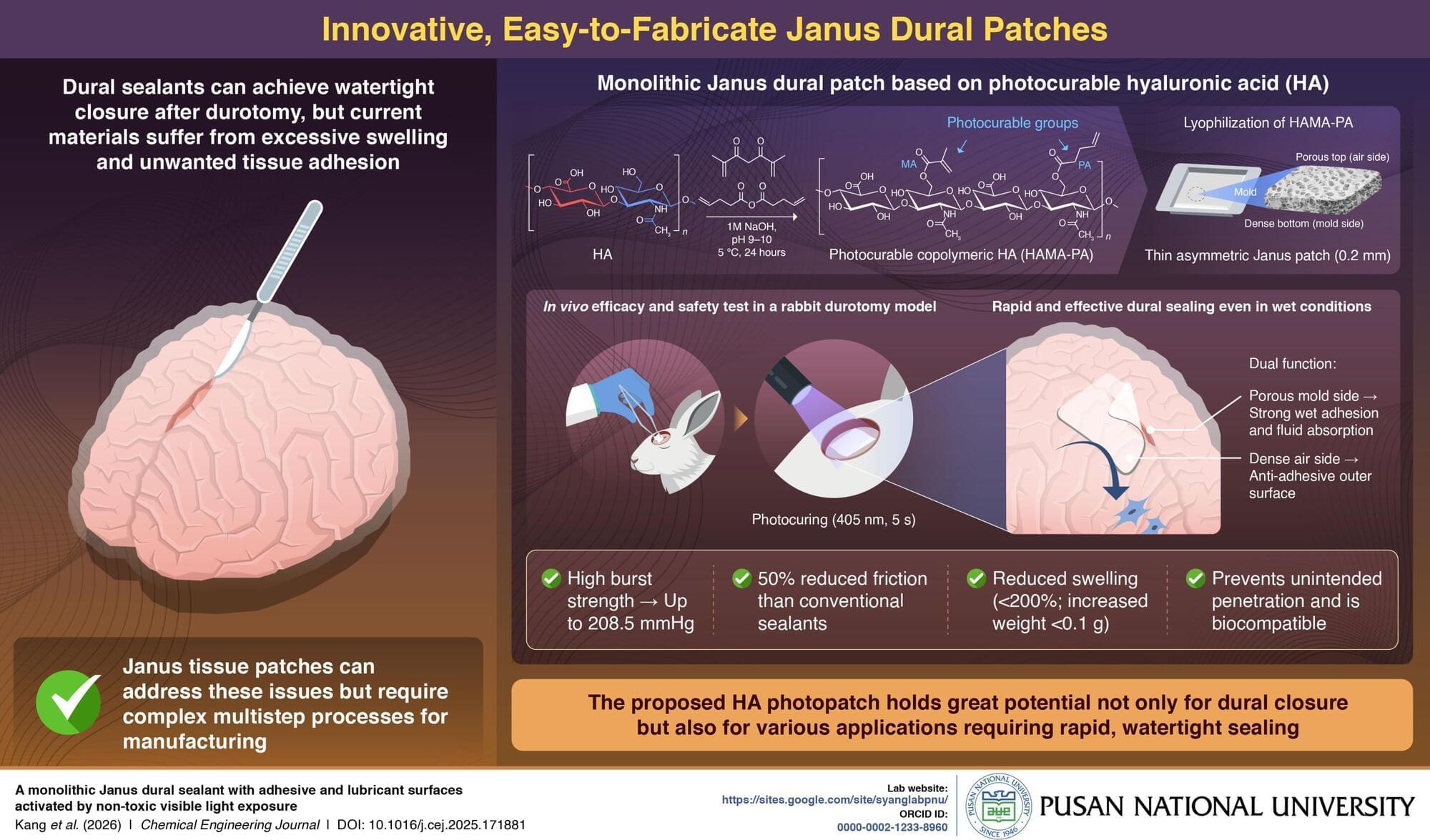
Durotomy is a common neurosurgical complication involving a tear in the dura mater, the protective membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Damage can cause cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage, leading to delayed healing, headaches, and infection, making a reliable watertight dural closure essential.
Tissue adhesives are increasingly being explored as alternatives to suturing for dural closure because they offer simpler and faster application. However, many existing glue-based sealants suffer from excessive swelling, leading to mass effect and unwanted tissue adhesion, which can lead to postoperative complications.
To address these limitations, researchers have investigated Janus tissue patches, which feature two distinct surfaces—one that adheres strongly to tissue and another that prevents unwanted adhesion. Unfortunately, most existing Janus patches rely on multiple materials and complex, multi-step fabrication processes, limiting their practical use.