Mayo Clinic researchers have uncovered how aging “zombie cells” trigger harmful inflammation that accelerates a severe and increasingly common form of fatty liver disease called metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). As obesity rates rise worldwide, MASH is projected to increase and is already one of the leading causes of liver transplantation.
“Liver scarring and inflammation are hallmarks of MASH. If left untreated, it can progress to liver cancer. This is why it’s so important to understand the mechanisms driving the disease so that we can prevent it or develop more effective treatments,” says Stella Victorelli, Ph.D., who is the lead author of the study published in Nature Communications.
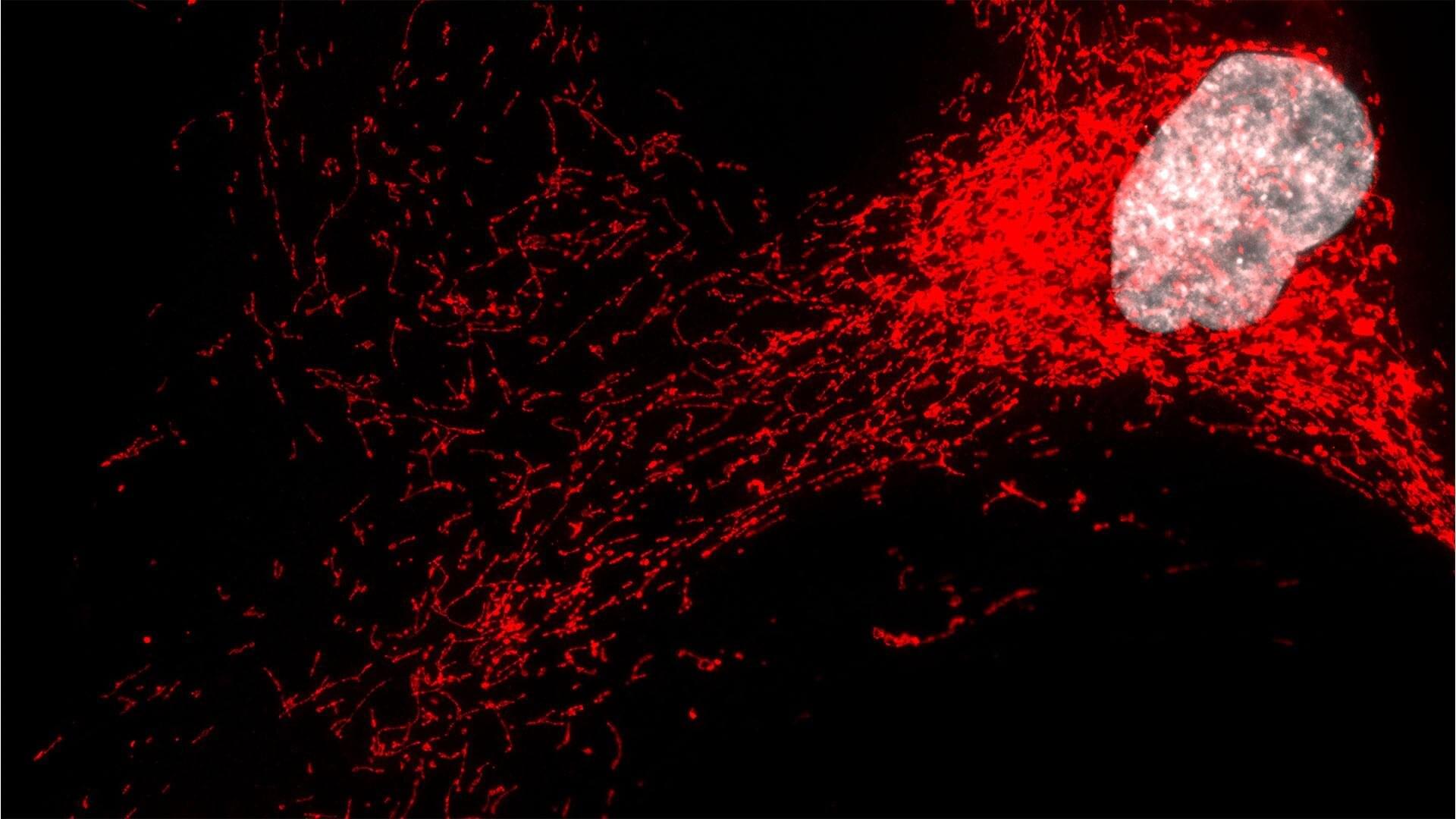
Dr. Victorelli and colleagues, who study aged or senescent “zombie” cells, identified a mechanism by which these cells drive liver scarring and inflammation. They found that small molecules called mitochondrial RNA, typically found within the cell’s energy-producing mitochondria, can leak into the main part of the cell, where they mistakenly activate antiviral sensors called RIG-I and MDA5—normally triggered when a virus infects a cell. In this case, the danger signal comes from the cell’s own mitochondria, prompting a wave of inflammation that can damage nearby healthy tissue.