Light-emitting semiconductors are used throughout everyday life in TVs, smartphones, and lighting. However, many technical barriers remain in developing environmentally friendly semiconductor materials.
In particular, nanoscale semiconductors that are tens of thousands of times smaller than the width of a human hair (about 100,000 nanometers) are theoretically capable of emitting bright light, yet in practice have suffered from extremely weak emission. KAIST researchers have now developed a new surface-control technology that overcomes this limitation.
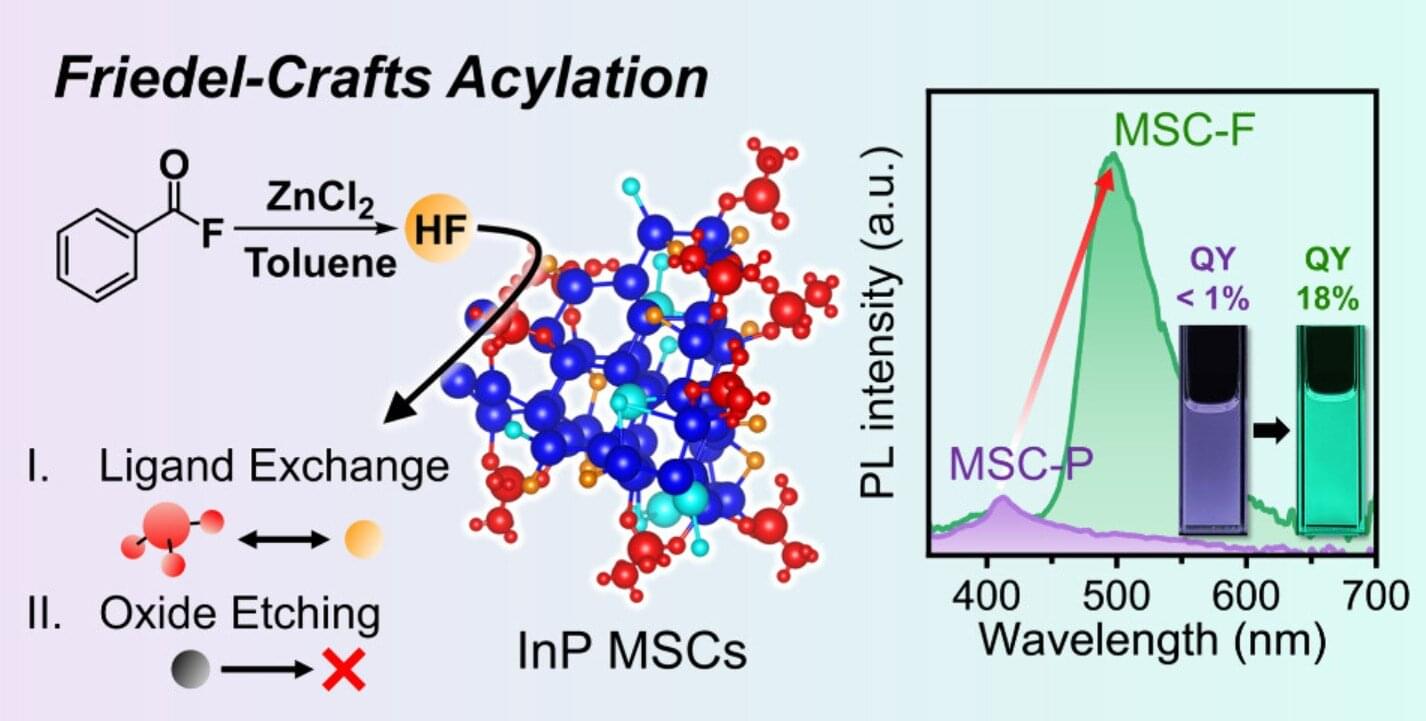
A KAIST research team led by Professor Himchan Cho of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a fundamental technology to control, at the atomic level, the surface of indium phosphide (InP) magic-sized clusters (MSCs)—nanoscale semiconductor particles regarded as next-generation eco-friendly semiconductor materials.