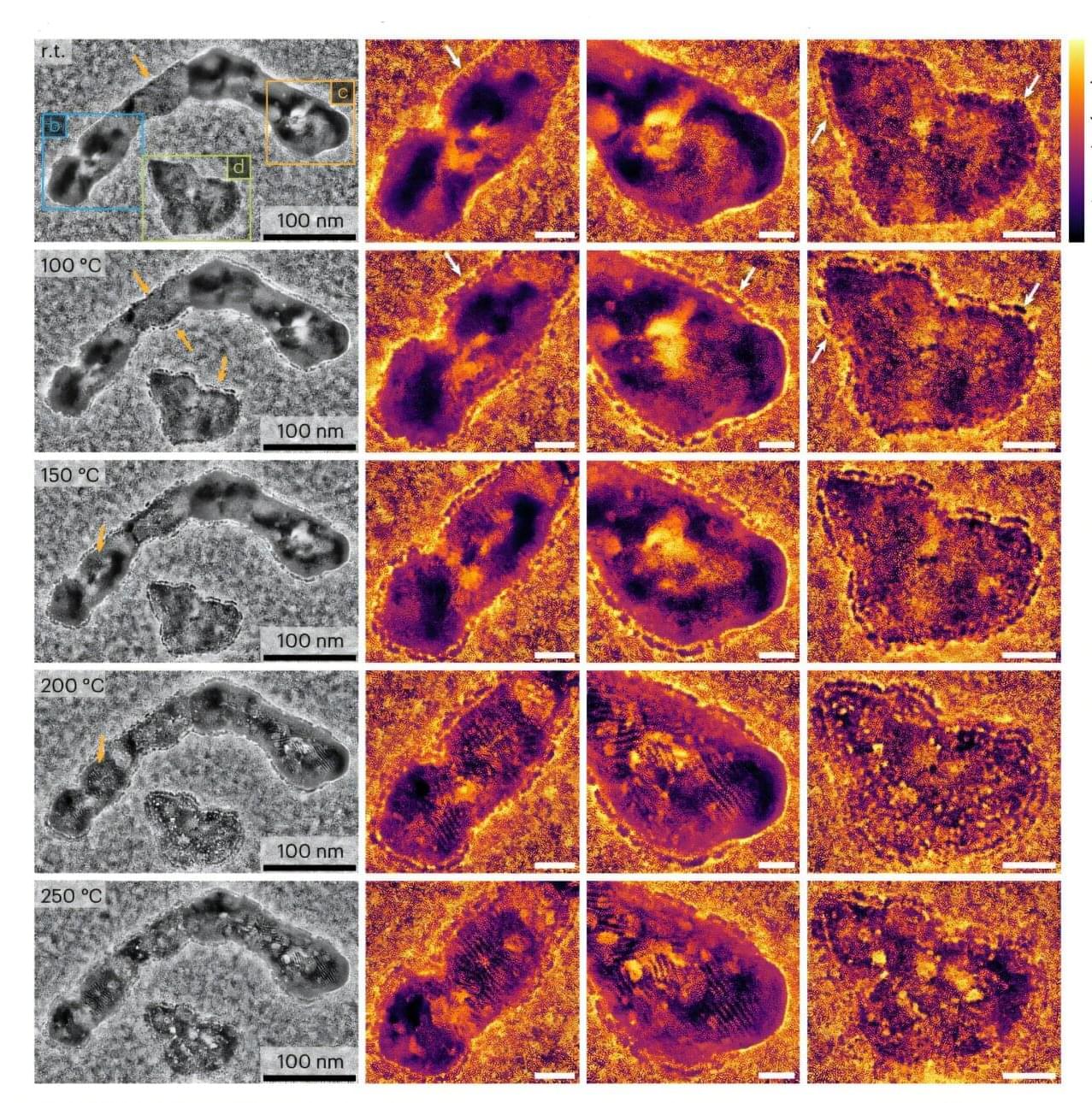
In a study appearing in Nature Catalysis, researchers from the Inorganic Chemistry Department of the Fritz Haber Institute reveal how structural changes on the surface and in the bulk region of the cobalt oxide catalyst Co3O4 influence its selectivity in the production of industrially relevant chemicals like acetone.
They discovered that a metastable, structurally “trapped” state exhibits the highest catalytic activity—an important finding for catalyst design.