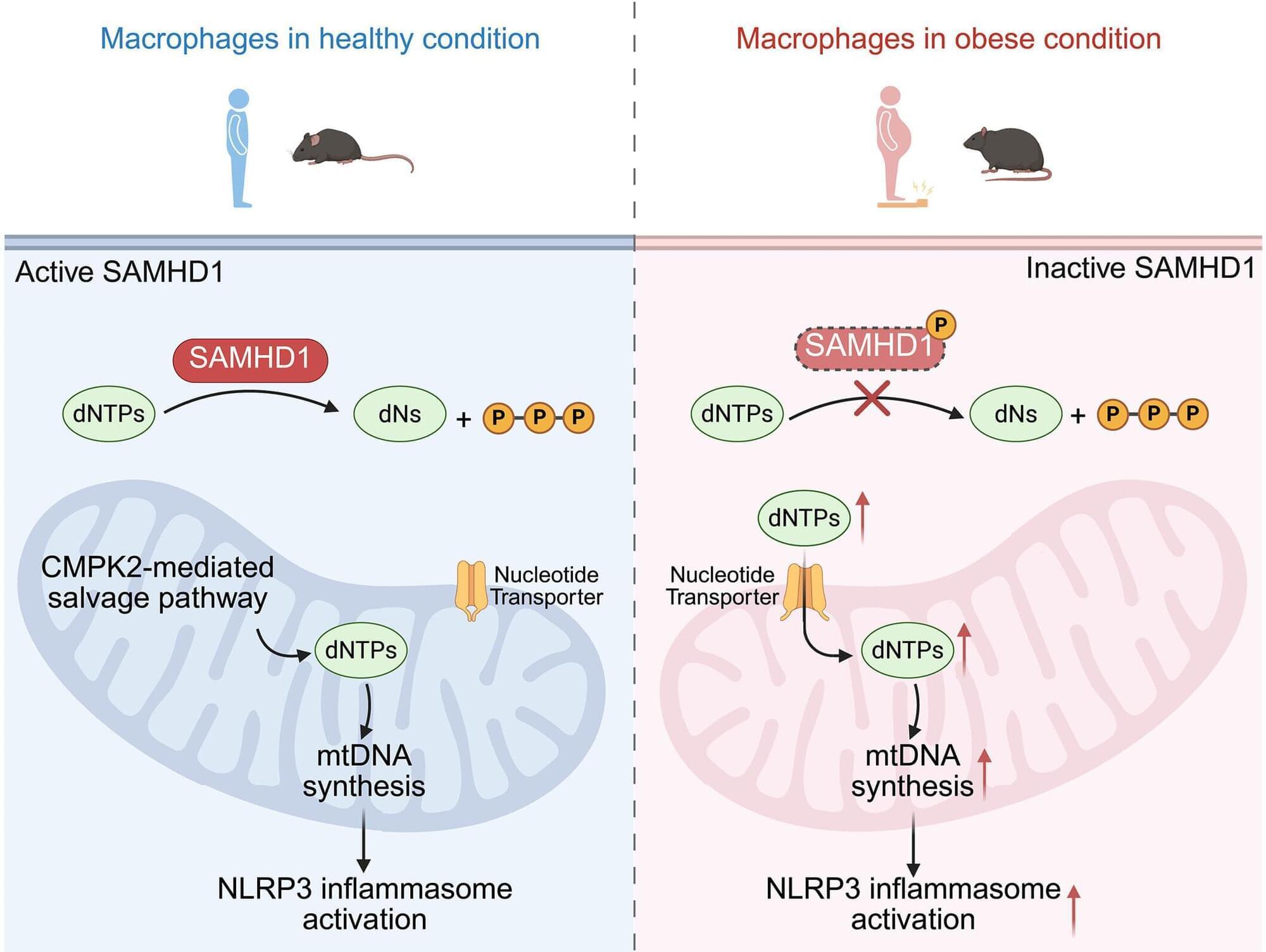
A team led by UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers has uncovered a molecular pathway that links obesity to widespread inflammation, providing long-sought insight into why obesity increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, and certain cancers.
The findings, published in Science, identify a molecular “switch” that triggers this inflammation and point to potential new therapeutic targets.
“It’s been known for a long time that obesity causes uncontrolled inflammation, but no one knew the mechanism behind it. Our study provides novel insights about why this inflammation occurs and how we might be able to stop it,” said Zhenyu Zhong, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Immunology and member of the Harold C. Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center at UT Southwestern. Dr. Zhong co-led the study with Danhui Liu, Ph.D., a former postdoctoral researcher in the Zhong Lab.